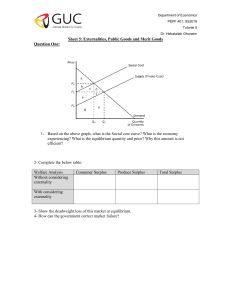
Opportunity Cost - What you give up the most Trade-Off - What you give up Marginal Thinking - How much more do you need Incentives - You want something - Positive: You want to go get something - Negative: You do something to not get something Trade - Exchange and Get Law of demand All else equal, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. If Price goes up, quantity demanded goes down If Price goes down, quantity demanded goes up. All else equal, there is a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied. If Price goes up, quantity supplied goes up If Price goes down, quantity supplied goes down. Demand increases Equilibrium price and quantity increase Supply increases Equilibrium price decreases and quantity increases Demand decreases Equilibrium price and quantity decrease Supply decreases Equilibrium price increases and quantity decreases (New Quantity - Old Quantity)/(New+Old)/2 Divided by (New Price - Old Price)/(New+Old)/2 Quantity Total Variable Cost Total Fixed Cost Total Cost = Total Variable Cost + Total Fixed Cost Average Variable Cost = Total Variable Cost / Quantity Average Fixed Cost = Total Fixed Cost / Quantity Average Total Cost = Total Cost / Quantity Marginal Cost = Change in Total Variable Cost/ Change in Quantity Perfectly Competitive Markets: Many Sellers, Similar Products, Free entry and exit Monopolistic Competition: Many Sellers, Differentiated Products, Low Entry and exit Monopoly: One Seller, Unique Product no subs, High Entry exit Oligopoly: Few Sellers, Homogenous products, mid entry exit Externality •Third-party problem (internal cost/benefit ≠ social cost/benefit) •Positive externality vs. negative externality Correcting externality (internalizing the externality) •Negative externality 1. Tax the product. 2. Regulate production. 3. Encourage research and development of alternative substitutes to the product. •Positive externality 1. Finance and/or subsidize production and consumption of the good. 2. Laws requiring consumption. 3. Encourage research and development of Property Rights ● Coase theorem - Don’t Interfere and parties can resolve.