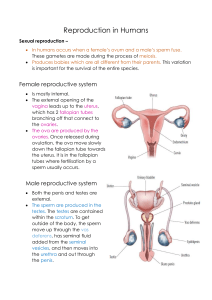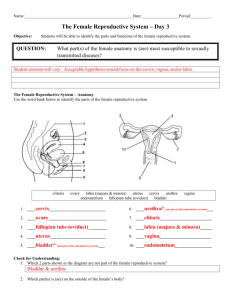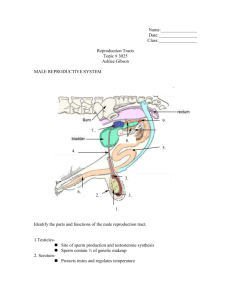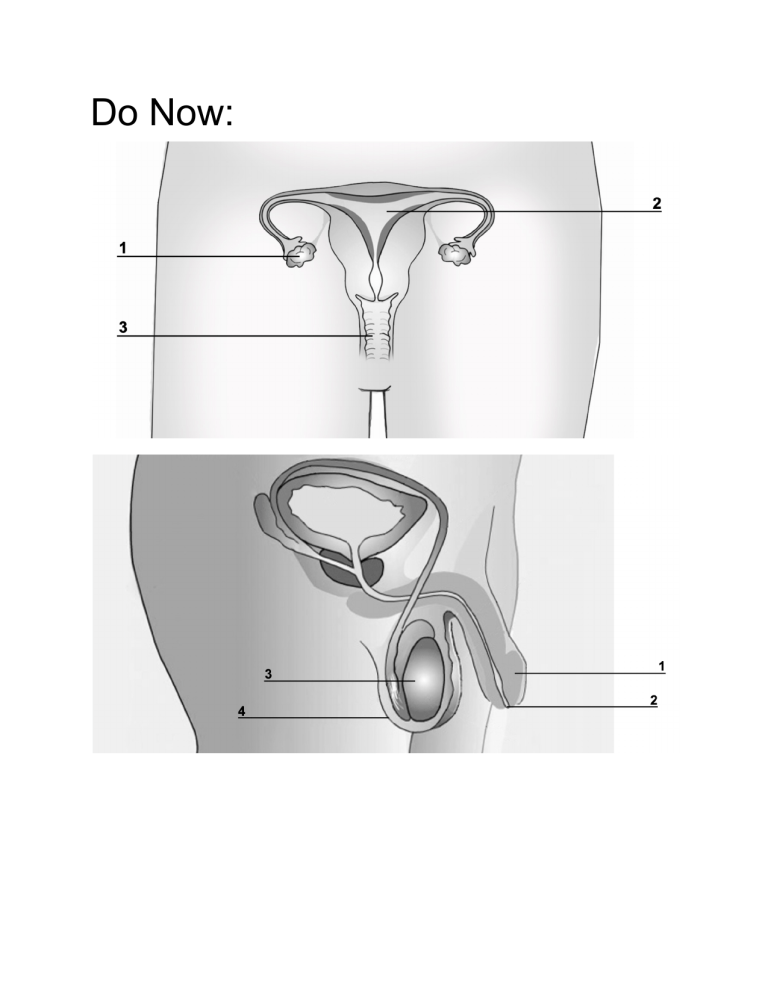
Do Now: MALE BODY Structure ____________ Letter from diagram Description Allows passage of _________ and _____________ Provides ____________ The average penis measures 3–4 inches when it's not erect (____________) and 5–7 inches when _____________ Foreskin Protects the ___________ of the penis Provides sensation Males who have been ____________________ don’t have one Scrotum Muscular sac which is shorter when cold, longer when warm Holds ____________ Controls ___________________ Provides sensation Testes Produces sperm and sex hormones (_______________ and _________________) Each is made of ______________________ feet of tightly coiled tubes Epididymis Vas ___________ Allows __________________ of sperm Provides storage for ____________ Allow __________________ of sperm Provides sensation Carries sperm from the __________________ Seminal Vesicle Prostate Cowper’s Glands Contributes _____________________ to semen for nourishing the sperm Produces most of the fluid that makes up semen Pair of glands Produces pre–ejaculatory fluid (called “__________________”) that cleans the urethra to _________________ sperm. FEMALE BODY Structure Uterus Letter from diagram Description Houses and protects ______________ Allows nutrient & waste exchange with placenta during pregnancy ______________________ an embryo before a placenta grows ____________ The bottom section of the __________________ Produces fluids to help ___________________ travel Produces a ________________________ to keep out germs during pregnancy Vagina Allows passage of ________________ Produces fluid daily to cleanse and ___________________itself. Allows passage of shed ___________________during menstrual period Allows passage of _______________ Provides ___________________ A _____________________tube. Three inches long when not aroused and five to six inches long when aroused and very stretchy Is the middle of the three openings between a female’s legs Ovary Provide storage for the ___________ Allow _________________of the ovum Produces sex hormones (____________; ________________ and ________________) Fallopian Tubes Allow passage of _____________________ toward uterus Allow passage of ___________________from uterus Fimbria Guides a mature _________________, when it is released from an ovary, into a Fallopian tube Fringe–like or ____________-___________ outer ends of the Fallopian tubes Skene’s Glands Area of firm tissue towards the front wall of the vagina surrounding the urethra Responds to pressure sometimes causing _________________________ that may or may not produce fluid Also known as the Graffenberg–spot (G–spot). _____________ Protect opening of urethra and vagina, as eyelids protect eyes Provide ___________________ Labia are folds of skin Outer labia (labia majora) have _____________ _________________ Clitoris Provides sensation Each internal branch of erectile tissue is about ______________inches long The glans (the visible part) is usually .25–.5 inches long, comparable in size to a pearl at the front of the ______________________ where the labia meet Clitoral Hood Protects the glans of the clitoris Provides _____________________ Like a cap, mostly covers the clitoris when it is not erect