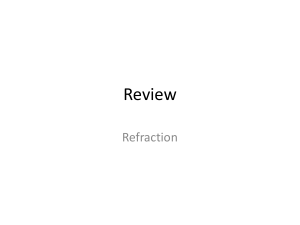
Interference Focus Question How do bubbles produce a rainbow effect? Review Vocabulary interference: results from the superposition of two or more waves; can be constructive or destructive diffraction: the bending of light around a barrier Interference • Depending on their phase relationship, the two waves undergo constructive or destructive interference. • When the light from the slits is projected on a screen, the constructive and destructive interference results in a pattern of light and dark bands called interference fringes. Diffraction Review Vocabulary diffraction: the bending of light around a barrier Reflection Focus Question Why does light reflected from a mirror make an image while light reflected from a piece of paper does not? New Vocabulary specular reflection diffuse reflection plane mirror Review Vocabulary normal: the line in a ray diagram that shows the orientation of the barrier or mirror and is drawn at a right angle, or perpendicular, to the barrier or mirror ray: a line drawn at a right angle to a wavefront; represents the direction of wave travel The Law of Reflection • The law of reflection states the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. This applies to both smooth and rough surfaces. Law of Reflection θi θr The Law of Reflection • Specular reflection is caused by a smooth surface, in which parallel light rays are reflected in parallel. • Diffuse reflection is caused by the scattering of light off a rough surface. Objects and Plane-Mirror Images • A plane mirror is a flat, smooth surface from which light is reflected by specular reflection. • An object is a source of light rays that are to be reflected by a mirrored surface, such as the bird shown below. • Some of the light travels from the bird to the mirror and reflects. Some of the reflected light from the bird hits the girl’s eyes. Quiz 1. Which is caused by a smooth surface, in which parallel light rays are reflected in parallel? A normal reflection C specular reflection B diffuse reflection D virtual reflection Quiz 2. Which is caused by the scattering of light off a rough surface? A specular reflection C diffuse reflection B normal reflection D virtual reflection Quiz 3. Which is a flat, smooth surface from which light is reflected by specular reflection? A diffuse mirror C plane mirror B convex mirror D concave mirror C, C, C Refraction Focus Question What happens to light when it enters a new medium? New Vocabulary index of refraction critical angle total internal refraction dispersion Review Vocabulary refraction: the change in direction of waves at the boundary between two different mediums Light and Boundaries • When light encounters a transparent or translucent medium, some light is reflected from the surface of the medium and some is transmitted through the medium. • When light crosses a boundary between two media, it bends. This phenomenon is called refraction. Snell’s Law of Refraction • The angle of incidence (θ1) is the angle at which the light ray strikes the surface. It is measured from the normal to the surface. • The angle of refraction (θ2) is the angle at which the transmitted light leaves the surface. It also is measured with respect to the normal. • The index of refraction (n) determines the angle of refraction between two mediums. Snell’s Law of Refraction Snell’s law of refraction relates the indexes of refraction, the angle of incidence, and the angle of refraction for any two substances. Snell’s Law of Refraction n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 Use with Example Problem 1. Problem A ray of light is incident upon a layer of flint glass (n = 1.62) at an angle of 19.0°. What is the angle of refraction? SOLVE FOR THE UNKNOWN • Use Snell’s law to find the angle of refraction. Response SKETCH AND ANALYZE THE PROBLEM • Sketch the situation. • List the knowns and unknowns. KNOWN n1= 1.00 n2 = 1.62 θ1 = 19.0° UNKNOWN θ2 = ? n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 n1 sin 1 2 sin n 2 1 1.00sin 19 sin 11.6 1.62 1 EVALUATE THE ANSWER • n1 < n2, so θ2 should be smaller than θ1. This agrees with our answer. The Meaning of the Index of Refraction • By examining refraction using the wave model of light and using some geometry, we find that sin θ2 v2 sin θ1 v1 • By combining this with Snell’s law, we see that n1 v2 n2 v1 The Meaning of the Index of Refraction If n2 = 1.00 (a vacuum), then v2 = c and we see that the index of refraction for a medium is related to the speed of light in the medium. Index of Refraction c n v Total Internal Reflection • When n1 > n2, the angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence. • At a certain angle of incidence, known as the critical angle (θc), the refracted light ray lies along the boundary of two mediums. Critical Angle n2 sin θC n1 Total Internal Reflection Total internal refraction occurs when light traveling from a region of higher n to a region of lower n strikes the boundary at an angle greater than the critical angle such that all light reflects back into the region of higher n. Total Internal Reflection The light traveling through a transparent optical fiber always hits the internal boundary of the optical fiber at an angle greater than the critical angle, so all of the light is reflected and none of the light is transmitted through the boundary. Quiz 1. Which determines the angle of refraction between two media? A index of refraction C index of reflection B index of dispersion D index of rotation Quiz 2. Which is the correct formula for the index of refraction? A n=v2/v1 C n=v/c B n=c/v D n=cv Quiz 3. Which is the certain angle of incidence when the refracted light ray lies along the boundary of two mediums? A refraction angle C critical angle B reflection angle D dispersion angle Quiz 4. Which occurs when light traveling from a region of higher n to a region of lower n strikes the boundary at an angle greater than the critical angle such that all light reflects back into the region of higher n? A total internal dispersion C total internal refraction B total optical refraction D total internal reflection Quiz 5. Which occurs when white light separates into a spectrum of colors when it passes through a glass prism? A reflection C refraction B dispersion D magnification A, B, C, C, B