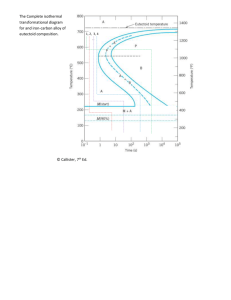
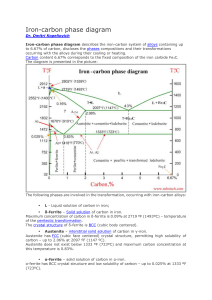
HEAT TREATMENT Dr. Maryam Abduladheem Lecture 1 HEAT TREATMENTS Heat treatment is the process of heating (but never allowing the metal to reach the molten state) and cooling metal in a series of specific operations which changes or restores its mechanical properties. STAGES of HEAT TREATMENT • Stage l — Heat the metal slowly to ensure a uniform temperature. • Stage 2 — Soak (hold) the metal at a given temperature for a given time. • Stage 3 — Cool the metal to room temperature. Heat treatment process Variables includes: 1.Heating temperature 2.Cooling temperature 3.Heating rate 4.Cooling rate 5.Soaking time 6.Environment * Heat treatment may use for: 1- Final product to alter the properties (in general). 2- To facilitate the manufacturing processes such as the rolling process. IRON-CARBON PHASE DIAGRAM It’s defined as:A map of the temperature at which different phase changes occur on very slow heating and cooling in relation to Carbon content. is Isothermal and continuous cooling transformation diagrams for plain carbon and alloy steels. Various Transformation Reactions and development of Microstructure • Peritectic Reaction: L+⇌ • Eutectic Reaction: Eutectic of austenite and cementite is known as ledeburite L ⇌ + Fe3C • Eutectoid Reaction: Eutectoid of ferrite and cementite is known as pearlite. The ferrite and cementite phases occur as alternate layers ⇌ + Fe3C • When Fe-alloy of 0.77% of C is cooled slowly it transforms from single phase of austenite to pearlite structure. ⇌ + Fe3C Microstructure of hypoeutectoid steel Microstructure of hypereutectoid steel