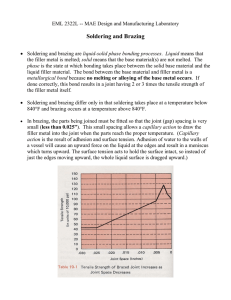
Brazing may be define as a techniques of joining two similar or dissimilar materials by additional of special filler metal. Brazing gives a much stronger joint than soft soldering but it requires greater heat which cannot be obtain from a copper bit in soft soldering. The filler metal used in brazing is known as a shelter. The melting temperature of a spelter should be above 4270C and brazing is carried out above this temperature. On the basis of method of heating brazing can be classified as ◦ Gas brazing ◦ Furnaces brazing ◦ Electric brazing ◦ Immersion or dip brazing ◦ Torch brazing ◦ Induction heating brazing In brazing operation the part to be joined are thoroughly cleaned of all oxides, oil, or grease. Part to be joined are fitted together so that they are in proper contact. The parts are held in position by suitable clamp devices. For producing a strong and rigid joint, it is necessary to hold the surface tightly in contact. Suitable flux is applied to the join with a fine brush. Use optimum amount of flux as excess flux hardens the surface of the joint and makes the filling and finishing operation difficult Heating is carried out till the flux begin to flow, the spelter is places on the joint and heating is continued till the spelter flows to all position by capillary action. Then cooling is done at a suitable rate to get the joint. After cooling, the excess flush is removed by a wire brush Cleaning oxide free and uncontaminated base metal surface are essential to ensure sound brazed joints of uniform quality. Grease, oil, dirty, oxides and other foreign matters or impurities will cause irregular flow of filler alloy, lack of bond at spots and porosity in the joint. Base metal surface may be cleaned mechanically or chemically Brazing joint design should be such that ◦ The filler metal can be placed on one side of the joint and pulled through the joint by capillary action. ◦ The joint meet service requirements e.g. Mechanical performance, pressure tightness, corrosion resistance, good appearance etc ◦Wettability of filler alloy. ◦The brazing alloy is subjected to a shearing stress The type of joint used for brazing include the lap, scarf butt joint, Squire butt joint, tee joint. The filer material used in brazing is known as spelter. It can be classified into two categories ◦Copper base spelter ◦Silver base spelter Depending upon the type of spelter used, brazing is classified as ◦ Copper brazing ◦ Silver brazing Though copper and silver are the main constituents of spelter, different element like zinc and cadmium in varying proportions are frequently added to the spelter to meet certain required conditions. A brazing filler materials must possess the following proprieties ◦Ability to wet the base metal on which it is used in order to make a strong and sound bond ◦Proper melting temperature and flow properties that permit distribution in properly prepared joints by capillary action. ◦Desirable mechanical and physical properties in the joint, such as strength and ductility Surface oxidation of the base metal hinder wetting and production of consistently sound brazed joint. There fore fluxes are used to prevent undesirable reaction during brazing Dissolve the oxide and remove it to the surface of the molten filler metal. Spread a head of the filler metal and so protect the metal surface from oxidation Promote capillary of the filler metal The main constituent of fluxes are ◦Fused borax (For high temperature) ◦Sodium ,potassium and lithium borate compound are used in high temperature melting point fluxes ◦Fluoborates ( Compound of fluorine, boron and active metals such as Na and K) ◦Chloride ◦Boric acid. It is employed principally as a cleaning agent ◦Sodium and potassium hydroxides Complete flux removal is essential after brazing because many fluxes especially those containing fluorides, may cause corrosion in the joint fluxes may be removed by ◦Washing the brazed part in hot water ◦Dipping the part in hot water ◦Dipping the part in chemicals ◦Mechanical means such as wire brushing ◦Rapid immersion of the warm brazed part in cold water Properly clean the joints so that it doesn’t contain harmful element Use the right flux in an optimal quantity The joint must be reasonably tight Apply correct heat to work piece and solder. Avoid prolonged heating Heat the work piece in uniform temperature Brazing is used to join a large variety of dissimilar metal It is used for brazing pressure tight joints Thin sheet, pipe that can’t be joined by welding can be brazed. Complex assemblies can be fabricated by this method Corrosion resistance joints can be produced by this method. Brazing process can be automated for bulk production Brazing fluxes may produced toxic fumes Brazing requires tightly mating parts. Brazed joint have poor strength than welding Large area can not be brazed easily due to luck of uniform heating of internal surfaces Fluxes residue if not properly removed can cause corrosion. Joining carbide tips with mild steel shank Joining of cast part to wrought parts Joining non – metals to metals Cycle industry Joining dissimilar metal Steam turbine industry Fastening of pipe fitting, tanks, heat exchangers and electrical repair work.