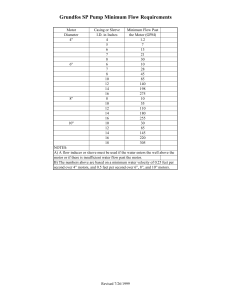
` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Module 5 – Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Learning After finishing this module, you are expected to: Objectives 1. Explain what is motor, motor branch-circuit and feeder conductors and protection 2. Determine the full load current of motors and sized of overload device Topics 1.0. 1.1. 1.2. 1.3. 1.4. 1.5. Overview Definition Table of FLC versus Motor Nameplate current Sizing a branch circuit conductor Branch - Circuit, Short - Circuit and Ground - Fault Protection. Sizing Contactor, Overload device and Disconnect switch. Industrial Electricity & Motor Control, Rex Miller & Mark Miller, C 2013 th Industrial Motor Control, 6 Edition, Stephen L. Herman, C 2010 NEC 2008 and PEC 2017 Warm Up Give Three things that you expect you will learn in this module. 1. _________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________ Pre-Test: 1. Explain the importance of proper sizing of the branch circuit conductor for a single or group of motors. 2. Explain the importance of proper sizing of the feeder short circuit and ground fault protective device. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 48 5 ` 1.0 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Overview Most electrical equipment is rated in volt-amperes (VA) or watt input. Basic understanding of Article 4.30 is the fact that motors traditionally have been rated in horsepower output. Circuits supplying motors are sized according to the input power of the motor. The input power includes the motor losses and the power factor of the motor. The losses are not the type of information found on the nameplate of a motor. Tables 4.30.14.2 and Table 4.30.14.4 contain accurate industry-wide input ampere ratings for motor. However, some motor are available with their output ratings expressed in watts and kilowatts. (One horsepower equals approximately 746 watts.) It is important to understand that circuits that supply motors not rated in horsepower still must be sized according to the input of the motor, rated in amperes. Sizing circuits based solely on kilowatts output results in seriously undersized conductors (because the current requirements of the losses and the power factor are neglected) and the improper application of overcurrent devices. See Article 4.30.1.6 for ampacity and motor rating determination. (NEC 2008, Article 430 and PEC 2017, Article 4.30) 1.1. Definitions Adjustable Speed Drive. A combination of the power converter, motor and motor-mounted auxiliary devices such as encoder, tachometer, thermal switches and detectors, air blowers, heaters, and vibration sensor. Adjustable Speed Drive System. An interconnected combination of equipment that provides a means of adjusting the speed of a mechanical loads coupled to a motor. A drive system typically consists of an adjustable speed drive and auxiliary electrical apparatus. Controller. For the purpose of this module, a controller is any switch or devices that is normally used to start and stop a motor by making and breaking the motor circuit current. Motor Control Circuit. The circuit of a control apparatus or system that carries the electric signals directing the performance of the controller but does not carry the main power current. 1.2. Table of FLC versus Motor Nameplate current Full Load Current (FLC). The motor full load current is the current indicated in the nameplate of the motor or as specified in the tables or from manufacturers data. The full load current ratings listed in Table 4.30.14.2 for Single Phase and Table 4.30.14.4 for Three phase motor. Motor Nameplate Current Rating. Overload devices must be sized based on motor nameplate current rating in accordance with section 4.30. Note: The motor nameplate full-load ampere rating is identified as full-load amperes (FLA). The FLA rating is the current in amperes the motor draws while producing its rated horsepower load at its rated voltage, based on its efficiency and power factor. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 49 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Table of Full Load Current of AC Motors. Source: PEC 2017 Source: PEC 2017 Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 50 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller The nameplate rating of motor: The nameplate data of AC Motor as specified if the Figure shown, compose of the following: a. Full-Load Ampere (FLA) b. Temperature Rise c. Power Factor d. Phase (1-Phase or 3-Phase) e. Volts f. Service Factor g. Cycle h. RPM i. HP j. Code letter k. Thermal Protection l. Impedance Protection m. Serial number n. Frame o. Duty There are three methods on how to determine the Full-Load Current of AC Motor. 1. By nameplate data (as illustrated above) 2. By Tables (PEC Table 4.30.14.2 & Table 4.30.14.4) 3. By Formula. By Formula: For Single Phase motor: 𝑁𝑎𝑚𝑒 𝑃𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑒 (𝑁𝑃) = 746𝑊 𝑥 𝐻𝑃 𝐸 𝑥 𝐸𝑓𝑓 𝑥 𝑃𝐹 Where: HP E Eff PF – Horse Power rating – voltage rating of the machine – Efficiency – Power Factor Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 51 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller For Three Phase motor: 𝑁𝑎𝑚𝑒 𝑃𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑒 (𝑁𝑃) = 746𝑊 𝑥 𝐻𝑃 √3𝑥𝐸 𝑥 𝐸𝑓𝑓 𝑥 𝑃𝐹 Where: HP E Eff PF √3 – Horse Power rating – Voltage rating of the machine – Efficiency – Power Factor - constant for Three phase Example 1: What is the full load current of 5 HP, 230 volts Single Phase motor? Solution: a. As per Table 4.30.14.2, the Full-Load Current is equals to FLC = 28 amperes. See the table below for specifying the full-load current. Source: PEC 2017 b. By Formula: Assume pf = 80% and Eff = 72.3% 𝐹𝑢𝑙𝑙 − 𝐿𝑜𝑎𝑑 𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 = 746𝑊 𝑥 𝐻𝑃 746 𝑥 5 = = 27.693 𝐴 𝐸 𝑥 𝐸𝑓𝑓 𝑥 𝑃𝐹 (230)(0.732)(0.80) Approximately 28 amperes. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 52 5 ` Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Example 2: What is the full load current of 7.5 HP, 230 volts Three Phase induction type squirrel cage motor? Solution: 1. As per Table 4.30.14.4, the Full-Load Current is equals to FLC = 22 amperes. See the table below for specifying the full-load current. Source: PEC 2017 2. By Formula: Assume pf = 80% and Eff = 79.8% 𝐹𝑢𝑙𝑙 − 𝐿𝑜𝑎𝑑 𝐶𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 = 746𝑊 𝑥 𝐻𝑃 √3 (𝐸)(𝐸𝑓𝑓)(𝑃𝐹) = 746 𝑥 7.5 (230)(0.798)(0.80) = 22.0 𝐴 Approximately 22 amperes. 1.3. Size of Branch Conductor serving a single motor: Conductor size. Conductor to a single motor must be sized not smaller than 125% of the motor FLC rating as listed in Table 4.30.14.2 and Table 4.30.14.4. To specify the motor branch circuit conductor, Table 3.10.2.6(B)(16) of the PEC 2017 edition will be used. This table shows the Ampacity of the conductors. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 53 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Source: PEC 2017 Example 3: What size of branch circuit conductor is required for 5 HP, 230 volts three phase induction type squirrel cage motor? Solution: Base from Table 4.30.14.4, the Full-Load Current (FLC) of 5HP, 230V, 3-phase motor is 15.2 amperes. Conductor size = FLC x 125% = 15.2 x 125% = 15.2 x 1.25 = 19 amperes. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 54 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Base from Table 3.10.2.6(B)(16), the conductor size is 3.5 mm2, TW rated 20 amperes at 60C. if THW, the conductor size is 2.0 mm2, rated 20 amperes at 75C. If THHN, the conductor size is 2.0 mm2, rated 25 amperes at 90C. Source: PEC 2017 Example 4: What size of branch circuit conductor is required for 15 HP, 230 volts three phase induction type squirrel cage motor? Solution: Base from Table 4.30.14.4, the FLC of 15HP, 230V, 3-phase motor is 42 amperes. Conductor size = FLC x 125% = 42 x 125% = 42 x 1.25 = 52.5 amperes. Base from Table 3.10.2.6(B)(16), the conductor size is 14 mm2, TW rated 55 amperes at 60C. if THW, the conductor size is 14 mm2, rated 65 amperes at 75C. If THHN, the conductor size is 8.0 mm2, rated 55 amperes at 90C. See Table 3.10.2.6(B). Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 55 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Source: PEC 2017 1.4. Several Motors – Conductor size. Circuit conductors that supply several motors (typically called as feeders) must not be sized smaller than 125% of the largest motor FLC, plus the sum of the Full-Load Current (FLCs) of the other motors in the group. Example 5: What size feeder conductor is required for a 5 HP & 10 HP, 230 volts three phase induction type squirrel cage. Solution: Base from Table 4.30.14.4, the FLC of 5HP & 10 HP, 230V, 3-phase motor is 15.2 and amperes and 28 amperes respectively. Motor feeder Conductor = FLC of largest motor x 125% + FLC of other motor = (28)(125%) + 15.2 = (28)(1.25) + 15.2 = 50.2 amperes. Referring to Table 3.10.2.6(B)(16), the conductor size is 14 mm2, TW rated 55 amperes at 60C. if THW, the conductor size is 14 mm2, rated 65 amperes at 75C. If THHN, the conductor size is 8.0 mm2, rated 55 amperes at 90C. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 56 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Example 6: What size feeder conductor is required for a 10 HP, 15 HP and 25 HP, 230 volts three phase motors, if the terminal rated for 75C? Solution: Base from Table 4.30.14.4, the FLC of 10HP, 15 HP and 25 HP, 230V, 3phase motor is 28, 42 and 68 amperes respectively. Motor feeder Conductor = FLC of largest motor x 125% + FLC of other motor = (68)(125%) + 42 + 28 = (68)(1.25) + 42 + 28 = 155 amperes. Referring to Table 3.10.2.6(B)(16), feeder conductor size is 60 mm2, THW rated 160 amperes at 75C. Example 7: What size feeder conductor is required for a 5 HP, 15 HP and 30 HP, 460 volts three phase motors, if the terminal rated for 75C? Solution: Base from Table 4.30.14.4, the FLC of 5HP, 15 HP and 30 HP, 460V, 3phase motor is 7.6, 21 and 40 amperes respectively. Motor feeder Conductor = FLC of largest motor x 125% + FLC of other motor = (40)(125%) + 21 + 7.6 = (40)(1.25) + 21+ 7.6 = 78.6 amperes. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 57 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Referring to Table 3.10.2.6(B)(16), feeder conductor size is 22 mm2, THW rated 85 amperes at 75C. Source: PEC 2017 1.5. Branch - Circuit, Short - Circuit and Ground - Fault Protection. 1. General. The motor branch-circuit short-circuit and ground fault protective device must comply with Section 4.30.4.2(b) and Section 4.30.4.2(c). 2. All Motors. A motor branch-circuit, short-circuit and ground-fault protective device capable of carrying the starting motor. 3. Rating or Setting. In accordance with Table 4.30.4.2. A protective device that has a rating or setting not exceeding the value calculated according to the values given in Table 4.30.4.2. shall be used. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 58 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Source PEC 2017 1.6. Feeder Short-Circuit and Ground Fault Protection Feeder Protection. 1. Motors Only. Feeder conductors must be protected against short circuit and ground faults by a protective device sized not more than the largest rating of the branch circuit short circuit and ground fault protective device for any motor plus the sum of the full-load currents of the other motors in the group. (Source: Understanding Basic Motor Control by Mike Holt) Example 8: What size of conductor and inverse time circuit breaker are required for a 5 HP, 230V, three phase motor? Solution: Step 1: Determine the FLC, refer to Table 4.30.14.4 of PEC Full-Load Current (FLC) = 15.2 amperes Step 2: Determine the branch circuit conductor: = FLC x 125% = 15.2 x 1.25 = 19 Amperes Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 59 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Based from Table 3.10.2.6(B)(16), use 3.5 mm2 ,TW rated 20 amperes Step 3: Determine the branch circuit protection [Table 2.40.1.6(A)], [Table 4.30.4.2]. =FLC x 250% = 15.2 x 2.50 = 38A, next size up = 40A = Use 40 AT, 240 V, 3-Pole, Inverse Time Circuit Breaker. Source: PEC 2017 Example 9: What size feeder conductor is required for a 5 HP, 15 HP and 30 HP, 460 volts three phase motors, if the terminal rated for 75C? Solution: Base from Table 4.30.14.4, the FLC of 5HP, 15 HP and 30 HP, 460V, 3phase motor is 7.6, 21 and 40 amperes respectively. Motor feeder Conductor = FLC of largest motor x 125% + FLC of other motor Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 60 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller = (40)(125%) + 21 + 7.6 = (40)(1.25) + 21+ 7.6 = 78.6 amperes. Referring to Table 3.10.2.6(B)(16), feeder conductor size is 22 mm2, THW rated 85 amperes at 75C. Size of protective device (Individual Motor) For 5 HP, 460V 3-Phase: = FLC x 250% = 7.6 x 2.5 = 19A, next size up = 20A USE: 20AT, 3P, 460V For 15 HP, 460V, 3-Phase = FLC x 250% = 21 x 2.5 = 52.5A, next size down = 50A USE: 50AT, 3P, 460V For 30 HP, 460V, 3-Phase = FLC x 250% = 40 x 2.5 = 100A, next size up = 100A USE: 100AT, 3P, 460V Size of main protective device (for group of Motors) = Largest rating of the branch circuit short circuit and ground fault protective device for any motor plus the sum of the full-load currents of the other motors in the group. = 100A + 21 + 7.6 = 128.6 A, next size up = 150A USE 150AT, 3P, 460V. Example 10: What size feeder conductor is required for a 5 HP, 15 HP and 30 HP, 230 volts three phase motors, if the terminal rated for 75C? Solution: Base from Table 4.30.14.4, the FLC of 5HP, 15 HP and 30 HP, 460V, 3phase motor is 15.2, 42 and 80 amperes respectively. Motor feeder Conductor = FLC of largest motor x 125% + FLC of other motor = (80)(125%) + 42 + 15.2 = (40)(1.25) + 21+ 7.6 = 157.2 amperes. Referring to Table 3.10.2.6(B)(16), feeder conductor size is 80 mm2, THW rated 190 amperes at 75C. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 61 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller Size of protective device (Individual Motor) For 5 HP, 230V 3-Phase: = FLC x 250% = 15.2 x 2.5 = 38A, next size up = 40A USE: 40AT, 3P, 240V For 15 HP, 230V, 3-Phase = FLC x 250% = 42 x 2.5 = 105A, next size down = 100A USE: 100AT, 3P, 240V For 30 HP, 230V, 3-Phase = FLC x 250% = 80 x 2.5 = 200A, next size up = 200A USE: 200AT, 3P, 240V Size of main protective device (for group of Motors) = largest rating of the branch circuit short circuit and ground fault protective device for any motor plus the sum of the full-load currents of the other motors in the group. = 200A + 42 + 15.2 = 257.2 A, next size down = 250A USE 250AT, 3P, 240V. or = 200A + 42 + 15.2 = 257.2 A, next size up = 300A USE 300AT, 3P, 240V. Either of these two rating of protective device will used the motors will be protected during the starting period. Size of Contactor: To size up the contactor, the formula will apply. = 𝐻𝑃 𝑥 1000 Example 11: What is the equivalent size of the contactor for a 10 HP, 230V, 3 Phase motor? Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 62 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller = 10 𝐻𝑃 𝑥 = 7.46 𝑘𝑊 1000 𝑈𝑠𝑒 ∶ 8 ~10 𝑘𝑊, 240𝑉, 3 − 𝑃ℎ𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 Example 12: What is the equivalent size of the contactor for a 30 HP, 460V, 3 Phase motor? = 30 𝐻𝑃 𝑥 = 22.38 𝑘𝑊 1000 𝑈𝑠𝑒 ∶ 23 ~25 𝑘𝑊, 460𝑉, 3𝑃ℎ𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟 OVERLOAD PROTECTION: Overload devices are intended to protect motors, motor control apparatus and motor branch circuit conductors against excessive heating due to motor overloads. Overload is the operation of equipment in excess of the normal, ful-load current rating, which, if it persist for a sufficient time, will cause damage or dangerous overheating of the apparatus. Overload Sizing for Continuous duty. 1. Motors Rated More than One Horsepower. Motors rated more than 1HP, used in a continuous duty application without integral thermal protection must have an overload device as follows: a. Separate Overload Device. A separate overload device must be selected to open at no more than the following percent of the motor nameplate full-load current rating: Service Factor. Motor with a marked service factor (SF) of 1.15 or more on the nameplate must have the overload device sized no more than 125 percent of the motor nameplate current rating. Temperature Rise. Motors with a nameplate temperature rise of 40C or less must have the overload device sized no more than 125 percent of the motor nameplate current rating. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 63 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller All other motors. No more than 115 percent of the motor’s nameplate current rating. (Source: Understanding Basic Motor Controls, Mike Holt and PEC 2017, section 4.30.3.2) Example 13: What size of an overload must be used to protect a 10 HP, 230V, 3 Phase motor with a service factor of 115%? Solution: From Table 4.30.14.4, the full-load current of 10 HP, 230V 3-Phase is 28 amperes. FLC = 28A Size of Overload Device = FLC x 125% = 28 x 1.25 = 35 amperes Overload settings should not be less than 35 amperes say 40 amperes. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 64 ` 5 Motors, Motor Circuit & Controller DO – IT – YOURSELF: Determine the size of the feeder conductors, protective devices and size of contactors for single or group of motors. (Use inverse time breaker for protective device) 1. What size feeder conductor is required for a 10 HP, 230 volts three phase induction type squirrel cage. 2. What size feeder conductor is required for a 15 HP & 10 HP, 230 volts three phase induction type squirrel cage. 3. What size feeder conductor is required for a 7.5 HP & 25 HP, 230 volts three phase induction type squirrel cage. 4. What size feeder conductor is required for a 7.5 HP, 20 HP, and 50 HP, 460 volts three phase induction type squirrel cage. 5. What size feeder conductor is required for a 25 HP, 30 HP, and 40HP, 230 volts three phase induction type squirrel cage. Note: Write the solution on a separate sheet of papers. Engr. Eddie L. Cabaltera | Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges 65