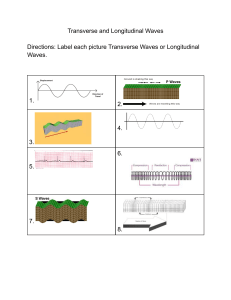
Name ____________________________ Date ____________________ Class _____________ Characteristics of Waves Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. ______ 1. Mechanical waves are created when a source of energy causes a medium to a. move. c. expand. b. compress. d. vibrate. ______ 2. Waves that move the particles of the medium parallel to the direction in which the waves are traveling are called a. longitudinal waves. c. surface waves. b. transverse waves. d. combination waves. ______ 3. The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave is the wave’s a. amplitude. c. frequency. b. wavelength. d. speed. ______ 4. The speed of a wave is its wavelength multiplied by its a. amplitude. c. frequency. b. vibration. d. reflection. ______ 5. The maximum distance that the particles of a medium move from the rest position is the a. amplitude of the wave. b. wavelength of the wave. c. frequency of the wave. d. speed of the wave. ______ 6. The interaction between two waves that meet is called a. reflection. c. diffraction. b. refraction. d. interference. ______ 7. What occurs when vibrations traveling through an object match the object’s natural frequency? a. reflection c. diffraction b. refraction d. resonance 1 Chapter Tests © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Name ____________________________ Date ____________________ Class _____________ Characteristics of Waves (continued) ______ 8. Waves combine to produce a smaller or zero-amplitude wave in a process called a. destructive interference. c. reflection. b. constructive interference. d. refraction. ______ 9. Mechanical waves are classified according to a. their size. c. how they move. b. their shape. d. their source. ______ 10. Why do you see lightning from a distant storm before you hear thunder? a. The thunder is produced after the lightning. b. Your eyes react faster than your ears. c. Light travels faster than sound. d. Sound travels faster than light. Completion Fill in the line to complete each statement. 11. The more ____________________ a mechanical wave has, the greater its amplitude. 12. As the frequency of a wave traveling at constant speed increases, its ____________________ decreases. 13. In ____________________ interference, the energy of the combined wave is greater than the energy of each of the two waves. 14. The crests and troughs of a standing wave are called ____________________. 15. In a longitudinal wave moving along a spring, areas where the coils are farthest apart are called ____________________. True or False If the statement is true, write true. If it is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. ____________ 16. In transverse waves, the particles of the medium move at right angles to the direction in which the wave is traveling. ____________ 17. A wave bending as it passes a point of land is an example of refraction. ____________ 18. Nodes are points on a standing wave where the amplitude of the wave is maximum. ____________ 19. Surface waves combine the properties of transverse and longitudinal waves so that the particles in the wave move with a(n) up-and-down motion. ____________ 20. Waves that require a medium through which to travel are called electromagnetic waves. 2 Chapter Tests © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Name ____________________________ Date ____________________ Class _____________ Characteristics of Waves (continued) Using Science Skills Use the figure below to answer the following questions in the spaces provided. 21. What does the person transfer to the rope by pulling it up and down at point A? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 22. What kind of wave is being generated? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 23. In what direction does the medium move relative to the direction of the wave? Explain. ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Essay Write an answer for each of the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 24. How can you measure the wavelength of a transverse wave? Of a longitudinal wave? 25. What causes refraction? 3 Chapter Tests © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Name ____________________________ Date ____________________ Class _____________ Characteristics of Waves (continued) Using Science Skills Use the figure below to answer the following questions in the spaces provided. 26. What type of mechanical wave is produced by the action of this coiled spring? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 27. Name and describe the parts of the wave labeled A and B. ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 28. What determines the amplitude of a wave of the type shown? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Essay Write an answer for each of the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 29. Compare and contrast the motions of ocean waves with the motions of longitudinal and transverse waves. 30. What is interference? Describe the effect of each of the two types of wave interference on amplitude. 4 Chapter Tests © Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.