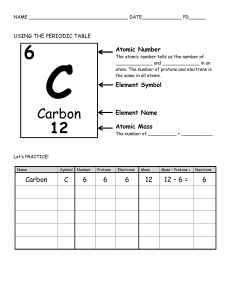
lesson 1: matter and it’s properties what is matter? matter is considered as anything that has mass and takes up space. what is mass? mass is the measurement of the amount of matter, and it can be measured with units such as grams or kilograms (g, kg). what is volume? volume is the amount of three-dimensional space an substance takes up. give an example of a time where you would need to measure volume: when baking desserts, you may need to measure how much water, flour, or oil goes into the mixture, so it would be ideal to use a measuring cup. what are atoms? atoms are the smallest unit of an element that carries the chemical identity of an element. ● there are smaller units called subatomic particles, they fall into three types; protons (p+), neutrons (n0), and electrons (e-) ● protons determine the atomic number of an element, neutrons filter out the isotopes of an element, and electrons determine the ionization state. (if an atom is a cation, anion, or a neutral atom) what are elements? elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into smaller substances, and is only made up of one type of atom. (these types of atoms have different amounts of neutrons and protons). ● for instance; an atom with 8 electrons, 8 protons, and 8 neutrons is an atom that carries the chemical identity for oxygen (atom used for the element “oxygen”), changing the amount of subatomic particles available can change the element, as well as checking if there are isotopes and the stability of an atom. what are compounds? unlike elements, compounds CAN be broken down into simpler and more smaller substances, and they’re made from atoms of two or more varied elements which are chemically bonded. ● compounds can be bonded in different ways, such as ionic or covalent bonding. - ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding in which an atom transfers its electrons to another atom. (making the first atom a cation (positive ion) and the other atom an anion (negative ion)) - covalent bonding is a type of chemical bonding in which both atoms shares its electrons with each other (both atoms can end up neutral if they balance the sharing of electrons) what is the difference between a molecule and an atom? an atom is the smallest unit of an element, whereas a molecule is composed up of two or more atoms, compounds can be examples of molecules. give three examples of both elements and compounds: elements compounds iodine water (hydrogen (H2) + oxygen (O)) uranium sodium chloride (sodium (Na) + chlorine (Cl)) lithium rust/iron oxide (iron (Fe) + oxygen (O)) what are the two properties that comes in with matter called? they are called extensive and intensive properties. what are intensive properties? intensive properties are characteristics in which you don’t need to depend on the amount of matter available in a substance. what are extensive properties? extensive properties are characteristics in which you DO need to depend on the amount of matter available in a substance. (IMPORTANT!!) give five examples of both intensive and extensive properties: intensive properties extensive properties color weight density size viscosity length boiling and melting point mass temperature volume what’s the difference between density and weight? density is always the same no matter the sample of a substance given, but weight depends on how much the substance is in terms of size. what are physical properties? physical properties are characteristics in which you can observe or measure without changing the identity of that substance; for instance; temperature. what are physical changes? physical changes refer to the change of a substance that doesn’t change the identity of that substance. ● examples of physical changes include; bending, cutting, grinding, melting, boiling, and freezing. can matter change states? (describe the term “change of state”) yes, matter can change through four different states, and they are as followed; solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. matter can change states through different ways, and they can be represented by this diagram. give a real-life example on each process shown in the diagram: melting (solid to liquid): leaving an ice cube out for a few minutes. freezing (liquid to solid): freezing water in an ice tray to make ice cubes. evaporation (liquid to gas): boiling water to turn it into water vapor. condensation (gas to liquid): clouds in the sky. sublimation (solid to gas): letting dry ice out (dry ice is a substance that is produced by solid carbon dioxide, and can pass gas out of itself instantly) deposition (gas to solid): frost ● both processes deposition and sublimation are both changes of state that don’t go through the liquid state. describe each state of matter in terms of particles: solids contain particles that are tightly packed together and that they barely vibrate (this is due to attractive forces), solids contain a definite volume, definite shape, and definite mass. liquids contain particles that are close to each other, just like solids, they have attractive forces. these attractive forces is strong enough to keep the particles of a liquid in the bottom of their container, but isn’t strong enough to keep their particles from flowing and gliding over each, although liquids have a definite mass and volume, they don’t have a definite shape, this is because liquids take the shape of their container. gases act differently opposed to solids and liquids, their particles are far apart and go through in a rapid motion, by increasing it’s kinetic energy or temperature, then these particles move around faster, since these particles aren’t close to each other, this means that they have an indefinite volume and an indefinite shape, but a definite mass. what is plasma? plasma is an exceptionally-high temperature and neutral state of matter in electrons strip off the atom (particles make up their atoms), and any substance that is in plasma form can conduct electricity. give examples of plasma: some natural examples of plasma is lightning, stars, fluorescent lights/, neon signs, and northern lights. what do each of the three states look like in h2o form? what are chemical properties? unlike physical properties, chemical properties refers to a characteristic in which substances can undergo through processes and changes into becoming or transforming into a completely different substance. what are chemical changes? also called chemical reactions, refers to changes in which one or more substances gets converted into different substances. ● these processes can also be portrayed or be depicted by a scientific equation, unlike regular equations, where theres an equal sign, scientific equations use arrows to mark a change or a compound being formed. use this equation to answer these following questions: 1) what does the elements on the left side represent? the elements shown on the left side represents reactants, these are the substances that react in a chemical change or a chemical reaction. 2) what does the compound on the right side represent? the newly formed compound on the right side represents products, in a math equation, you would need to two numbers to use to form a product, the same kind of logic is applied in scientific equations, you would either add or subtract the reactants together to get a newly formed substance made out or composed of the reactants. give 5 examples of chemical changes: 1) burning paper, this is because the paper turns into a new substance which is ashes. 2) a substance/solution changing color 3) milk going sour 4) rusting is considered as a chemical change because when metal forms with oxygen particles/atoms, they bond and change into rust. 5) burning of wood (IMPORTANT!!) how is energy involved in physical and chemical changes? energy comes in many different forms, (such as kinetic, potential, nuclear, light, heat/thermal, etc..), and energy must be used to create physical/chemical changes, for example; when dry ice vaporizes, carbon dioxide molecules absorb energy what does the law of conservation (of energy) state? that energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only released and absorbed. ● ● this law can be applied to electrons and their energy levels, by using the bohr model, you can see that there are 4 rings surrounding the atom with different amounts of electrons on each ring (level 1: 2, level 2: 8, level 3: 18, level 4: 32), the bigger the ring is, the higher the level. when energy gets absorbed, electrons gain energy, making them go up a level, and the opposite is applied when energy gets released, electrons lose energy, make them go down a level. can matter be separated? in specific cases it can, if a substance is a pure substance, then it can’t be seperated, but if it’s a mixture, then it is able to be separated. what is a mixture? a mixture is a mix or blend of two or more kinds of matter that retain its own identity and properties, mixtures can be mixed and separated by physical means. ● mixtures can be separated physically by filtration, sublimation, evaporation, and magnetic separation. ● mixtures, just like pure substances, come in two types; homogenous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures what is a homogeneous mixture? homogeneous mixtures are mixtures in which the components (the “kinds of matter”) are evenly substituted or spread out, meaning that the components are uniform in composition. what is a heterogeneous mixture? unlike homogeneous mixtures, heterogeneous mixtures are mixtures in which the components ARE NOT evenly substituted or spread out, meaning that the components aren’t uniform in composition. what does the term “uniform in composition” mean? the term “uniform in composition” means that the components of a mixture are evenly spread out. (IMPORTANT!!) give 3 examples of both homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures: homogeneous mixtures heterogeneous mixtures salt and water blood air granite maple syrup salad what are pure substances? pure substances are substances that, in some cases, cannot be broken down into smaller pieces. there are only two types of pure substances, and they are elements and compounds, meaning that pure substances cannot be broken down if they’re elements, and they CAN be broken down if they’re compounds. ● pure substances have a fixed composition what makes a pure substance different from a mixture. pure substances are different than mixtures in three different ways. 1) any given sample of a pure substance has the same characteristic properties. 2) any given sample of a pure substance has the same composition. 3) in water, there’s always 88.8% oxygen and 11.2% hydrogen. can a pure substance be separated by physical means? pure substances contain fixed properties and a fixed composition means that you cannot easily separate it by physical means. lesson 2: elements what is the periodic table? the periodic table is a chart or diagram that a russian chemist named dmitri mendeleev created in which it consists all the elements in our world, there is 118 elements and they’re arranged according to their similar chemical properties and their categories. what are the horizontal rows of the periodic table called? the horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods, and physical, as well as chemical properties, change somewhat regularly throughout/across a period. each period contains an energy shell, and as there’s a new period, the amount of shells increases, meaning that the first period has one shell, and seventh period has seven shells. what are the vertical columns of the periodic table called? the vertical columns of the periodic table are either called groups or families, each group contains elements with similar chemical properties or characteristics. groups contains elements that arranged from lowest to highest when you’re going from up to down. how are elements represented in the periodic table? they’re represent by squares, and each element displayed contains a symbol and numbers on them, the element of carbon would look like this for example: what is the atomic number? the atomic number represents the amount of protons in an element, since carbon has an atomic number of 6, there are 6 protons in a carbon atom. what is the atomic mass? the atomic mass is a number that is equivalent or highly approximated by the amount of protons added with neutrons. ● formula for atomic mass = neutrons + protons ● formula for neutrons = atomic number or protons - atomic mass describe how an atom can change what the element is: if an atom changes the amounts of protons available, it can change what the element is; for instance, oxygen has an atomic number of 8, meaning that there are 8 protons, but carbon has an atomic number of 6, meaning that there are 6 protons. in conclusion, this means that with a different number of protons, there will be a different atomic number, changing what the element is. what are some methods you can to change the element? scientists and chemists use a process called protonation, in which they add a proton to an element’s atom, molecule, or ion. what are the categories in which elements can be separated in? there are four categories or types of elements that can be shown in the periodic table and they are as such; metals, non-metals, metalloids, and noble gases. explain what metals are and their properties: a metal is a category or type of element, metals are good heat and electricity conductors, they’re solids (crystalline solids, to be exact) that are in room temperature, they’re malleable; meaning that you can press or hammer them down, or roll them into thin sheets, and they’re ductile, meaning that you can draw them into fine wire. give examples of metals: 1) gold 2) aluminum 3) bronze 4) lead 5) zinc explain what non-metals are and their properties: unlike metals, non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity, most of non-metals are gases, and when they’re not, they’re brittle (or fragile) solids. non-metals are also dull and have a lower melting point than metals, and they’re neither ductile nor malleable. ● bromine is the only non-metal that is a liquid what are the similarities between non-metals and metals? both are elements, they have the same atomic structure, and they share electrons to make molecules. give examples of non-metals: 1) carbon 2) oxygen 3) nitrogen 4) phosphorus 5) iodine explain what metalloids are and their properties: metalloids are substances or a type of element that is between metals and non-metals, meaning that they have some characteristics of non-metals and some characteristics of metals. metalloids are ductile and malleable, they’re somewhat lustrous and also brittle, all metalloids are solids and at room temperature, and they’re semi-conductors of electricity and heat. metalloids also behave like non-metals more than metals. give examples of metalloids: 1) boron 2) abdullah germanium 3) pollanium 4) tellurium explain what noble gases are: they’re rare gases that are found in group 18 of the periodic table, they’re generally unreactive and they’re mostly found or are in room temperature. give examples of noble gases: 1) helium 2) argon 3) krypton 4) neon