
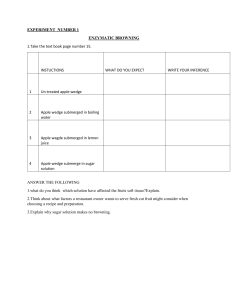
Chemistry Investigatory Project Browning of Apples By: - Akash Garhwal Class: - XII Science School: - Kendriya Vidyalaya Sikar Kendriya Vidyalaya Sikar Exam roll no:This is to certify that Akash Garhwal, a student of Class XII Sci. has successfully completed the project guided by Mr. Ajay Kumar (subject teacher) during the academic year 2017-18 in practical fulfilment of Chemistry practical examination conducted by AISSCE . Signature of Examiner:-> Sign. Of Chemistry Teacher :-> AIM:To study the factor those are affecting apple slices turning brown and the best way to preserve the apple slices. ACKNOWLEDGEMT: In the accomplishment of this project successfully. Many people have best owned upon me their blessings and the heart pleaged support, their time I am utilizing to thank all the people who have been concerned with the project. Primarily I would thank god for being able to complete this project with success. Then I would like to my principal Mr. Prahalad Singh and Chemistry teacher Mr. Ajay Kumar , whose valuable guidance has been the once that helped me this project and makes it full proof success his suggestions and his instructions has served as the major contributor toward the completion of this project Then I would like to thank my parents and friends who have helped me with their valuable suggestions and guidance has been helpful in various phase of the completion of the project. CONTENT:1) Theory 2) Material required 3) Procedure 4) Result 5) Conclusion THEORY:Apples contain an enzyme called “polyphenol oxidase“(phenolase). In the presence of oxygen from air, this enzyme catalysis the formation of brown pigment called “melanins”. Treatment of the apple slices with ascorbic acid, citric acid, or acetic acid will reduce the level of browning. The reduction in browning is dependent on the type of substance and its concentration. Soaking in water will temporarily reduce the level of browning by restricting the amount of oxygen in contact with apple slices. When fruit or vegetable is peeled or cut, enzyme contained in the plant cell are released. In presence of air, the enzyme phenolase catalyses one step in the biochemical conversion of plant phenolic compound to form brown pigment called melanins. This reaction, called enzymatic browning, occurs readily at warm temperature when pH is between 5.0 and 7.0. The presence of Iron or Copper can increase the rate of reaction. This can easily be observed when fruit is cut with a rusty knife or mixed in a copper bowl. Bruising or other injury to the plant tissue disrupts the arrangement of chemicals within the cells and allows these chemicals to make contact with oxygen. This may lead to browning of uncooked fruits. Enzymatic browning can be significant problem, limiting the shelf life of many fruits and vegetables which have had little heat applied during processing. However, enzymatic browning is not always a defect. The browning reaction contributes to the desirable colour and flavour of raisins, prunes, coffee, tea and cocoa. Material Required:- Apples pH paper Tongs Glasses Pens Knife Plastic Gloves A timer Lemon juice Orange juice Soda Mineral water Baking soda - Water Procedure:The method I used was to 1. First get each substance and then to take the pH stripes and test the pH of each liquid, then cut apples into slices and line up slices of apple on table 2. Plac e an untreated apple slice on a paper towel. Label the towel “Control”. 3. Usin g tongs, dip an apple slice into lemon juice for 30 seconds, place it on towel, and label with the same name of solution. 4. Rins e the tongs and repeat the same procedure for the other five solutions. 5. Soa k one slice in water for 30 second. Place it on a towel and label the towel “Water Soak”. 6. The n to set the timer, then to record how long it takes for each apple slice with different substance on it to turn dark brown. 7. Note the time and temperature in your data table. Compare your result with those obtained. OBSERVATI ON:- What Substance Prevent Apples from Browning ? 30 25 20 15 Time(Mins) 10 5 0 Lemon juice Orange juice Tomato juice Milk Black coffee Water RESULT:My results were that the lemon juice is the best preservative to put on apple slices and that baking soda is worst. The order of the preservatives from best to worst goes from lemon juice, to soda, to mineral water, to water, to an apple slice with nothing on it (control), to orange juice and ending with baking soda. My results for the second experiment were that the best temperature to put apple slice at is a warm such as 100˚ Fahrenheit, then at room temperature of39˚ Fahrenheit, and ending with the worst temperature to put apple slices at when wanting to preserve them which is a freezing temperature such as 32˚ Fahrenheit. CONCLUSION:- I come to the conclusion that lemon juice is the best substance to put on apple slices when wanting to preserve them because it is high in citric acid. It is also has Vitamin A, C and E in it. These are good because it lowers the pH level of the apple causing it to turn brown slower. It is best to put apple slices at a hot temperature because if you put it at a cold, the ice breaks down the cell wall of the apple and introduces the enzyme called “polyphenol oxidase” to air which turns the apple brown. Fig.:- Browning of apple with different substance


![The Apple ][: A Landmark in Personal Computing](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/025535874_1-5e426f6af7f22f9073597a7a0d454bc7-300x300.png)