Nursing Midterm Study Guide: Health Assessment & More
advertisement

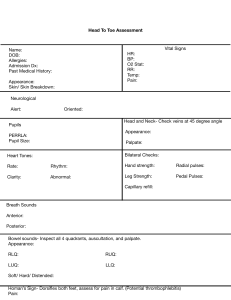
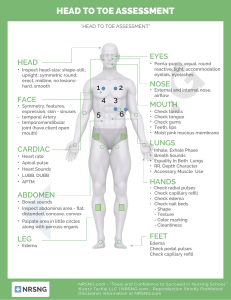
Virginia Commonwealth University School of Nursing NURS 261 – Study Guide for Midterm 1. What are the different types of health assessments, and when would each be performed? Describe the differences between a comprehensive assessment, screening assessment, focused assessment, and a follow up assessment. Comprehensive onset in primary care, admission to hospital, long term care (detailed hx and physical examination) Problem-Based/Focus walk-in clinic, ER (assessment limited to a specific problem) e.g. sprained ankle Episodic/Follow-up when a pt is following up with a healthcare provider about a previously identified problem or an individual being treated for an ongoing illness (e.g. diabetes; follow up after taking antibiotics) Shift changes of each shift for hospitalized patients Screening/Examination health care provider office- preventative care or health fair 2. What are the steps in clinical judgement process? 3. What are the factors in symptom analysis (OLDCARTS)? Systematic method of collecting data about the history and status of symptoms o Onset- Where did the symptoms begin? o Location- Where are the symptoms? o Duration- How long do the symptoms last? o Characteristics – Describe the characteristics of the symptoms. o Aggravation and alleviating factors- What affects the symptoms o Related symptoms-Are other symptoms present? o Treatment-Describe self-treatment before seeking care. o Severity- Describe the severity of the symptom 4. How does the nurse assess pain? What scales can be used? Collect subjective data, interviews patients about present health status, how they manage their pain. Use OLD CARTS Rely on self-report of patient Pain Scales Numeric (NRS) 0-10 , 0 no pain 5 moderate 10 worst pain possible Wong-Baker FACES, No Hurt-Hurts to Hurts Worst Alternative coding 0-10 (2) 5. Review Health promotion/protection education for different systems Health Promotion- desire to increase well-being (individual) o Primary- prevent a disease from developing (immunizations) o Secondary-screening effort (BP screening) o Tertiary-acute or chronic disease minimize, max health benefits (diabetes mgt) Health Protection- desire to actively avoid illness (guidelines prevent spread of communicable diseases) o Detect illness early o Maintaining functioning within its constraints 6. Identify infection control procedures to be used when conducting a health assessment. (i.e. when do you wear gloves, and when don’t you?) Gloves o To protect from bloodborne pathogens carried by patient o To protect patient from microorganism on the hands of the nurse o To reduce the potential of infection transmission from patient to patient via the nurse giving an injection emptying a urinary catheter drainage bag giving a bed bath inserting a peripheral IV (an IV in a smaller vein) removing a peripheral IV removing a urinary catheter Mask, Eye/Face shield o During procedures that may result in splashes or sprays of blood, fluids, secretions o Not usually done during health assessment. Gowns o To protect arms-exposed skin and prevent contamination of clothing with patients’ blood or fluids 7. What are the differences between subjective and objective data? Symptoms are considered subjective data that is perceived and reported by the patient (e.g. pain, itching, nausea) Signs are considered objective data that can be observed, felt, heard, or measured (e.g. rash, swelling) 8. What assessment techniques are used to evaluate vital signs? BP Pulse RR Pulse O2 Temperature 9. Define orthostatic hypotension and describe how to assess for it. Series of BP measurements Lying, sitting and standing position It is a 20 to 30 mm drop when patient goes from lying to sitting position to standing 10. State the technique for conducting the two-step blood pressure measurement. Requires that you take the blood pressure by feeling the brachial artery and then using a stethoscope. So, in a sense you will be taking the blood pressure twice using the same arm but with two methods. 11. Give an example of how each physical assessment technique is used: inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation. Inspection- Pain, Respiration, Visual exam of body, movement and posture. Palpation- HR hands to feel texture, size, shape, consistency, pulsation Percussion-evaluate size, boarders, consistency of internal organs (fluid) Auscultation- BP listening to sounds heat blood vessels, lungs, intestine. 12. What is the usual order of physical assessment techniques? GENERAL: Inspection, Palpation, Percussion, Auscultation ABDOMEN: Inspect, auscultate, percuss, then palpate an abdomen 13. Identify the use of the bell and diaphragm of a stethoscope. When do you use the diaphragm and/or bell? o Bell Low(soft) pitch sounds- extra heart sounds, vascular (bruit-whooshing) o Diaphragm high pitch sounds breath, bowel, normal heart 14. What is meant by general survey (also known as general inspection), and what are the elements included? 15. What are the four domains of mental status that are assessed by a nurse? 1. Intellectual 2. Emotional 3. Psychological 4. Personality Four main headings to Mental Status Assessment: 1. Appearance 2. Behavior 3. Cognition 4. Thought Process Changes in Mental status when changes to: Orientation, Time, Person, Place and Situation 16. What are the components of a health history? Be able to give an example of each element. Biographical Data - Name, Gender, DOB Reason for seeking care - Chief complaint History of present illness - symptom analysis (OLD CARTS) Present Health Status - Acute and Chronic conditions, medications, allergies Past Health History - Childhood illnesses, Surgeries, Hospitalizations, Accidents, Immunizations, last exam, Obstetric Family-History -Blood relatives identify illnesses of genetic, environmental that may affect current or future health Personal and Psychosocial History - affects it reflects physical or mental health o How do you feel about yourself? o Role in family o Diet-nutrition o Functional ability self-care ADL o Mental Health- Stress o Tobacco, Alcohol, Drug use o Health promotion activities- specific routines: exercise? stress mgmt? seatbelt use? o Environment potential hazards w/in home, work? Review of Systems - past and present health, symptom analysis if symptom indicated. o Integumentary o Head and Neck o o o o o o o o Breasts Respiratory Cardiovascular GI Urinary Reproductive Musculoskeletal Neurological 17. What systems are part of integumentary system. 18. Know the difference between a macule, papule, vesicle, and pustule. Macule- Freckles, flat mole (sunspots) (flat, circumscribed change in color, 1cm) Papule-Wart, Elevated firm (skin tags), 1cm, circumscribed Vesicle-Chickenpox, singles, acute eczema: Elevated, superficial, filled serous fluid ,1 cm Pustule-Acne, Impetigo, Herpes Simplex: Elevated filled with purulent fluid 19. Discuss how skin color may affect assessment and how findings may differ based on skin color. For example, how does a bruise appear differently in light skinned and dark-skinned individuals? 20. Describe how to palpate the skin for moisture, temperature, texture, turgor, and mobility, including what part of the hand is used for palpation. Texture: Smooth, soft, intact, even surface, with calluses on hands, feet, elbows, and knees Temperature and moisture: Warm and dry. Using dorsal of hand Mobility and turgor: Should move easily when lifted, with immediate return after released. Slightly pinching skin on forearm or under clavicle Thickness: Varies with age and area. o Palms and soles thickest. o Eyelids thinnest. o Callus: Thick from friction and pressure. 21. Discuss at least one health promotion or health protection strategy for the integument. Health Promotion- Skin Cancer using sunscreen Health Protection- use of gloves to prevent infection in aseptic procedure 22. What are the health history questions (Review of System) related to the integumentary system? Problem Based History system analysis (old carts) o When did it start? o Does anything make it better or worse? o What were you doing? o Do you have dry or sensitive skin? Present Health Status o Do you have any chronic illnesses? o Do you take any medications? o Have you noticed any changes in the way your skin, hair, nails look or feel? Sensation? o What type of work do you do? Past Health History/Family o Have you ever had problems with your skin? o Has anyone in your family ever had skin related problems? Personal and Psychosocial o What do you do to keep your skin healthy? 23. What are the early signs of melanoma, also known as the signs of a worrisome lesions? Asymmetry (not round) Border (poorly defined) Color (uneven) Diameter (> 6mm) Elevation (flat to raised) Feeling (itching, tingling, stinging) 24. Document the expected findings for assessment of visual acuity, distance and close vision? Reading pattern smooth: 20/20 (Is this all?) 25. What does PERRLA stand for, and how do you assess it? Pupils are Equal and Round and React to Light and Accommodate Constrict when focusing on a Close object DD Dilate when focusing on a Distant object 26. Describe how to conduct two valid assessments of auditory acuity, and what the expected results are. Whisper Test- able to repeat back 50% of the words. Standing at side of Pt 1-2 ft away covering 1 ear. Shield mouth Finger rubbing test- index finger with thumb briskly rubbing 3 to 4 inches from head - Won’t hear if have high frequency hearing loss 27. What is the expected finding when inspecting the auditory canal? 28. Describe inspection of the teeth, buccal membrane, and hard and soft palates. Include the expected findings for the assessment. Teeth- White, smooth edges, caries? gingiva pink Buccal Membrane - pink with slight vascularity; symmetrical pillars; clear saliva; Hard Palates - smooth, pale, immovable with irregular transverse rugae Soft Palate -smooth, pink with uvula in midline; symmetrical 29. What questions are included in the health history (Review System) for HEENT? Present Health Status o Have you noticed any changes in your overall health or changes to head, eyes, ears, nose or mouth? o Do you have any chronic conditions or infections that affect HEENT? o Do you take any medications? If so what, how often? Past Health History o Have you ever had an injury to HEENT? If so, describe o Have you ever had surgery HEENT? Family Health History o Is there a history of cancer Mouth or throat? o Does anyone have a condition impacting hearing, vision, thyroid? Personal Psychosocial History o When were you last routine exam? Dental/vision/hearing o Do you use corrective devices? o Describe some of your daily practices to maintain Health of HEENT? o Do you know of any occupational risks to HEENT? Problem Based History OLD CARTS o How long have you been having…? o What is the location o What other symptoms o Triggers o Treatment 30. Identify the anatomical landmarks for auscultating the anterior and posterior chest for upper lobes, middle lobes, and lower lobes lung sounds, that is, ICS and vertical anatomical landmarks of the thorax. 31. Document the expected findings of the assessment of the lungs sounds. Breathing quiet and effortless at rate of 16/ BPM Thorax symmetric, with ribs sloping downward 45 degrees Muscle development of thorax equal bilaterally Spinous process alignment; scapulae symmetric AP diameter of chest 1:2 ratio to lateral diameter Trachea midline Breath sounds clear 32. Where you expect to hear bronchial, bronchovesicular, and vesicular breath sounds. Bronchial- Over Trachea (1,2) Bronchovesicular- Over main Bronchi (3-6) Vesicular- Over lesser bronchi, bronchioles, lobes (7,8) 33. Describe the physical assessment of the lungs, including inspection, palpation, and auscultation. Inspect for appearance, posture, and breathing effort o Count respirations, observe pattern and chest expansion o Inspect nails for color and angle o Inspect skin, lips for color o Anterior/Posterior thorax for shape, symmetry, muscle development Auscultate anterior thoraxes o Vesicular breath sounds, bronchovesicular, bronchial Auscultate posterior thoraxes o Vesicular and bronchovesicular sounds expected 1-10 left to right Palpate o Posterior and anterior thoracic muscles for tenderness, symmetry (chest expansion) using thumbs at base 12 o Fremitus using 2 hands checking for vibrations on back top to bottom 1-4 34. What health history questions (Review of System) are included for the heart and neck vessels? Present Health Status o Do you have any chronic illnesses such as diabetes, renal failure, chronic hypoxia or hypertension? o Are you taking any medications If yes, what? Adverse effects? Take them as prescribed? Over the Counter drugs? Past Health History o As a child did you have congenital heart disease or heart defect? o During childhood did you have growing pains? Rheumatic fever, heart murmur? o High Cholesterol or triglycerides? o Surgery on heart? If so what procedure? Success? o Any test done on heart EKG? What treatments did you receive? Family History o Anyone in your family have diabetes, CV disease, hyperlipidemia, hypertension? Is so, Who? Personal Psychosocial History o Do you exercise? What kind, how much? o Describe personality type? o How often do you take time to relax? o Describe usual eating habits? o Do you drink or drugs or caffeine or smoke? If so, what how often how much? Problem based History (OLD CARTS) o Chest Pain? o SOB? o Cough? o Urinating during the night? o Fatigue? o Fainting? o Swelling of extremities o Leg Cramps or Pain? 35. Describe the landmarks used to auscultate the heart. Identify which valve sounds are most audible at each landmark, and if the heart sound signals the beginning or end of systole or diastole. 36. What is a heart murmur? Abnormal sound produced by blood flowing rapidly in an unusual direction (stenosis) (insufficiency) leaky valve Caused by valvular defects Systolic – obstruction of outflow of the semilunar valves or AV incompetency. Diastolic- in filling phase of cardiac cycle, indicate heart disease (valves) 37. Identify a heart murmur as systolic or diastolic, based on placement of S1 and S2. To determine of an abnormal sound occurs in systole or diastole, determine if the sound occurs after S1 or after S2 o During Diastole: When 80% of blood fills ventricles S3 may be heard just after S2 Over 30 problems with over fill heart failure or mitral or tricuspid regurgitation. End of diastole completed filling, S4 may be heard. Just before S1 (stiff ventricle) To remember the cadence of the S3 and S4 heart sounds is to use the word “tennessee” and “kentucky” Ken-tuck-y S1 S2 S3 Ten-ness-ee S4 S1S2 Systolic ejection clicks may be heard if either the aortic or pulmonic valve is stenotic or deformed 38. What questions should be included in evaluating specifically chest pain? Where are you feeling the pain? What does it feel it? Does it radiate to other areas? How severe is it 0-10? When did the pain start? How long does it last? Related symptoms? What were you doing when the symptoms started? What makes the pain worse? What relieves the pain? 39. Explain how to assess the PMI. Point of Maximal impulse or Apical pulse Palpate over apex of heart at 5 ICS, LMC (left ventricle apex) 40. Describe the routine exam of the peripheral vascular system, including pulses that should be palpated. Palpate: femoral, popliteal, anterior tibial and dorsalis pedis pulses Temporal: lateral to each eyebrow- amplitude Carotid: lower 3rd of neck, one at a time-amplitude Inspect: Jugular- pulsations Measure Blood pressure Inspect and Palpate upper extremities, pulses Inspect and Palpate lower extremities, pulses Brachial- antecubital fossa Radial- on thumb side of forearm, same time both Ulnar- medial side of forearm For amplitude: o Femoral o Popliteal o Tibial o Dorsalis Pedis 41. Define the scale used to describe amplitude of peripheral pulses. 0+ absent 1+ diminished barely palpable 2+ normal 3+ Full Volume 4+ Full Volume bounding hyperkinetic 42. Differentiate between arterial and venous insufficiency symptoms. What questions would you ask to differentiate one from the other? Arterial insufficiency: o Usually calf o Pain worse with activity – prolonged walking o If pain is relieved by rest it is called “intermittent claudication” (artery 50% occlusion), if not relieved by rest it is called “rest pain” o Worse with legs elevated, better when dependent Venous insufficiency: o Intensifies with prolonged standing or sitting o Pain worse in dependent position o Pain is better when legs are elevated and worse at end of the day VESSEL: Various positions that help alleviate discomfort/pain Explanation of pain Skin (color/temp/nails) Strength of pulse Edema Lesions 43. Define the scale used to describe the level of pitting edema. 1+ barely perceptible pit 2+ deeper pit in a few seconds 3+ deep pit, rebounds in 10-20 seconds 4+ deep pit, rebounds > 30 seconds OTHER What are the purposes of a nursing health assessment? P1 o Systematic model of collecting and analyzing data for the purpose of planning patient centered care. Develop a plan of care that will help maximize patient’s potential. Objective and Subjective information o What the patient feels/communicates (subjective) o Clinical findings (objective) collected during physical examination Review PowerPoints as well! Know temperatures (axillary, oral) Why vitals are important – symptoms for issues with vitals Quizlets are solid for this class New world – NCLEX prep