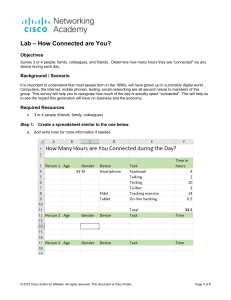
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Course Introduction ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 2 Cisco Career Certifications Three Levels of Certification CCIE CCNP CCNA ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 Expert Professional Associate Expert Level: CCIE (Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert) Professional Level: CCNP ( Cisco Certified Network Professional ) Associate Level: CCNA ( Cisco Certified Network Associate ) © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 3 Cisco Different Certifications Fields CCIE Routing and Switching CCNP CCNP Network Design CCIE Security Network Service Provider CCIE ServiceCCIE Provider Storage Networking CCIP None CCVP CCNA ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 CCNA CCIE Voice CCSP Network Security CCIP CCDA or CCNA CCNA Network Implementation CCIE Service Provider CCDA CCNA CCNA CCNA Voice Networks Storage Networking © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 4 Course Topics Computer Network ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 5 Lecture 1 Network introduction Lecture 2 OSI layer Lecture 3 Network layer (ICMP ,ARP) Lecture 4 The difference between the router, switch and the rest of the linking devices & Network Device Domains (Collision Domains ,Broadcast Domains) Describe switching concepts (MAC learning, Frame flooding, MAC address table) Lecture 5 IP-V4 Addressing Lecture 6 Subnetting Lecture 7 Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) Lecture 8 Route Summarization Lecture 9 Router components & Router Access & Router Configuration Lecture 10 Cisco Router and switch Password Setting & Configuring a banner & Remote Access Telnet Lecture 11 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) & DHCP Operation & Configuring a Cisco Router as a DHCP Server & DHCP Relay Agent Lecture 12 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 6 Exam Schedule Week 8 Midterm Week 14 Practical Exam Grading Policy ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 Points Description 90 Final exam 20 Midterm 10 Section 15 Practical Exam 15 Activity 150 Total © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 7 Communicating over the Network Network Fundamentals ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 8 Objectives 1. Network definition. 2. Network components. 3. Network Types 4. Network topologies. 5. Cabling. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 9 Network definition Network Fundamentals ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 10 1- Network definition • Network: Group of components or devices which are connected together to give the user a certain service (application). ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 11 Importance of Networks Data network is a result of business need. –Easy access and sharing of information (share data) –Sharing of expensive devices and network resources (cost) –Modern Technologies (IP telephony, Video Conferencing, ….etc) ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 12 2- Network components • Network has three main components End devices (servers and hosts) - Source of applications (network aware applications) - ex: HTTP (Hyper Text Transmission Protocol), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) Telnet Network Devices - Devices that interconnect different computers together - ex: Repeaters, hub, bridge, switch, router, NIC and modems Connectivity - Media that physically connect the computers and network devices - ex: Wireless and cables ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 13 End devices End devices: Computers (work stations, laptops, file servers, web servers) Network printers VoIP phones Security cameras Mobile handheld devices (such as wireless barcode scanners, PDAs) End devices are referred to as hosts. A host device is either the source or destination of a message. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 14 Network types Network Fundamentals ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 15 Physical Types of Network Local Area Network (LAN) Local Area Network (LAN) An individual network usually spans a single geographical area, providing services and applications to people within a common organizational structure, such as a single business, campus or region. (It is a group of network components that work within small area.) <10km ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 16 Ethernet Port ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 17 Wide Area Networks (WANs) Define Wide Area Networks (WANs) - LANs separated by geographic distance are connected by a network known as a Wide Area Network (WAN) (It is a group of LANs that are interconnected within large area) Cairo site ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 Alex site © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 18 Serial Port ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 19 Logical Types of Network (or management) Peer to Peer Networking (work group) In its simplest form, a peer-to-peer (P2P) network is created when two or more PCs are connected and share resources without going through a separate server computer. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 20 Logical Types of Network (or management) Server based Networking ( Domain ) A client-server network is designed for end-users, called clients, to access resources such as files, songs, video collections, or some other service from a central computer called a server. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 21 Network topologies Network Fundamentals ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 22 4- Network Topologies • Topology: How devices are connected together ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 23 Bus Topology – In a physical bus topology, a single cable effectively connects all the devices. – All devices receive the signal. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 24 Ring Topology – Signals travel around ring. – Single point of failure. In a ring topology, all the hosts are connected in the form of a ring or circle. A ring topology connects one host to the next and the last host to the first. This creates a physical ring of cable. If the first host needs to send data to the last host, the data must path through all the hosts before reaching the end host. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 25 Full-Mesh Topology – Highly fault-tolerant – Expensive to implement A mesh topology is implemented to provide as much protection as possible from interruption of service. Each host has its own connections to all other hosts. Although the Internet has multiple paths to any one location, it does not adopt the full mesh topology. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 26 Partial-Mesh Topology – Trade-off between fault tolerance and cost ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 27 Star Topology –In a physical star topology, each device in the network is connected to the central device with its own cable. – Transmission through a central point. – Single point of failure. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 28 Types of Cables & Connectors Network Fundamentals ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 29 Types of Cables Copper cable Coaxial Twisted Pair Fiber Cable Fiber Optic Cable ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 30 Coaxial cable ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 31 Twisted-Pair Cable Two basic types of twisted-pair cable exist: shielded twisted pair (STP). unshielded twisted pair (UTP) ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 32 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) STP and UTP use RJ-45 (Registered Jack 45) connector ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 33 UTP Cables Connections types: Straight-through UTP Cables A straight-through cable has connectors on each end that are terminated the same in accordance with either the T568A or T568B standards. Identifying the cable standard used allows you to determine if you have the right cable for the job. More importantly, it is a common practice to use the same color codes throughout the LAN for consistency in documentation. Use straight-through cables for the following connections: Switch to a router Ethernet port. Computer to switch. Computer to router. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 34 UTP Cables Connections types: Crossover UTP Cables For two devices to communicate through a cable that is directly connected between the two, the transmit terminal of one device needs to be connected to the receive terminal of the other device. The cable must be terminated so the transmit pin, Tx, taking the signal from device A at one end, is wired to the receive pin, Rx, on device B. Similarly, device B's Tx pin must be connected to device A's Rx pin. If the Tx pin on a device is numbered 1, and the Rx pin is numbered 2, the cable connects pin 1 at one end with pin 2 at the other end. These "crossed over" pin connections give this type of cable its name, crossover. To summarize, crossover cables directly connect the following devices on a LAN: Switch to switch. Switch to hub. Hub to hub. Router to router Ethernet port connection. Computer to computer. Computer to router Ethernet port. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 35 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 36 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 37 Straight-Through vs Crossover cables ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 38 Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Straight-through ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 Cross-over © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Rollover Cisco Public 39 Straight-through ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 40 Cross-over ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 41 Rollover ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 42 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 43 How to Make an Ethernet Cable https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WvP0D0jiyLg ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 44 UTP Straight-through Cable Hub or Switch Host or Router The cable that connects from the switch port to the computer NIC port is called a straight-through cable. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 45 UTP Cross-over Cable Hub or Switch Hub or Switch The cable that connects from one switch port to another switch port is called a crossover cable. Connects like devices. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 46 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 47 Access Methods Type: Carrier Sence Multiple Access with Collision Detection CSMA/CD operation ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 48 There are different types of Media Access Control methods in a LAN Ethernet * Star topology *Twisted pair * CSMA/CD Token Ring FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface) ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 49 Methods of Sending Data in the Network Unicast means send data for one or all receivers. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 Multicast means send data for some receivers or all. © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Broadcast means send data for all receivers. Cisco Public 50 Transmission types Single Transmission in one direction only Half duplex Transmission in the two directions but not at the same time Full duplex Transmission in the two directions at the same time ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 51 Text Books and Download Cisco Packet Tracer CCNA-200-301-Official-Cert-Guide - volume 1 https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EPGHrEn5XjflHNOfl1jqQxY3LAgcNFzG/vi ew CCNA-200-301-Official-Cert-Guide - volume 2 http://www.mediafire.com/file/ob42yfmr2nps3zj/CCNA-200-301Official-Cert-Guide+-+volume++2+.pdf/file Download Cisco packet tracer https://drive.google.com/file/d/1F8DYtZJ0PJfwfqMpHMrT1Zz5c9V6Fr6v/vi ew?usp=sharing ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 52 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 53 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 54