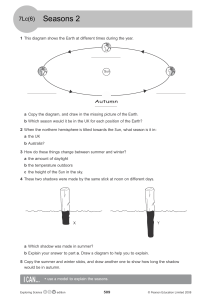
24.2 Sun and Seasons http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007299181x/student_view0/cha pter2/seasons_interactive.html Earth Motions 1. Earth moves in two major ways: – Rotation: spinning of earth on its axis – Revolution: earth orbits around the sun What Causes Seasons? 1. Tilt of the earth as it moves around the sun - Earth is tilted by 23.5 degrees 2. As the earth orbits, different parts of the earth get direct and intense solar radiation Seasons 3. Opposite in the N and S hemisphere 4. When N tilted to the sun (summer), S tilted away (winter) 5. If the earth was not tilted= no seasons Seasons and Latitudes 1. Polar: Cold, don’t have 4 seasons – (66.4 N or S to poles) 2. Temperate: 4 seasons (23.5-66.5 N or S) 3. Tropics: Warm all year, no seasons (23.5 N or S) – Get intense rays all year long • Solstice: sun is directly overhead at latitude 23.5 N or S • Equinox: neither hemisphere is tilted toward the sun, and the lengths of daylight and darkness are = VERNAL EQUINOX : March 21 1st day of spring Days get longer and warmer Sun’s direct & intense rays fall on the EQUATOR (and move north throughout spring) (equal day and night @ equator) SUMMER SOLSTICE: June 21 1ST day of SUMMER Longest day of the year – Shortest night Sun’s direct & intense rays are over 23.5 N (Tropic of Cancer) AUTUMNAL EQUINOX: Sept 23 1st day of Fall Sun’s direct & intense rays fall on the EQUATOR Days get cooler and shorter (equal day and night @ equator) WINTER SOLSTICE: Dec 21 1ST day of Winter Longest night – shortest day Sun’s direct & intense rays are over 23.5 S (Tropic of Capricorn)