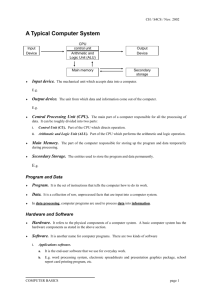
Central Processing Unit (CPU) Information Technology CPU • A computer does mainly four functions: – Receive input: through various input device – Process Information: Perform arithmetic or logical operations on the information – Produce output: thru output device – Store Information: storage device • Computer hardware falls into two categories – Processing hardware: Central Processing Unit, where data processing is done – Peripheral devices: interact with the CPU Central Processing Unit (CPU) • The part of the computer that executes program instructions is known as the processor or central processing unit(CPU). • The central processing unit consists of three main components, the control unit, the arithmetic unit(ALU), and the registers. The CPU has two parts- the control unit and the arithmetic logic unit. Control Unit • It directs the movement of electronic signals between memory(which temporarily holds data, instructions and processed information) and the ALU. It also directs these control signals between the CPU and input/output devices. • Each instruction in the instruction set is expressed in microcode – a series of basic directions that tells the CPU how to execute more complex operations. Microcode is the lowest-level instructions that directly control a microprocessor. Arithmetic Logic Unit • Performs two types of operationsarithmetic and logical. Arithmetic operations are the fundamental mathematical operations consisting of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Logical operation consist of comparisons. • Many instructions carried out in the control unit involve moving data from one place to another- from memory to storage device, from memory to the printer or monitor and so on. Arithmetic Logic Unit • Operations Performed by the ALU Arithmetic Logical Operations The ALU Addition Equal to includes a Subtraction Not equal to group of high Multiplication Greater than; not speed greater thannot less Division Less than; memory than Exponentiation Greater than or equalthan to; not greater locations(Re Less or equal than or equal to less or equal to; not gister) built than or equal to directly into the CPU, which are used to hold data that is Registers CPU and Memory Register Workspace ALU Does all the computing ROM Control Unit Controls & checks RAM Register • Register are a number of small, highspeed memory units. • They hold the material that the CPU is currently working with and they can be thought of as being the CPU’s workspace. • The ALU works on the data held in the registers acting on the instructions which are also held there. Machine Cycle • Every time the CPU executes an instruction, it takes a series of steps called the machine cycle. The machine cycle consists of two subcycles- the instruction cycle and the execution cycle. The machine four steps -- fetching, decoding, executing and storing. The first two forms the instruction cycle and the last two forms the execution cycle. Machine Cycle 1.Fetching: fetches the instruction from the memory 2.Decoding: breakdown or decode the command 3.Executing: execute the command, CPU carries out the instruction in order by converting them into microcode. 4.Storing: The CPU may be required to store the results in the memory. Working of CPU and Memory • Page 90 and 91 (write 15 steps and draw the diagram)