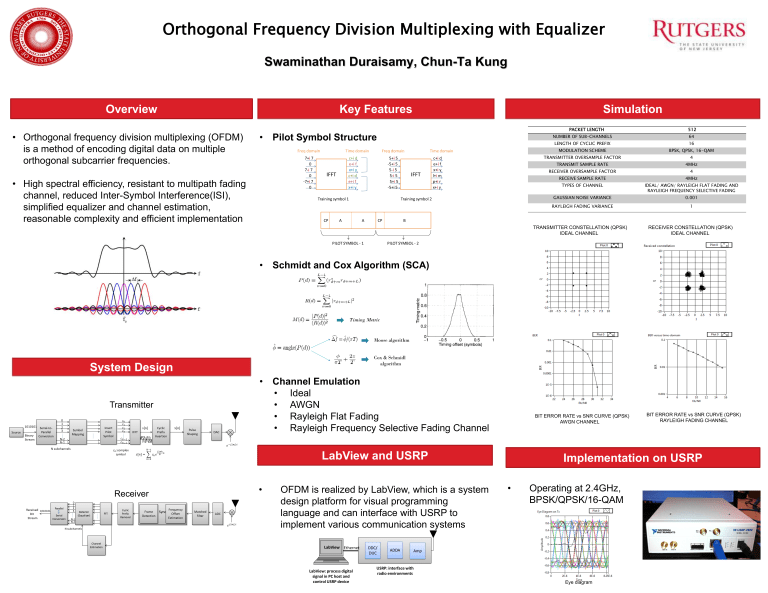
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing with Equalizer Swaminathan Duraisamy, Chun-Ta Kung Overview • Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is a method of encoding digital data on multiple orthogonal subcarrier frequencies. Key Features • Simulation PACKET LENGTH Pilot Symbol Structure • High spectral efficiency, resistant to multipath fading channel, reduced Inter-Symbol Interference(ISI), simplified equalizer and channel estimation, reasonable complexity and efficient implementation NUMBER OF SUB-CHANNELS 64 LENGTH OF CYCLIC PREFIX 16 MODULATION SCHEME BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM TRANSMITTER OVERSAMPLE FACTOR 4 TRANSMIT SAMPLE RATE 4MHz RECEIVER OVERSAMPLE FACTOR 4 RECEIVE SAMPLE RATE 4MHz TYPES OF CHANNEL IDEAL/ AWGN/ RAYLEIGH FLAT FADING AND RAYLEIGH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE FADING GAUSSIAN NOISE VARIANCE 0.001 RAYLEIGH FADING VARIANCE 1 TRANSMITTER CONSTELLATION (QPSK) IDEAL CHANNEL • 512 RECEIVER CONSTELLATION (QPSK) IDEAL CHANNEL Schmidt and Cox Algorithm (SCA) Timing Metric Moose algorithm Cox & Schmidl algorithm System Design • Transmitter Channel Emulation • Ideal • AWGN • Rayleigh Flat Fading • Rayleigh Frequency Selective Fading Channel BIT ERROR RATE vs SNR CURVE (QPSK) AWGN CHANNEL LabView and USRP Receiver • OFDM is realized by LabView, which is a system design platform for visual programming language and can interface with USRP to implement various communication systems BIT ERROR RATE vs SNR CURVE (QPSK) RAYLEIGH FADING CHANNEL Implementation on USRP • Operating at 2.4GHz, BPSK/QPSK/16-QAM Eye diagram