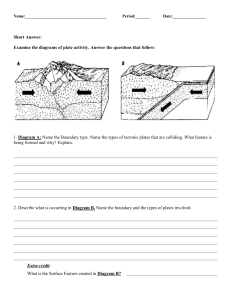
Plate Tectonics Saturday, September 17, 2022 11:50 PM Plate Tectonics Theory • States that the Earth’s layer is fragmented into either small or large plate that interact in various ways • Had its beginnings in 1915 when Alfred Wegener proposed his Theory of Continental Drift. Lithosphere • Consists of layers; the crust and the upper mantle. • The solid, outer part of the Earth. Types of Crusts • The earth’s outer surface is its crust, a cold, thin, brittle outer shell made of rock. • The crust is very thin relative to the radius of this planet. • Extends from surface to about 32 km below, underneath some mountains, the crusts thickness extends to 72 km. 1. Continental Crust • Forms the land that we see today. • Made up of many different types of igneous,, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. • The average composition is granite, which is much less dense than basaltic rocks of the oceanic crust.. • Less dense and therefore more buoyant than oceanic crust (4 billion y/o). • Contains some of the oldest rocks on Earth • Mostly composed of granite. 2. Oceanic Crust • Composed of mafic magma that erupts on the seafloor to create basalt lava flows or cools deeper down to create the intrusive igneous rock gabro. • Relatively thin and lies above the mantle. • The age of the oceanic crust does not go back farther than about 200 million years, thus making it younger than continental crust. • Subduct under continental plates, which makes it more dense. Tectonic Plates • Massive, irregularly-shaped slab of solid rock, generally composed of both continental and oceanic crust • A rigid sections of the lithosphere that move as a unit. Major Tectonic Plates • • • • • • • African Antarctic Eurasian North-American South-American Indo-Australian Pacific Minor Plates • • • • • • • Arabian Caribbean Nazca Scotia Philippine Cocos Juan de Fuca How are plates divided? • Most geologic activity stems from th interplay where the plates meet or divide • The movement of the plates create three types of tectonic boundaries; a. Convergent - where plate moves into one another b. Divergent - where plates move apart c. Transform fault - where plates move sideways in relation to each other