Tissues, Organ Systems, Digestion & Nutrition Lab Exercise
advertisement
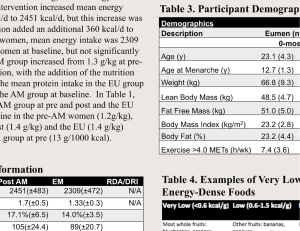
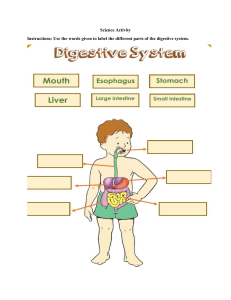
Name: ______________________ Laboratory Exercise 1 Date: _______________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ TISSUES & ORGAN SYSTEMS Objectives: By completing this exercise, you will: 1. Recognize the four main types of tissues that are epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissues. In addition, differentiate specific tissues in epithelial (3 types), connective (6 types) and muscle (3 types). 2. List function and location of each specific tissue type. 3. List the organ systems and describe their general functions. Activity A: Tissue types If available, view prepared slides on the following tissues and sketch each of them. If prepared slides will not be available, use internet pictures to sketch each tissue given by names below. When drawing, make sure to note the structural differences between specific tissues. 1. Epithelial Tissues a. Simple squamous (lung) c. Simple cuboidal (kidney) 2. Connective Tissues a. Loose connective tissue (dermis-skin) b. Stratified squamous (esophagus) d. Simple columnar (small intestine) b. Adipose tissue c. Blood d. Fibrous connective (tendon) e. Cartilage f. Bone 3. Muscle Tissue a. Skeletal muscle (striated muscle) b. Cardiac muscle c. Smooth muscle (non-striated) Page 1 of 7 4. Nervous Tissue (brain or spinal cord) Activity B: Tissue Function & Location Fill in the correct information into each box in the table below: Tissue type 1. Simple squamous epithelium 2. Simple cuboidal epithelium 3. Simple columnar epithelium 4. Stratified squamous epithelium 5. Function Location Loose connective tissue 6. Adipose tissue 7. Blood 8. Fibrous connective tissue 9. Cartilage 10. Bone 11. Skeletal muscle tissue 12. Cardiac muscle tissue 13. Smooth muscle tissue 14. Nervous tissue Activity C: Organ systems and their functions Organ System 1. Component Organs Integumentary system 2. Digestive system 3. Respiratory system 4. Cardiovascular system 5. Immune system 6. Lymphatic system 7. Endocrine system 8. Reproductive system 9. Nervous system 10. Muscular system Page 2 of 7 General Function(s) 11. Skeletal system 12. Excretory/Urinary system DIGESTION & NUTRITION Objectives: 1. Assess the various diets and feeding methods/mechanisms of animals and humans. 2. Name the stages of food processing and which part of the digestive tract each stage occurs. 3. Identify the parts of the digestive system on models, and describe the function of each. 4. Estimate your basal metabolic rate (BMR) as well as your food intake and energy consumption for three days. Activity A: Diets and Feeding Methods Complete the table below. For diet, you may choose from herbivore, carnivore and omnivore. There are several feeding mechanisms such as suspension feeders, substrate feeders, fluid feeders or bulk/large piece feeders (ingestion by chunks). Organism Cow Earthworm Hydra Whale Intestine worm Shark Female mosquito Scallop Grasshopper Humans Diet Feeding Mechanism/method Activity B: Food Processing and Animal Digestive Systems On each diagram, write correct name to each part indicated: mouth, tongue, pharynx, salivary duct, salivary glands, esophagus, crop, proventriculus, gizzard, stomach, intestine, large intestine, caeca, cloaca, rectum and anus. Then color the alimentary canals to show where each stage of food processing occurs. Use yellow for ingestion, (including swallowing and storage), red for digestion, green for absorption, and blue for elimination. If two processes occur in the same area, mix the colors. Ingestion Digestion Absorption Page 3 of 7 Elimination Page 4 of 7 Activity C: Human Digestive System Picture the parts of the human digestive system and their relationship to one another. Label these parts of the digestive system on the diagram below: stomach, oral cavity, small intestine, esophagus, rectum, pancreas, gall bladder, mouth, large intestine, tongue, salivary glands, anus, liver, pyloric sphincter, and pharynx. Locate the digestive organs on the human torso model. Note their relative positions. Remove the organs from the model, and try to put them back in their proper positions. Activity D: Energy output: Estimates of the BMR and activity The total energy expended each day includes the energy required at rest and that expended during physical activity. For most people, the calories consumed at rest make up most of the total daily energy expenditure. This energy is used to pump blood, inflate the lungs, transport ions, and carry-on other functions of life. Measurement of this resting energy expenditure shortly after awakening and at least 12 hours after the last meal is known as the basal metabolic rate (BMR). While most of our caloric output is spent at rest, most people are physically active and expend calories beyond the BMR. The additional number of activity calories expended will vary with the individual, and with the duration, intensity, and types of activities performed. The increased caloric output can be estimated by multiplying an activity Page 5 of 7 factor or AF (see table below) by the BMR. Aerobic activities such as running, swimming, and bicycling, normally burn more calories than anaerobic activities such as weight lifting. Estimating BMR Procedure: NB: Record the data in the table next page. Step 1: Determine the total calories you consumed by using the figures below for estimates. Include fluids except water. The major sources of food calories are carbohydrates, fats (lipids), and proteins. One gram (g) of each of the three energy nutrients provides the body with approximately the following number of calories: 1 g carbohydrate = 4.0 kcal 1 g fat = 9.0 kcal 1 g protein = 4.0 kcal Activity Activity Factor (AF) Lying in bed all day - equal to BMR 1.00 - 1.29 Mild activity - 1 hour of aerobic exercise 1.30 - 1.49 Moderate activity - 1 hour of aerobic exercise 1.50 - 1.69 Heavy activity - 2 hours of aerobic exercise 1.70 - 1.99 Rigorous athletic training 2.0 and above Step 2: Estimate your basal metabolic rate (BMR) using the formula below: Your weight in kilograms: _________ kg Female BMR = 0.7 kcal/kg/hr Male BMR = 1.0 kcal/kg/hr Use the above conversion factors to calculate your kilocalories per hour. Then multiply this figure by 24 (hours per day) and enter your answer in the space below. ______ kg (your weight) x _______ (male or female BMR) x 24 (hours per day). In one day (24 hours), your BMR is approximately _____________ kcal. Step 3: Select one AF from the table in the right column that best reflects your total activity for a 24-hour period (for each of the 3 days). NB: The typical AF for the casual university routine (without exercise) is 1.30. Step 4: Calculate the total number of calories expended (output) for each day as follows: Total calories expended (kcal) = _______________________ Activity AF (from Step 3) x BMR (from Step 2) Page 6 of 7 3-Day Dietary Record Evaluation Weight: ______________ kg 1. Record the total number of calories consumed over 3 days (based on Step 1 of procedure). Day 1 = _________kcal 2. Total: __________kcal Day 2 = _________kcal Day 3 = _________kcal Total: __________kcal Day 2 = _________kcal Day 3 = _________kcal Total: __________kcal Divide the figures in no. 3 data by 3, 500 kcal/lb to convert to kilocalories to pound (lbs), and then convert the result to kg (1 kg = 2.2 lbs). Indicate whether this represents a weight loss (circle the appropriate word). Day 1 = ____ kg gained/loss 5. Day 3 = _________kcal Subtract the kilocalories expended from the total kilocalories consumed (data in no. 2 from data in no. 1) and indicate whether the difference represents a gain (+) or a loss (-). Day 1 = _________kcal 4. Day 2 = _________kcal Record the number of calories expended over 3 days (based on Step 3 and 4). Day 1 = _________kcal 3. BMR: __________ kcal (Based on Step 2 of procedure) Day 2 = ______ kg gained/loss Day 3 = ______ kg gained/loss Total: _____ kg gained/loss Record the total volume of water consumed over 3 days. Day 1 = ________ mL Day 2 = ________ mL Day 3 = ________ mL Total: _________ mL Based on the recommendation of a least 1.0 mL of water per kilocalorie of energy expended each day, did you meet this requirement each day? YES/NO (circle the appropriate word). Day 1 = YES/NO Day 2 = YES/NO Day 3 = YES/NO List 3 specific suggestions for improving your food intake (in terms of nutrients). 1. ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. ___________________________________________________________________________ What adjustment need to be made to your water intake? ______________________________________________________________________________ NB: Attach your 3-day dietary record to this lab exercise. Page 7 of 7