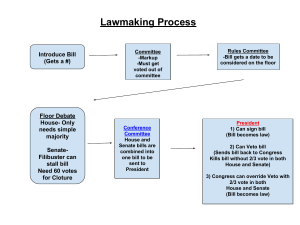
3 ways that members of Congress try to bring federal government projects and money to their districts: 1. Pressure agency officials to give a favorable hearing on their state’s requests 2. Encourage constituents to write, phone, or email agency officials to make their request or needs known 3. Lawmakers assign one or members of their staff to act as specialists in contracts and grants Private bill applies to few people Public bill applies to whole nation Joint resolution passed when they agree with a bill Concurrent resolution is passing bill without the president’s approval Reasons why few bills become public bills a) it is a long, complicated process b) sponsors must be willing to bargain and compromise c) bills are introduced knowing that they will never be passed New ideas for bills come from various people In the house the members drop their bill in the hopper. In the senate the senator must be recognized. all important work on tax laws occurs in the House Ways and Means Committee. Groups involved in writing laws Executive branch, interest groups, standing committees of congress, congressional staffs, private citizens. Only a member of congress can introduce a bill house Place it in hopper Give it a title, summary, a number and record it- 1st reading Speaker forwards the bill to the appropriate standing committee Committee or subcommittee can pigeonhole it or give it a bad recommendation Can report on the bill favorably, amend it or release a committee bill 2nd reading- read in its entirety 3rd reading-read title and number only, final vote, if passed the bill is forwarded by the speaker Senate Bill introduced by senator Titled and numbered Referred to appropriate committee 2nd reading- read in its entirety. Filibuster may occur 3rd reading and final vote Sent to president for action if passed in identical form as the house bill If senate changes the bill house can accept the senate version and bill goes to president Conference committee can settle the differences between the two versions If conference committee cannot solve problems it dies If president signs the bill it becomes a law President can ignore the bill for 10 days Any bill that is not approved during the congressional session the billd dies President can veto it or pocket veto it Congress can override a presidential veto by ⅔ vote in house and the senate Only 3% of presidential vetoes are overridden Filibuster- talking a bill to death can be stopped by cloture-60% of senators to agree to end the filibuster