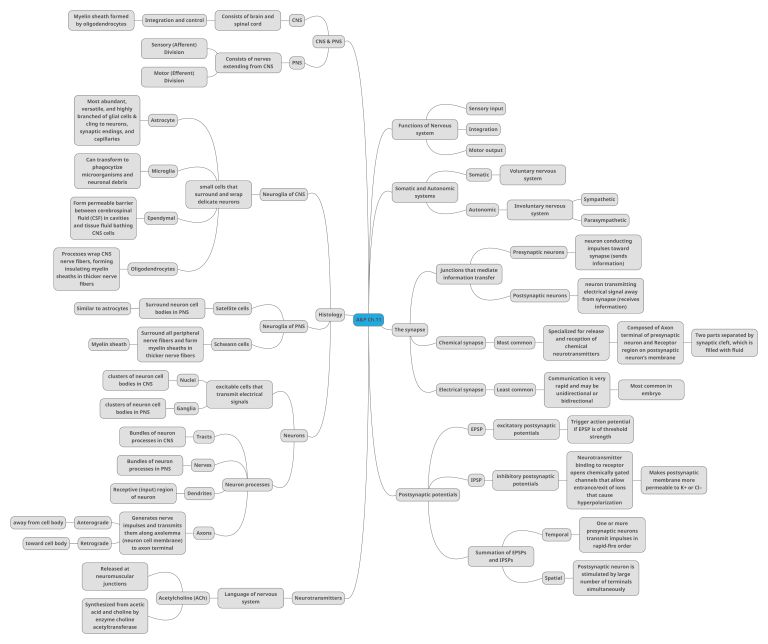
Myelin sheath formed Integration and control by oligodendrocytes Consists of brain and spinal cord CNS CNS & PNS Sensory (Afferent) Division Consists of nerves extending from CNS Motor (Efferent) PNS Division Most abundant, Sensory input versatile, and highly branched of glial cells & Astrocyte cling to neurons, Functions of Nervous synaptic endings, and system capillaries Integration Motor output Can transform to phagocytize Microglia microorganisms and Voluntary nervous Somatic neuronal debris small cells that surround and wrap Somatic and Autonomic Neuroglia of CNS systems delicate neurons Form permeable barrier system Involuntary nervous Autonomic between cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in cavities system Ependymal Sympathetic Parasympathetic and tissue fluid bathing CNS cells neuron conducting impulses toward Presynaptic neurons Processes wrap CNS synapse (sends nerve fibers, forming insulating myelin Oligodendrocytes information) junctions that mediate sheaths in thicker nerve information transfer fibers neuron transmitting Postsynaptic neurons Surround neuron cell Similar to astrocytes bodies in PNS nerve fibers and form Myelin sheath myelin sheaths in Histology Neuroglia of PNS A&P Ch.11 The synapse Specialized for release Chemical synapse Schwann cells bodies in CNS bodies in PNS excitable cells that Bundles of neuron processes in PNS Receptive (input) region of neuron away from cell body Anterograde Retrograde Electrical synapse Least common EPSP Neurons Tracts filled with fluid neuron’s membrane embryo excitatory postsynaptic potentials Trigger action potential if EPSP is of threshold strength Neurotransmitter binding to receptor Nerves IPSP Neuron processes Dendrites inhibitory postsynaptic potentials Postsynaptic potentials opens chemically gated Makes postsynaptic channels that allow membrane more entrance/exit of ions permeable to K+ or Cl– that cause One or more Axons Temporal to axon terminal Summation of EPSPs Spatial junctions Acetylcholine (ACh) Language of nervous system transmit impulses in Postsynaptic neuron is Released at neuromuscular presynaptic neurons rapid-fire order and IPSPs acetyltransferase region on postsynaptic bidirectional (neuron cell membrane) enzyme choline synaptic cleft, which is unidirectional or impulses and transmits acid and choline by neuron and Receptor Most common in Generates nerve Synthesized from acetic Two parts separated by hyperpolarization them along axolemma toward cell body terminal of presynaptic rapid and may be signals Ganglia processes in CNS Composed of Axon Communication is very Nuclei Bundles of neuron chemical neurotransmitters transmit electrical clusters of neuron cell and reception of Most common thicker nerve fibers clusters of neuron cell from synapse (receives information) Satellite cells Surround all peripheral electrical signal away stimulated by large number of terminals simultaneously Neurotransmitters