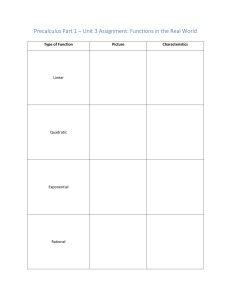
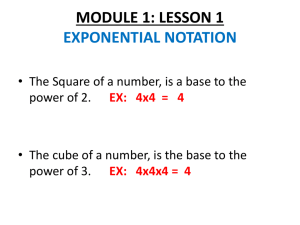
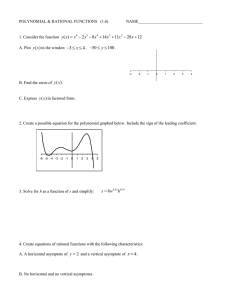
Algebra 2 Honors Semester 2 Exam Study Guide Vocabulary Module 5: Prime Polynomial: A polynomial that cannot be written as a product of two polynomials with integer coefficients. Quadratic form: A form of polynomial equation, expression in x. au^2 + bu + c, where u is an algebraic Identity: An equation that is true for every value of the variable. Polynomial identity: A polynomial equation that is true for any values that are substituted for the variables. Synthetic substitution: The process of using synthetic division to find a value of a polynomial function. Depressed polynomial: A polynomial resulting from division with a degree one less than the original polynomial. Multiplicity: The number of times a number is a zero for a given polynomial. Module 6: Composition of functions: suppose f and g are functions such the range of g is a subset of the domain of f. The composition function of g can be described by f of g = f[g(x)] Inverse relations: Two relations, one of which contains points of the form (a, b) while the other contains points of the form (b, a). Inverse functions: Two functions, one of which contains points of the form (a, b) while the other contains points of the form (b, a). Nth root: If an=ban=b for a positive integer n, then a is the nth root of b. The inverse of raising a number to the nth power is finding the nth root of a number. Index: In nth roots, the value that indicates to what root the value under the radicand is being taken. Radicand: The expression under a radical sign. Principal root: The nonnegative root of a number. Rational exponent: An exponent that is expressed as a fraction. Radical function: A function that contains radicals with variables in the radicand. Square root function: A radical function that contains the square root of a variable expression. Cube root function: A radical function that contains the cube root of a variable expression Like radical expressions conjugates: Radicals in which both the index and the radicand are the same. Radical equation: An equation with a variable in a radicand. Module 7: Exponential function: A function in which the independent variable is an exponent. Exponential growth: Change that occurs when an initial amount increases by the same percentage over a given period of time. Asymptote: A line that a graph approaches. Growth factor: the base of an exponential expression or 1 + r. Exponential decay: Change that occurs when an initial amount decreases by the same percentage over a given period of time. Decay factor: The base of an exponential expression or 1 – r. Exponential equation: An equation in which the independent variable is an exponent. Compound interest: Interest calculated on the principal and on the accumulated interest from previous periods. It’s paid on the principle of an investment and any previously earned interest. Exponential inequality: An inequality in which the independent variable is an exponent. E: An irrational number that approximately equals 2.7182818…. Sequence: A list of numbers in a specific order. Term of a sequence: A number in a sequence. Finite sequence: A sequence that contains a limited number of terms. Infinite sequence: A sequence that continues without end. Geometric sequence: A pattern of numbers that begins with a nonzero term and each term after is found by multiplying the previous term by a nonzero constant r. Common ratio: The ratio of consecutive terms of a geometric sequence. Constant value. Explicit formula: A formula that allows you to find any term anan of a sequence by using a formula written in terms of n. Recursive formula: A formula that gives the value of the first term in the sequence and then defines the next term by using the preceding term. Find the nth term of a sequence by performing operations to one or more of the preceding terms. Geometric means: the terms between two nonconsecutive terms of a geometric sequence. Series: The indicated sum of the terms in a sequence. Geometric series: The indicated sum of the terms in a geometric sequence. Sigma notation: A notation that uses the Greek uppercase letter S to indicate that a sum should be found. Regression function: A function generated by an algorithm to find a line or curve that fits a set of data. Coefficient of determination: An indicator of how well a function fits a set of data. Module 8: Logarithm: In x = b^y, y is called the logarithm, base b, of x. Logarithmic function: A function of the form f(x)=logbx, where b > 0 and b ≠ 1. Logarithmic equation: An equation that contains one or more logarithms. Common logarithms: Logarithms of base 10. Natural base exponential function: An exponential function with base e, written as y=e^x Natural logarithm: The inverse of the natural base exponential function, most often abbreviated as ln x. Module 9: Rational Expression: A ratio of two polynomial expressions. Complex Fraction: A rational expression with a numerator and/or denominator that is also a rational expression. Reciprocal Function: An equation of form f(x)= expression that cannot equal 0. where n is a real number and b(x) is a linear Vertical Asymptote: A vertical line that a graph approaches. Horizontal Asymptote: A horizontal line that a graph approaches. Hyperbola: The graph of a reciprocal function. Excluded Values: Values for which a function is not defined. Rational Function: An equation of the form f(x)= expressions and b(x) ≠ 0. where a(x) and b(x) are polynomial Oblique Asymptote: An asymptote that is neither horizontal nor vertical. Point Discontinuity: An area that appears to be a hole in a graph. Direct Variation: When one quantity is equal to a constant time another quantity. Constant of Variation: The constant in a variation function. Joint Variation: When one quantity varies directly as the product of two or more other quantities. Inverse Variation: When the product of two quantities is equal to a constant k. Combined Variation: When one quantity varies directly and/or inversely as two or more other quantities. Rational Equation: An equation that contains at least one rational expression. Rational Inequality: An inequality that contains at least one rational expression