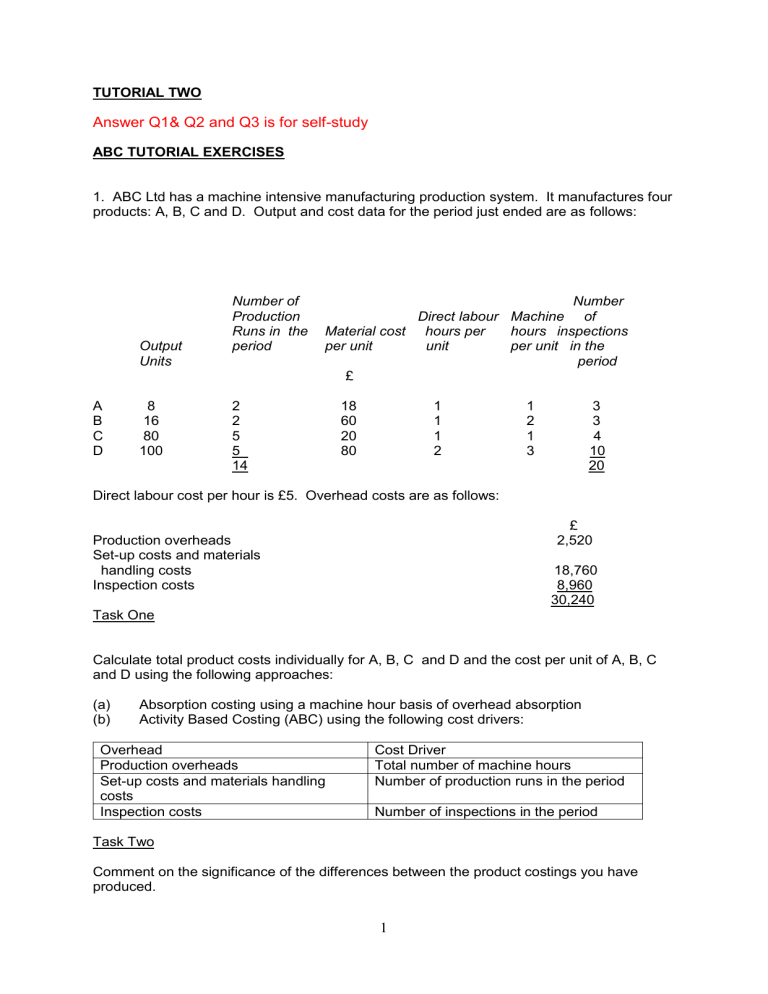
TUTORIAL TWO Answer Q1& Q2 and Q3 is for self-study ABC TUTORIAL EXERCISES 1. ABC Ltd has a machine intensive manufacturing production system. It manufactures four products: A, B, C and D. Output and cost data for the period just ended are as follows: Output Units A B C D 8 16 80 100 Number of Production Runs in the period Number Direct labour Machine of Material cost hours per hours inspections per unit unit per unit in the period £ 2 2 5 5 14 18 60 20 80 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 3 3 3 4 10 20 Direct labour cost per hour is £5. Overhead costs are as follows: £ 2,520 Production overheads Set-up costs and materials handling costs Inspection costs 18,760 8,960 30,240 Task One Calculate total product costs individually for A, B, C and D and the cost per unit of A, B, C and D using the following approaches: (a) (b) Absorption costing using a machine hour basis of overhead absorption Activity Based Costing (ABC) using the following cost drivers: Overhead Production overheads Set-up costs and materials handling costs Inspection costs Cost Driver Total number of machine hours Number of production runs in the period Number of inspections in the period Task Two Comment on the significance of the differences between the product costings you have produced. 1 2. Questions for ‘The costs of activity-based management’, Armstrong (2002), 27, 99-120 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. According to Armstrong, in the 1970’s and 1980’s, how were the salaries of office workers costed compared with the wages of production workers? Why does Armstrong describe the costing of office staff salaries as an employment shelter? Why was ABC popular with production managers? What does Armstrong regard as the key difference between ABC and ABM? What does Armstrong regard as the problem with ABM for staff functions? What does Armstrong regard as the hidden agenda of ABC and why? Why does Armstrong think treating indirect costs as direct is problematic? According to Armstrong, what type of control measures arise from ABM, how have they been applied and what have been some of the results? 3. The following information relates to E.Z. plc for period January – March. (Self-study) Product Wood Machine hours/unit Direct labour hours/unit Output (units) Purchase orders Set ups Cartons Metal 10 6 10,000 10 12 5,000 Plastic 8 6 12,000 8 20 4,000 12 3½ 8,000 12 10 2,000 Overheads traced to activities: £ Purchasing Setting up Packaging Supervision of direct labour Other production overhead (Deemed to be output related) 90,000 126,000 440,000 32,000 480,000 Required: (a) E.Z. plc uses a machine hours Overhead Absorption Rate. Calculate the overhead cost/unit for each product on this basis. (b) Compare to the results using an Activity Based Costing approach. 2