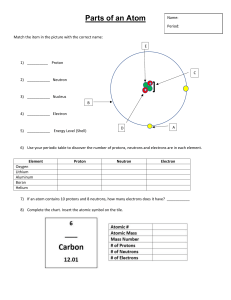
Electric Forces and Electric field Mass of proton=1.673×10-27kg Mass of neutron =1.675×10-27kg Proton(+), Electron(-) and Neutron (no electric charge)--neutral Proton(+e) and electron(-e) q=Ne **e=1.60×10-19C Gains of electron acquires an excess of (-) charge, Loss of electrons acquires a (+) charge (+) and (+) - - - - repulsion - - - - (-) and (-) *(like charges repel) (+) and (-) - - - - attraction *(unlike charges attract each other) LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ELECTRIC CHARGE* During any process, the net electric charge of an isolated system remains constant N. B electric force also called electrostatic force Electric conductor *substances that readily conduct electric charge(ELECTRONS MOVE FREELY) E.g copper,Al,Ag and gold are used in electric wiring Electric insulator * materials Tha conduct electric charge poorly (ELECTRONS CANNOT MOVE FREELY).( E. g rubber, plastics and wood*prevent electric charge from going where it is not wanted) CHANGING BY CONDUCTION* Charging a neutral object by touching it with a charged object *Transfer electrons * neutral object get the same charge as charged object CHANGING BY INDUCTION *Charged object never touches the neutral object * A separation of charge can be used to give an object a net charge CHANGING BY INDUCTION AND GROUNDING *Charging a neutral object by induction then grounding *Transfer electrons COULOMB’s LAW states that the magnitude F of electrostatic force exerted by one point charge q1 on another charge q2 is directly proportional to the magnitud |q1| and|q2| of charges and inversely proportional to the square of distance r between them. Net force=F 12 +F 13 N. B. F 2 =F x 2 + F y 2 *Fx= Fcos 0 , Fy= Fsin0 and tanO=Fy/Fx ELECTRIC FIELD is a vector *SI units :(N/C). E=F/q (+) electric field lines (outward) and (-) electric lines (inwards) THANK YOU!!!! WORK HARD LIKE A DONKEY, DON’T GIVE UP….. KEEP GOING AND LET YOUR DREAM COME TRUE… DON’T COMPARE YOURSELF WITH OTHER PEOPLE.