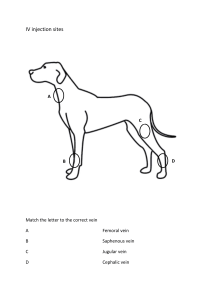
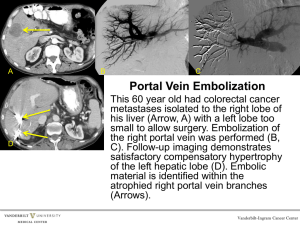
Homeostasis Lab Part I: Liver Table 1: Blood Glucose Levels After Eating Test tubes in order of color change (which changed 1st, 2nd, and 3rd) Source of Serum (did it come from a mesenteric artery, hepatic portal vein, or hepatic vein?) B1 hepatic portal vein C1 hepatic vein A1 mesenteric artery Questions 1. Which blood vessel, the mesentery artery, the hepatic portal vein, or the hepatic vein contains the most glucose after eating? hepatic portal vein 2. Explain why the hepatic portal vein contains more glucose than the hepatic vein after eating. It grabs the sugar from what you just ate and transports it to the liver after eating. Table 2: Blood Glucose Levels Before Eating Test tubes in order of color change (which changed 1st, 2nd, and 3rd) Source of Serum (did it come from a mesenteric artery, hepatic portal vein, or hepatic vein?) C2 hepatic vein A2 mesenteric artery B2 hepatic portal vein Questions 1. Which blood vessel, the mesentery artery, the hepatic portal vein, or the hepatic vein contains the most glucose before eating? Hepatic vein 2. Explain why the hepatic portal vein contains less glucose than the hepatic vein before eating. You haven’t eaten anything so there is nothing to absorb. Part II: Kidneys Questions 1. Which parts of the nephron are located in the renal cortex? Distal Tubule, Glomerulus, Proximal Tubule 2. Which components of the nephron are located in the medulla? Collecting Duct and Loop of Henle Table 3: Focus on Filtration Substance Enter Bowman’s Capsule? Why Glucose Yes Small Cells No Too big Proteins No Too big Amino acids Yes Small Salts Yes Small Urea Yes Small Water Yes Small Questions 1. What would happen to the blood volume over time if water were not reabsorbed? It would get low 2. How would this lack of water reabsorption affect blood pressure? It would not be as leaky 3. Fill in the table below indicating which molecules will be reabsorbed into the blood Table 4: Focus on Reabsorption Substance Reabsorbed? Why? Glucose Yes Need it Amino acids Yes Need them Salts Yes Maintain Ph and blood volume Urea Yes Secreted Water Yes Maintain Ph and blood volume Table 5: Osmoregulation Event Change in blood ADH output concentration Water Reabsorption Type of Urine produced Dehydration due to sunbathing in the afternoon and forgetting your water bottle Increase Increase Increase Scant, concentrated Drinking large amounts of water throughout the day Decrease Decrease Decrease Copious, dilute Going to the movie theater and eating a large bucket of salty popcorn without water to wash it down Increase Increase Increase Scant, concentrated Questions 1. If the blood is more basic than normal, what pH do you think the urine will be? basic 2. If the blood is more acidic than normal, what pH do you think the urine will be? acidic