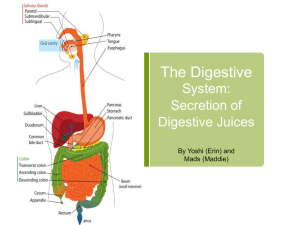
Structure of the stomach. Made up of two parts. Fundus- part to which the esophagus is attached. Constitutes the main body of the stomach Pylorus- part leading into the intestine. Constricted area leading into the intestine. Main functions of the stomach is as a storage organ for undigested food. (1 to 5 hours) pH of normal stomach contents is about 1.6 to 1.8. 3 types of cells found in gastric glands: Parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid Chief cells produce pepsin and possibly other enzymes Mucous cells Secrete mucin. Gastric secretion Beaumont's work on gastric digestion: Dr. William Beaumont 1822 found that the lining of the empty stomach was covered with a layer of mucus which was neutral or alkaline 'in reaction. When food entered the stomach or when the stomach lining was stimulated by mechanical irritation the membrane became bright red and a colorless juice welled up from the openings of small glands. found that fatty foods required a longer time to digest than lean. Gastric Glands are numerous small glands scattered throughout the walls of the stomach Gastric juice Digestive fluid secreted by gastric glands. Usually 2 to 3 liters is secreted every 24 hours. light-colored, thin fluid decidedly acidic in reaction. Resting stomach usually contains about 50 ml. of a liquid. Psychic stimulation; the thought, sight, and taste of food will increase the flow of gastric juice. Presence of food in the stomach amount of secretion depends on the kind of food. Presence of protein digestion products in the intestine Gastrin Produced by mucous membrane An internal messenger, or hormone, stimulating the gastric glands. Is thought by some to be histamine. Enterogastrone a hormone that liberated from the intestinal mucosa Enzymes found in the gastric Juice: Pepsin- acts on proteins, the most important. Rennin- in some species acts on casein causing milk to curdle Lipase- hydrolyzes fat. Hypo-acidity Acidity in stomach is less than normal. common in cancer of the stomach and pernicious anemia Pepsinogen Hyperacidity Acidity in the stomach is greater. Common in ulcers of the stomach Phenolphthalein gives the total acidity because this indicator changes color on the alkaline side of neutrality, at a pH of about 9.0; Topfer's reagent indicates free HCI because it changes color at a pH of about 3.0 to 4.0. Mett's method Hollander's theory HCI is produced in the parietal cells by the hydrolysis of chlorides such as NaCl. The NaOH formed is immediately neutralized by reacting with buffers such as NaH2PO4 and NaHCO3 HCI in the gastric juice converts pepsinogen to the active enzyme pepsin. Active pepsin converts more pepsinogen into pepsin. (autocatalytic reaction) Measurement of Peptic activity the zymogen, or inactive precursor, of pepsin 2 methods the body converts Pepsinogen into pepsin: How are total acidity and free HCl determined in a gastric analysis? hydrolyzes proteins into proteoses and peptones attacks peptide linkages in which tyrosine and phenylalanine are involved. Optimum pH .5 and 2.0. Will clot milk at a pH of 5 fine glass tubes containing coagulated egg albumen are placed in a beaker, together with a sample of the gastric contents incubated at 37°C in 24hrs Sorensen titration Van Slyke amino nitrogen determination Rennin Pepsin most important enzyme in the gastric juice Proteolytic enzyme found in the gastric juice of some animals. Casein is precipitated in human stomach by pepsin and not rennin. Is used to clot milk for making cheese and preparing junket. Acts best at a pH of 6.0 to 6.5 Chemistry in the precipitation of casein by rennin: Rennin acts on a protein of milk changing it into paracasein. Paracasein combines with calcium to form calcium paracaseinate precipitation of calcium paracaseinate the milk is said to curdle. Gastric absorption Very little absorption of food materials takes place in the stomach. Some monosaccharides, salts, and drugs may be absorbed. Chyme liquefied stomach contents Gastric Lipase A fat-hydrolyzing enzyme produced by gastric secretion. most active at pH 5 How long does food normally stay in the stomach? Action of gastric lipase: The amount of fat hydrolyzed in the stomach is small, and only fats which are in an emulsified form are attacked. Fats do not emulsify well in an acidic medium; hence emulsification does not take place to any great extent in the stomach. Carbohydrates requires about 2 hours. fatty foods and meat requires 4 or 5 hours How does the stomach empty itself? By peristalsis, it moves the chyme toward the pyloric opening into the intestine. Can stomach digest itself? Other Digestion in the Stomach: Increased acidity makes starch digestion takes place. Digestion of this sugar formation of glucose and fructose. Importance of the germicidal action of the gastric juice: It prevents intestinal infections. If the acidity of the stomach contents is low, fermentations will occur. Protoplasm of the living cells is alkaline in reaction. Since pepsin requires an acid medium, conditions are not correct in the living cells for its action. Living cells contain an antienzyme which inhibits the action of pepsin. Therefore no, stomach cannot digest itself.