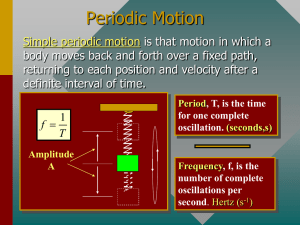
SHM - P1 - 2022 [41 marks] 1. An object performs simple harmonic motion (shm). The graph shows how [1 mark] the velocity v of the object varies with time t. The displacement of the object is x and its acceleration is a. What is the variation of x with t and the variation of a with t? Markscheme A 2. The bob of a pendulum has an initial displacement x0 to the right. The [1 mark] bob is released and allowed to oscillate. The graph shows how the displacement varies with time. At which point is the velocity of the bob at its maximum magnitude directed towards the left? Markscheme C 3. Which is correct for the tangential acceleration of a simple pendulum at small amplitudes? [1 mark] A. It is inversely proportional to displacement. B. It is proportional to displacement. C. It is opposite to displacement. D. It is proportional and opposite to displacement Markscheme D 4. A mass–spring system oscillates vertically with a period of T at the [1 mark] surface of the Earth. The gravitational field strength at the surface of Mars is 0. 3 g. What is the period of the same mass–spring system on the surface of Mars? 0. 9T B. 0. 3T C. T D. 3T A. Markscheme C 5. An object moves with simple harmonic motion. The acceleration of the object is [1 mark] A. constant. B. always directed away from the centre of the oscillation. C. a maximum at the centre of the oscillation. D. a maximum at the extremes of the oscillation. Markscheme D 6. A travelling wave has a frequency of 500 Hz. The closest distance between two points on the wave that have a phase difference of 60°( π3 rad) is 0. 050 m. What is the speed of the wave? 25 m s−1 B. 75 m s−1 C. 150 m s−1 D. 300 m s−1 A. Markscheme C [1 mark] 7. A simple pendulum and a mass–spring system oscillate with the same time period. The mass of the pendulum bob and the mass on the spring are initially identical. The masses are halved. What is A. [1 mark] time period of pendulum when the masses have been changed? time period of mass–spring system √2 2 1 C. √2 D. 2 B. Markscheme C 8. The motion of an object is described by the equation [1 mark] acceleration ∝ − displacement. What is the direction of the acceleration relative to that of the displacement and what is the displacement when the speed is a maximum? Markscheme D 9. An object undergoes simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude x0. x0 When the displacement of the object is 3 , the speed of the object is v. What is the speed when the displacement is x0? [1 mark] A. 0 B. v3 √2 C. 3 v D. 3v Markscheme A 10. A particle performs simple harmonic motion (shm). What is the phase [1 mark] difference between the displacement and the acceleration of the particle? A. 0 B. π2 C. π D. 32π Markscheme C 11. Which graph shows the variation with time t of the kinetic energy (KE) of [1 mark] an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (shm) of period T? Markscheme D 12. A string fixed at both ends vibrates in the first harmonic with frequency [1 mark] 400 Hz. The speed of sound in the string is 480 m s–1. What is the length of the string? A. 0.42 m B. 0.60 m C. 0.84 m D. 1.2 m Markscheme B 13. The graph shows the variation of the displacement of a wave with distance along the wave. The wave speed is 0.50 m s-1. What is the period of the wave? A. 0.33 s B. 1.5 s C. 3.0 s D. 6.0 s Markscheme C [1 mark] 14. Object P moves vertically with simple harmonic motion (shm). Object Q [1 mark] moves in a vertical circle with a uniform speed. P and Q have the same time period T. When P is at the top of its motion, Q is at the bottom of its motion. What is the interval between successive times when the acceleration of P is equal and opposite to the acceleration of Q? A. T4 B. T2 C. 34T D. T Markscheme B 15. The four pendulums shown have been cut from the same uniform sheet of[1 mark] board. They are attached to the ceiling with strings of equal length. Which pendulum has the shortest period? Markscheme D 16. An object at the end of a spring oscillates vertically with simple harmonic [1 mark] motion (shm). The graph shows the variation with time the object. t of the displacement x of What is the velocity of the object? A. − 2πA sin( πt ) T T B. 2πA sin( πt ) T T C. − 2πA cos( πt ) T T D. 2πA cos( πt ) T T Markscheme B 17. A mass on a spring is displaced from its equilibrium position. Which graph [1 mark] represents the variation of acceleration with displacement for the mass after it is released? Markscheme D 18. A particle moving in a circle completes 5 revolutions in 3 s. What is the frequency? A. B. C. D. [1 mark] 3 Hz 5 5 Hz 3 3π Hz 5 5π Hz 3 Markscheme B 19. An object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM) has a period T and [1 mark] total energy E. The amplitude of oscillations is halved. What are the new period and total energy of the system? Markscheme C 20. Two travelling waves are moving through a medium. The diagram shows, [1 mark] for a point in the medium, the variation with time t of the displacement d of each of the waves. For the instant when t = 2.0 ms, what is the phase difference between the waves and what is the resultant displacement of the waves? Markscheme D 21. A system that is subject to a restoring force oscillates about an equilibrium position. [1 mark] For the motion to be simple harmonic, the restoring force must be proportional to A. the amplitude of the oscillation. B. the displacement from the equilibrium position. C. the potential energy of the system. D. the period of the oscillation. Markscheme B 22. A particle is displaced from rest and released at time t = 0. It performs simple harmonic motion (SHM). Which graph shows the variation with time of the kinetic energy Ek of the particle? [1 mark] Markscheme D 23. Two sound waves from a point source on the ground travel through the [1 mark] ground to a detector. The speed of one wave is 7.5 km s–1, the speed of the other wave is 5.0 km s–1. The waves arrive at the detector 15 s apart. What is the distance from the point source to the detector? A. 38 km B. 45 km C. 113 km D. 225 km Markscheme D 24. What is true about the acceleration of a particle that is oscillating with simple harmonic motion (SHM)? [1 mark] A. It is in the opposite direction to its velocity B. It is decreasing when the potential energy is increasing C. It is proportional to the frequency of the oscillation D. It is at a minimum when the velocity is at a maximum Markscheme D 25. A mass at the end of a vertical spring and a simple pendulum perform [1 mark] oscillations on Earth that are simple harmonic with time period T. Both the pendulum and the mass-spring system are taken to the Moon. The acceleration of free fall on the Moon is smaller than that on Earth. What is correct about the time periods of the pendulum and the mass-spring system on the Moon? Markscheme B 26. A simple pendulum bob oscillates as shown. [1 mark] At which position is the resultant force on the pendulum bob zero? A. At position A B. At position B C. At position C D. Resultant force is never zero during the oscillation Markscheme D 27. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position take a maximum positive value? Markscheme D [1 mark] 28. The graph shows the variation with position s of the displacement x of a wave undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). [1 mark] What is the magnitude of the velocity at the displacements X, Y and Z? Markscheme B 29. A spring loaded with mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion. The [1 mark] amplitude of the motion is A and the spring has total energy E. What is the total energy of the spring when the mass is increased to 3m and the amplitude is increased to 2A? A. 2E B. 4E C. 12E D. 18E Markscheme B 30. A particle undergoes simple harmonic motion (SHM). The graph shows the[1 mark] variation of velocity v of the particle with time t. What is the variation with time of the acceleration a of the particle? Markscheme A 31. In simple harmonic oscillations which two quantities always have opposite [1 mark] directions? A. Kinetic energy and potential energy B. Velocity and acceleration C. Velocity and displacement D. Acceleration and displacement Markscheme D 32. A pendulum oscillating near the surface of the Earth swings with a time [1 mark] period T. What is the time period of the same pendulum near the surface of the planet Mercury where the gravitational field strength is 0.4g? A. 0.4 T B. 0.6T C. 1.6T D. 2.5T Markscheme C 33. A mass oscillates with simple harmonic motion (SHM) of amplitude xo. Its [1 mark] total energy is 16 J. x0 What is the kinetic energy of the mass when its displacement is 2 ? A. 4 J B. 8 J C. 12 J D. 16 J Markscheme C 34. A body undergoes one oscillation of simple harmonic motion (shm). What [1 mark] is correct for the direction of the acceleration of the body and the direction of its velocity? A. Always opposite B. Opposite for half a period C. Opposite for a quarter of a period D. Never opposite Markscheme B 35. A particle oscillates with simple harmonic motion (shm) of period T. Which [1 mark] graph shows the variation with time of the kinetic energy of the particle? Markscheme D 36. A particle is oscillating with simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude [1 mark] x0 and maximum kinetic energy Ek. What is the potential energy of the system when the particle is a distance 0.20x0 from its maximum displacement? A. 0.20Ek B. 0.36Ek C. 0.64Ek D. 0.80Ek Markscheme C 37. A mass is connected to a spring on a frictionless horizontal surface as shown. [1 mark] The spring is extended beyond its equilibrium length and the mass executes simple harmonic motion (SHM). Which of the following is independent of the initial displacement of the spring? A. The angular frequency of the oscillation B. The total energy of the mass C. The average speed of the mass D. The maximum kinetic energy of the mass Markscheme A 38. A simple pendulum has mass M and length l. The period of oscillation of the pendulum is T. What is the period of oscillation of a pendulum with mass 4M and length 0.25l? [1 mark] A. 0.5T B. T C. 2T D. 4T Markscheme A 39. Which of the following experiments provides evidence for the existence of [1 mark] matter waves? A. Scattering of alpha particles B. Electron diffraction C. Gamma decay D. Photoelectric effect Markscheme B 40. The period of a particle undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM) is T . The ratio [1 mark] acceleration of the particle is proportional to displacement of the particle from its equilibrium position T −2 . B. T −1 . C. T . D. T 2 A. Markscheme A 41. A particle of mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion (SHM) of [1 mark] angular frequency ω. The amplitude of the SHM is A. What is the kinetic energy of the particle when it is half way between the equilibrium position and one extreme of the motion? 2 2 A. mA4 ω B. 3mA2ω2 8 C. 9mA2ω2 32 D. 15mA2ω2 32 Markscheme B © International Baccalaureate Organization 2022 International Baccalaureate® - Baccalauréat International® - Bachillerato Internacional® Printed for AMMAN ACAD