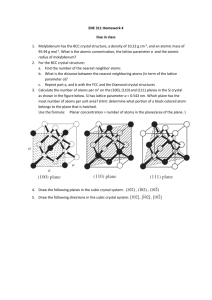
EE530 Advanced Semiconductor Device Physics Lecture – 02 Crystal Structure 1 Materials Solid state materials are classified as: 1) Conductors, 2) Insulators, & 3) Semiconductors Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 2 Structure “Spatial arrangements of atoms within a material” Solid State materials exist in three forms Amorphous Crystalline No recognizable long-range order in positioning of atoms Atoms are arranged perfectly in a orderly three dimensional arrangement Polycrystalline Multiple crystalline sections, placed along with each other, either disjoined or misaligned Intermediate case between Amorphous and Crystalline Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 3 Structure Amorphous Polycrystalline Crystalline Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 4 Crystal Structure Crystal Lattice Periodic and systematic arrangement of atoms in the crystal Unit Cell A small portion of any given crystal that could be used to reproduce the crystal a Unit Cell a Crystal Lattice Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer Crystal and unit cells 5 Crystal Structure Unit Cell We need unit cell only to reproduce the crystal structure Both the configurations given in figure are acceptable a a Unit Cell Unit Cell A unit cell need not to be primitive cell, i.e., the smallest possible unit cell Idea is to employ unit cells with orthogonal sides even if it is bigger than primitive cell Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 6 Unit Cell vs. Primitive Cell A red colored primitive cell within a unit cell The length of an edge of unit cell is called lattice constant, unit is Å (angstrom). 1 Å = 0.1 nm Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 7 1.1 Simple Cube (SC) 6 neighboring atoms Total 8 atoms contributes Example: Polonium Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 8 1.2 Body Centered Cube (BCC) 8 neighboring atoms Total 9 atoms contributes Example: Sodium and Tungsten Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 9 1.3 Face Centered Cube (FCC) 12 neighboring atoms Total 14 atoms contributes Example: Aluminum, Copper, Gold and Platinum Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 10 1.4 Diamond Lattice Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 11 Unit Cell of Silicon Si has the diamond lattice unit cell Unit Cell Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer Primitive Cell 12 Unit Cell of Gallium Arsenide GaAs has the zincblende lattice unit cell, similar to that of Si However, the lattice constant is larger than that of Si Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 13 1.5 Zincblende Lattice Example: GaAs Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 14 1.5 Zincblende Lattice 3D Animation http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=MD79L2 W9sp4#! Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 15 1.5 Zincblende Lattice 3D Animation Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 16 Summary Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 17 1.6 Example At 300K the lattice constant for Silicon is 5.43A. Calculate the number of Silicon atoms per cubic centimeter and the density of Silicon at room temperature. 8/a3 = 8/(5.43x10-8)3 = 5x1022 atoms/cm3 Density = no. of atoms/cm3 x atomic weight (g/mol)/Avogadro Constant (atoms/mol) = 2.33g/cm3 Dr. Tauseef Tauqeer 18