Lecture-1-Handouts---Introduction---Principles-of-Management-06102022-122313pm
advertisement

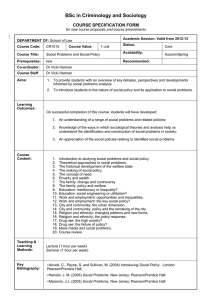
Lecture 1 – Introduction Principles of Management BS (A & F) / BS (Economics) 1 Introduction with the Students 2 5 6 Introduction to Teacher 3 Introduction to this Course 4 Rules & Expectations Who are Managers and What is Management? What is an Organization? Sajal Maqsood Introduction to the Course Course Title • Principles of Management Course Code • MGT 111 Credit Hours / Value • Three Sajal Maqsood Course Outline Lecture # Topics Introduction to Management and Organization Lecture 1 What is management? Why are managers important? Lecture 2 Management functions. Management roles and skills. What is an organization Historical Background of Management/Management Yesterday and Today History of management. Lecture 3 Classical approach. Scientific Management principles. Contemporary approach - Systems & contingency approach. General Administrative Theory Lecture 4 The Hawthorne Studies. Contemporary approach of Management Sajal Maqsood Lecture # Lecture 5 Lecture 6 Lecture 7 Lecture 8 Topics Course Outline Decision Making 8 step process 3 perspectives of decision making. Types of problems & decisions Decision making conditions & style. Decision making biases and errors Foundations of Planning What is planning? Why do managers plan? Types of goals and plans. Approaches to establishing plans. Characteristics of well-designed goals. Steps in goal setting Organizational Structure and Design Definitions and six key elements of organizational design Organizational design decisions/Two types of organizational design Contingency variables/ factors for organizational structure Common organizational designs (traditional / contemporary) Midterm Exams M I Minhas Lecture # Topics Human Resource Management HRM and its process Lecture 9 HR Planning Job Analysis Recruitment &Selection and orientation Lecture 10 Training and Development Performance Management and appraisal Motivating Employees What is motivation? Early theories of motivation. Lecture 11 Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory. McGregor’s theory X and theory Y Herzberg’s two-factor theory McClelland’s three needs theory Contemporary theories of motivation Goal-setting theory Reinforcement theory Lecture 12 Designing motivating jobs (Enlargement/ Enrichment) Equity theory Expectancy theory M I Minhas Lecture # Lecture 13 Topics Being an Effective Leader. Who are leaders and what is leadership? Early leadership theories (trait/ behavioral theories). Contingency theories of leadership (Fiedler/ Hersey and Blanchard/ Path goal model) Contemporary views of leadership and managing power. Course wrap up Controlling What is controlling? Lecture 14 Why is controlling important. Control Process Types of controls Final Project Update/discussion Lecture 15 Course wrap up Lecture 16 Final Presentations Final Exams M I Minhas Grading Policy Grading Instrument Marks Quizzes 15% Assignments + project 20% Mid Term Exam 25% Final Exam 40% Sajal Maqsood Reference Material Text Book Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Reference Books Management by Stephen P. Robbins and Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, (8 & 13th Ed.). Management a Pacific rim focus, enhanced edition by Bartol, Tein, Mathews and Martin. Management by James A.F Stoner, R. Edward Freeman, Daniel R. Gilbert, Jr, 2004 (6th Edition). Management, challenges for tomorrow’s leaders by Pamela S. Lewis, Stephen H. Goodman, Patricia M. Fandt and Joseph F. Michlitsch, 5th edition, 2007, Thomson: South-Western. Management by Gary Dessler (2nd edition). Management by Griffin (5th edition). Sajal Maqsood Classroom Conduct • A decent conduct, based on mutual respect, honesty and truthfulness • Active class participation • Read research papers and books • Please avoid any action that may cause disturbance during the lecture • • • • Entering late in the class Unnecessarily leaving the class Talking to other scholars/students Use of mobile phones • Free-riding behavior in the group assignments/tasks will be taken seriously Sajal Maqsood Academic Honesty All academic work submitted for assessment shall be original and a product of one’s/group’s own effort; any dishonest work shall be rejected for assessment or for any recognition or award. Sajal Maqsood Academic Dishonesty • Academic Dishonesty shall mean lack of truthfulness or sincerity on academic matters when interacting with the faculty member regarding an academic exercise. • • • • Lying to the instructor in an attempt to explain an incident of academic misconduct. Lying to instructor or using a false or forged excuse in order to get an extension in due date. Submitting a written summary about an out-of-class event that the student did not attend. Changing, altering, attempting to change or alter, or assisting another in changing or altering any grade or other academic record, including grades or records contained in a grade book or computer file, that is received for or in any way attributed to academic work. Sajal Maqsood Cheating • Cheating shall mean using or attempting to use unauthorized material, information, study aids, or another person’s work in any academic exercise. For example: • • • • Copying from assignments of other scholars. Receiving unauthorized help on an assignment, particularly on an individual assignment. Asking a scholar who has taken a test or examination to leak question paper or its contents. Copying from another scholar during a test or exam with or without that scholar’s consent/information. • Using unauthorized material to complete an assignment. • Asking a proxy to take a test or exam, or submit an assignment. Sajal Maqsood Forgery Forgery shall mean an act to imitate or counterfeit documents or signatures. Sajal Maqsood Plagiarism Plagiarism shall mean representing intellectual or creative work of someone else, as one's own, either knowingly or unknowingly, or due to negligence. • Using work, in whole or in part, which was done by someone else? • Paraphrasing or copying material from a written source, including the Internet, without quotation marks, footnoting or referencing it. Sajal Maqsood Facilitating Academic Misconduct • Facilitating Academic Misconduct shall mean helping or attempting to help another scholar/student commit an act of academic misconduct. • Writing or providing all or part of, a paper, essay, problem set, computer program, or any other assignment, for another scholar/student. • Helping someone else cheat during a test or exam, and extend solicited/unsolicited help in any other way. • Taking a test or examination as a proxy for someone. • Attending classes, or calling present during roll call, as a proxy for someone. Sajal Maqsood Special Needs • Scholars/Students with special educational needs are entitled to special provisions, including extra attention, time and/or any possible arrangements. • Please, inform the course instructor about your specific requirements within first week of the commencement of the course. Sajal Maqsood Chapter 1 Introduction to Management & Organizations Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Who are Mangers? • Manger • Someone who coordinates and oversees the work of other people so that organizational goals can be accomplished. Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Classifying Managers • First-Line Managers • • Individuals who manage the work of non-managerial employees. Middle Managers • • Individuals who manage the work of first-line managers. Top Managers • Individuals who are responsible for making organization-wide decisions and establishing plans and goals that affect the entire organization Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–1 Managerial Levels Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood What is Management? • Managerial Concerns • Efficiency • • • “Doing things right” Getting the most output for the least inputs Effectiveness • • “Doing the right things” Attaining organizational goals Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–2 Effectiveness and Efficiency in Management Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood What Do Managers Do? • Functional Approach • Planning – Defining goals, establishing strategies to achieve goals, developing plans to integrate and coordinate activities. • Organizing – Arranging and structuring work to accomplish organizational goals. • Leading – Working with and through people to accomplish goals. • Controlling – Monitoring, comparing, and correcting work. Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–3 Management Functions Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood What Do Managers Do? • Management Roles Approach (Mintzberg) • Interpersonal roles • • Figurehead, leader, liaison Informational roles • • Monitor, disseminator, spokesperson Decisional roles • Entrepreneur, Disturbance handler, resource allocator, negotiator Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood What Do Managers Do? • Management Roles Approach (Mintzberg) Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood What Do Managers Actually Do? • Interaction • • • • with others with the organization with the external context of the organization Reflection • • thoughtful thinking Action • practical doing Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood What Do Managers Do? • Skills Approach • Technical skills • • Knowledge and proficiency in a specific field Human skills • • Human Skills The ability to work well with other people Conceptual skills • Technical Skills Conceptual Skills The ability to think and conceptualize about abstract and complex situations concerning the organization Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood What Do Managers Do? Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–5 Skills Needed at Different Management Levels Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1– 6 Conceptual Skills • Using information to solve business problems • Identifying of opportunities for innovation • Recognizing problem areas and implementing solutions • Selecting critical information from masses of data • Understanding of business uses of technology • Understanding of organization’s business model Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1– 6 Communication Skills • Ability to transform ideas into words and actions • Credibility among colleagues, peers, and subordinates • Listening and asking questions • Presentation skills; spoken format • Presentation skills; written and/or graphic formats Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1– 6 Effectiveness Skills • Contributing to corporate mission/departmental objectives • Customer focus • Multitasking: working at multiple tasks in parallel • Negotiating skills • Project management • Reviewing operations and implementing improvements • Setting and maintaining performance standards internally & externally • Setting priorities for attention and activity • Time management Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1– 6 Interpersonal Skills • Coaching and mentoring skills • Diversity skills: working with diverse people and cultures • Networking within the organization • Networking outside the organization • Working in teams; cooperation and commitment Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–7 Management Skills and Management Function Matrix Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood How the Manager’s Job Is Changing? • The Increasing Importance of Customers • Customers: the reason that organizations exist • • • Managing customer relationships is the responsibility of all managers & employees. Consistent high quality customer service is essential for survival. Innovation • Doing things differently, exploring new territory, and taking risks • • Managers should encourage employees to be aware of and act on opportunities for innovation. Sustainability • Meeting the needs of people today, without compromising the ability of future generations • • Integrating economic, environmental, and social opportunities into business strategies Increasing long-term shareholder value Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–8 Changes Impacting the Manager’s Job Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood What Is An Organization? • An Organization Defined • A deliberate arrangement of people to accomplish some specific purpose (that individuals independently could not accomplish alone). • Common Characteristics of Organizations • • • Have a distinct purpose (goal) Composed of people Have a deliberate structure Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–9 Characteristics of Organizations Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–10 The Changing Organization Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Why Study Management? • The Value of Studying Management • The universality of management • • Good management is needed in all organizations. The reality of work • • Employees either manage or are managed. Rewards and challenges of being a manager • Management offers challenging, exciting and creative opportunities for meaningful and fulfilling work. • Successful managers receive significant monetary rewards for their efforts. Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–11 Universal Need for Management Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Exhibit 1–12 Rewards and Challenges of Being A Manager Management by Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, Prentice Hall International Edition, 11th Ed. Pearson. Sajal Maqsood Sajal Maqsood