Lipids Exam Questions: Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Hormones
advertisement

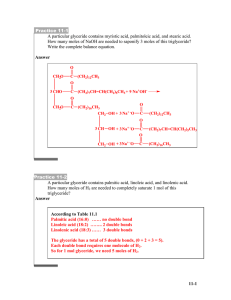
B3 Lipids Question 1 Determine the number of double bonds in linoleic acid, C18H32O2, and linolenic acid, C18H30O2, and suggest which fatty acid will have a higher iodine number. • Refer Data Booklet Table 34 • linoleic has 2 C=C / double bonds and linolenic has 3 C=C / double bonds; linolenic acid (will have higher iodine value); Question 2 Explain why it is important to include the fatty acids linoleic and linolenic acid in a balanced diet. • Textbook page 567 • essential fatty acids / cannot be synthesized in body; • lowers LDL cholesterol level / lowers risk of heart disease / Question 3 (a) The partial equation for the enzyme-catalysed hydrolysis of a triglyceride is shown below. Draw the structural formulas of the products A and B. • A: CH3(CH2)16COOH • B: CH2OHCHOHCH2OH Question 3 (b) Deduce whether the fatty acid obtained in part (a) will have a higher or lower melting point compared to oleic acid, CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. Outline your reason. • higher (melting point); • saturated fatty acids / no C=C bonds; Reason: close packing, stronger van der Waals’ forces, larger surface area of contact. Question 4 Some synthetic hormones are similar in structure to testosterone and are used as anabolic steroids. Outline one medical and one non-medical use of anabolic steroids. • Medical use: recovery from injury/surgery/starvation/illness/disease; • Non-medical use: increase in muscle mass / enhances performance/strength in sports and bodybuilding Question 5 Triglycerides are one of three types of lipid found in the human body. The following equation represents the formation of a triglyceride. X + 3RCOOH triglyceride + 3Y (a) Identify the compounds X and Y. • X is glycerol/propane-1,2,3-triol/CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH2(OH); • Y is water/ H2O; Question 5 (b) Draw the structural formula of a triglyceride formed from one molecule each of octanoic acid, lauric acid and stearic acid. The formulas of the acids are shown in Table 34 of the Data Booklet. Question 5 (c) Explain whether the triglyceride in part (b) is a solid or a liquid at room temperature. • solid as contains (three) saturated/straight fatty acid chains; • can pack closer together; • have stronger London/dispersion/van der Waals’ forces between chains; Question 5 (d) Identify the type of reaction that occurs during the formation of a triglyceride. • esterification / condensation Question 5 (e) Explain why fats have a higher energy value per mole than carbohydrates. • fats contain less oxygen than carbohydrates / are in a less oxidized state (so more energy is released) Question 6 Unsaturated fats contain C=C double bonds. The amount of unsaturation in a fat or oil can be determined by titrating with iodine solution. (a) Define the term iodine number. • the number of grams/mass of iodine that add to/react with 100 g of the fat/lipid/oil; Question 6 • the number of grams/mass of iodine that add to/react with 100 g of the fat/lipid/oil; Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 Hormones play an important role in the body. (a) Outline the function and production of hormones in the body. • chemical messenger; • secreted directly into the blood by endocrine glands; Question 8 (b) In many communities there are people who use steroids appropriately, and others who abuse them. Outline one appropriate use and one abuse of steroids. • build up depleted muscle due to lack of activity; assist in recuperation from an illness; stimulation of bone marrow; treatment of delayed male puberty; asthma inhalers; treatment of female-to-male gender changes; treatment of inflammation; Award [1] for any one use. • muscle/strength build up for an unfair advantage in sport by athletes; Award [1] for abuse. Question 9 Calculate the number of carbon-carbon double bonds in linolenic acid, C18H30O2, given that 7.7 g of iodine, I2, react with 2.8 g of linolenic acid.