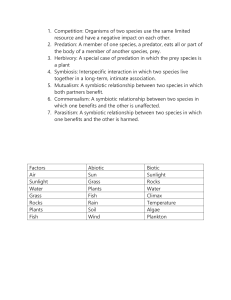
1. Competition: Organisms of two species use the same limited resource and have a negative impact on each other. 2. Predation: A member of one species, a predator, eats all or part of the body of a member of another species, prey. 3. Herbivory: A special case of predation in which the prey species is a plant 4. Symbiosis: Interspecific interaction in which two species live together in a long-term, intimate association. 5. Mutualism: A symbiotic relationship between two species in which both partners benefit. 6. Commensalism: A symbiotic relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is unaffected. 7. Parasitism: A symbiotic relationship between two species in which one benefits and the other is harmed. Factors Air Sunlight Water Grass Rocks Plants Fish Abiotic Sun Grass Plants Fish Rain Soil Wind Biotic Sunlight Rocks Water Climax Temperature Algae Plankton the bee get nectar from the flower by the flower gets it pollen spread: Mutualism Birds eats fly predation Cattle egrets foraging in fields among zebra is an example of commensalism. As zebra and other large animals graze on the field, they cause movements that stir up various insects. Ticks sucking the dog blood: parasitism Dears battling each other competition