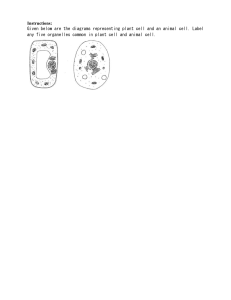
Organization of the Body Medical Terminology The Human Body The Human Body How does your body grow? The body is arranged in 6 basic levels: The Human Body Organelles Cell Tissue Organ Organ Systems Organism The Cell The basic structural unit of the body. The Cell Cytology The basic structural unit of the body. The study of the formation, structure, and function of cells. The Cell Cytology Organelles The basic structural unit of the body. The study of the formation, structure, and function of cells. The organs of the cell. The Cell The Cell In your journal draw a full page cell with organelles. The Cell https://youtu.be/UHJGy1ZW7kE In your journal, draw a full page cell with organelles. Nucleus Cell Membrane The Cell’s Organelles Cytoplasm Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Body Lysosome Ribosomes The Cell’s Organelles Nucleus The control center of the cell. Contains genetic information The Cell’s Organelles Cell Membrane The “container” of the cell. The Cell’s Organelles Cytoplasm Fluid that fills the cell so organelles can float inside. The Cell’s Organelles Mitochondria Powerhouse of the cell. The Cell’s Organelles Endoplasmic Reticulum Make proteins. The Cell’s Organelles Golgi Body Factory where ER proteins are transported. The Cell’s Organelles Lysosome Location of Digestive enzymes. The Cell’s Organelles Ribosomes Proteins made for the cell to use. The control center of the cell. Contains genetic information Nucleus The Cell’s Organelles The “container” of the cell. Cell Membrane Fluid that fills the cell so organelles can float inside. Cytoplasm Powerhouse of the cell. Mitochondria Make proteins. Endoplasmic Reticulum Factory where ER proteins are transported. Golgi Body Lysosome Ribosomes Location of Digestive enzymes. Proteins made for the cell to use. The Nucleus The control center of the cell. Contains genetic information Genetic Information of the cell stored as Chromosomes Humans have 46 chromosomes. The Nucleus The control center of the cell. Contains genetic information Genetic Information of the cell stored as Chromosomes Humans have 46 chromosomes. DNA – Deoxyribonucleic acid = A full set of chromosomes. Cell Division The process used for growth and development of cells. Also, to replace old, dead, or damaged cell. How cells divide and make more cells = Mitosis. Genetics – The study of genes and how they are transferred from individuals to their offspring. Cell Division The process used for growth and development of cells. Also, to replace old, dead, or damaged cell. How cells divide and make more cells = Mitosis. Genetics – The study of genes and how they are transferred from individuals to their offspring. Genetic disorders – The inheritance of defective genes. Makes identical cells. Mitosis The process of cell division How cells divide and make more cells. Makes identical cells. Mitosis The process of cell division How cells divide and make more cells. Meiosis – The process of cell division of the sex cells. Mitosis - Mitosis vs Meiosis For Growth and making specialized cells. Meiosis For making babies. Cells with specialized functions: (5). Muscle Cells = long & slender cells. Epithelial Cells = Flat, square cells of skin and linings. Specialized Cells Fat Cells = Large, empty spaces for fat storage. Nerve Cells = Long with “tails” for the travel of nerve impulses. Blood Cells – Vary in shape and size according to their function. Cells with specialized functions: (5). Muscle Cells = long & slender cells. Epithelial Cells = Flat, square cells of skin and linings. Fat Cells = Large, empty spaces for fat storage. Nerve Cells = Long with “tails” for the travel of nerve impulses. Specialized Cells Blood Cells – Vary in shape and size according to their function. Vocabulary Tissues Histology Biopsy Pathologist Tissues – A group of similar cells working together to perform a specific function. Histology – The study of the structures and functions of tissues. Biopsy – Removal of tissue samples for microscopic examination. Pathologist – A physician who studies tissue. What is the basic structural unit of the body? Exit Ticket What is the basic structural unit of the body? Exit Ticket The Cell