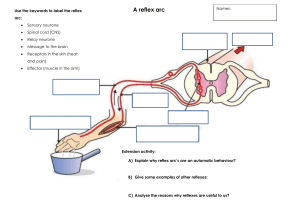
Cebu Doctors’ University A.Y. 2022- 2021 Bachelor of Arts In Psychology 1 Name: Go, Samantha Isabel B. Date: August 22, 2022 Section: AB-Psych 1-A Seubject: Psych 101 I. Research on at least 10 human reflexes and describe their purpose. 1. Gag reflex – is a muscular reflex at the back of the throat. Prevents choking and swallowing small objects. Purpose/ Trigger: When something touches the back of the throat. 2. Pupillary Light Reflex – is a reflex that happens in the eye. Usually occurs when intensity of light hits our eyes, causing it to dilate or constract. Purpose/ Trigger: Light. 3. Protective Reflex – protects our body from things that can harm it. Purpose/ Trigger: Feeling of Danger or in situations where you are in harms way. 4. Sneeze Reflex – Usually happens when our nasal passageway gets irritated causing us to sneeze. Purpose/ Trigger: Irritation in the nasal passageway. 5. Corneal reflex – Refers to blinking of both eyes when the cornea of either eye is touched. This reflex is responsible to act when dust or foreign particles accidentally enters our eyes. Purpose/ Trigger: Touch or foreign particles. 6. Patellar reflex – sudden kicking movement of the lower leg in response to a sharp tap on the patellar tendon. Purpose/ Trigger: A tap on the Patellar tendon, which lies just below the kneecaps. 7. Yawn reflex – it isn’t actually cause you are sleepy. It occurs when the body requires more oxygen. Purpose/ Trigger: body requiring more oxygen. 8. Cough reflex – a protective reflex in response to heat, acid and other foreign bodies in the airways. Purpose/ Trigger: blockage or something in the airways. 9. Diving reflex – it is a psychological response that overrides basic homeostatic reflexes. Purpose/ Trigger: submerged under water. 10. Scratch reflex – is a response to our sensory neurons that has been activated whose peripheral terminals are located on the surface of the body. Purpose/ Trigger: activation of our sensory nuerons or a stimulation with an external object or parasite. II. Research at least 10 conditions that are affected by or damage a certain part/ area of the brain. 1. Damage part/ area of the brain: Parts of the braini involving in the memory, entorhinal cortex and hippocampus Impairment: Alzheimer’s Disease, most common form of dementia among aging people. AD slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and, eventually, the ability to carry out the simplest tasks of daily living. 2. Damage part/ area of the brain: lower back of the brain to the spinal fluid Impairment: Medulloblastomas, these cancerous brain tumors are most common in children, though they can occur at any age. Are all classified as Grade IV tumors. This means they are malignant (cancerous) and fastgrowing. 3. Damage part/ area of the brain: temporal lobes Impairment: Epilepsy, is a common seizure disorder. There are four main types of epilepsy: focal, generalized, combination focal and generalized, and unknown. A doctor generally diagnoses someone with epilepsy if they have had two or more unprovoked seizures. 4. Damage part/ area of the brain: basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Impairment: Parkinson’s Disease, a brain disorder that causes unintended or uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination. 5. Damage part/ area of the brain: Near the brain’s pituitary gland Impairment: Craniopharyngiomas, as it slowly grows, it can affect the function of the pituitary gland and other nearby structures in the brain. Many experts consider it to be a chronic disease, as they tend to recur even when they have been completely removed (resected) surgically. The tumor itself is usually not dangerous, as it is benign and only very rarely becomes malignant. 6. Damage part/ area of the brain: amygdala Impairment: Anxiety, is a normal reaction to stress and can be beneficial in some situations. It can alert us to dangers and help us prepare and pay attention. Anxiety disorders differ from normal feelings of nervousness or anxiousness and involve excessive fear or anxiety. 7. Damage part/ area of the brain: cerebellum, spinal cord, nerves Impairment: Ataxia, a term for a group of disorders that affect co-ordination, balance and speech. Any part of the body can be affected, but people with ataxia often have difficulties with: balance and walking. speaking. swallowing. 8. Damage part/ area of the brain: nerve cells in the brain Impairment: Huntington's disease, a condition that stops parts of the brain working properly over time. It's passed on (inherited) from a person's parents. It gets gradually worse over time and is usually fatal after a period of up to 20 years. 9. Damage part/ area of the brain: cerebellum Impairment: Multiple system atrophy, a rare condition of the nervous system that causes gradual damage to nerve cells in the brain. This affects balance, movement and the autonomic nervous system, which controls several basic functions, such as breathing, digestion and bladder control. 10. Damage part/ area of the brain: cerebellum Impairment: Autism, a developmental disability caused by differences in the brain. People with ASD often have problems with social communication and interaction, and restricted or repetitive behaviors or interests. People with ASD may also have different ways of learning, moving, or paying attention.