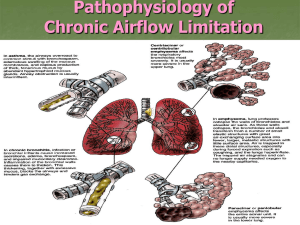
COPD Overview Ian McLeod, PA-C, ATC PHA 521 – Foundations of Clinical Practice II Spring 2022 Northern Arizona University © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease COPD Defined • Life threatening lung disease that interferes with normal breathing – not just a “smoker’s cough” • Progressive disease state characterized by airflow limitation that is not fully reversible • Mixture of • Airway disease • Parenchymal destruction • Abnormal pulmonary inflammatory response • Resulting in • Chronic inflammation • Lung elastic recoil decreases • Expiratory small airway collapse COPD Pathophysiology COPD Pathophysiology COPD Defined • Chronic bronchitis • Excessive bronchial mucus • Daily productive cough > 3 months in 2 consecutive years • Emphysema • Abnormal permanent enlargement of air space distal to terminal bronchiole • Destruction of alveolar walls w/o obvious fibrosis COPD Pathophysiology Emphysema • Abnormal permanent enlargement of the air spaces • Alveolar ducts • Alveoli • Loss of elastic recoil → increased lung compliance Emphysema Emphysema • Emphysema has an association with a deficiency of the enzyme alpha1 anti-trypsin Emphysema Chronic Bronchitis • Excessive mucus production • Hypertrophy of mucosal glands • Increase # of goblet cells • Inflammatory infiltration • Bronchiolar fibrosis • Hyper-responsiveness COPD Presentation • > 45 years old (35 y/o) • Characteristic symptoms • Chronic and progressive dyspnea • Initially with heavy exertion • Occurs at rest with severe disease • Cough • Sputum production • Other symptoms • • • • Frequent winter “bronchitis” Wheezing Purse-lip breathing Right sided heart failure • No clinical features / history suggestive of asthma COPD vs. Asthma Clinical features COPD Asthma Smoker or ex-smoker Nearly all Possibly Symptoms under age 45 Rare Often Chronic productive cough Common Uncommon Breathlessness Persistent and progressive Variable Night time waking with breathlessness and or wheeze Uncommon Common Significant diurnal or day to day variability of symptoms Uncommon Common Clinical Presentation Emphysema Chronic Bronchitis • • • • • • • Mild dyspnea that progresses slowly • Cough with copious sputum • Cyanotic • Wheezing • Rhonchi • Fluid retention Pronounced dyspnea Absence of cough Absence of sputum Tachypnea Cachexic Hyperinflation presentation • Barrel-chest • Distant / diminished lung sounds • Hyper-resonant COPD Pathophysiology © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease COPD Diagnostic Testing • Spirometry • CBC → what would you expect to see…think back to diagnostic medicine • Alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficiency screening • Development of COPD in Caucasian < 45 years old • Family history of deficiency • Strong family history of COPD • CXR Smoking Effects on FEV1 © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease © 2022 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Questions?