Liabilities: Financial & Non-Financial Accounting Principles
advertisement

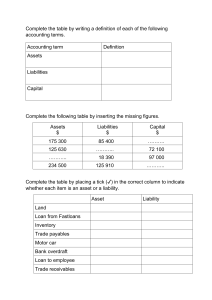
CHAPTER 1 Related standards: PAS 1: Presentation of Financial Statements PAS 32: Financial Instruments: Presentation PFRS 9: Financial Instruments Learning Competencies Know the recognition criteria for liabilities and their essential characteristics. Identify the characteristics of a financial liability. Know the initial and subsequent measurements of financial and non-financial liabilities. Know how to classify liabilities as current and noncurrent. Liabilities PAS 1 prescribes the basis for presentation of general purpose financial statements to improve comparability both with the entity's financial statements of previous periods and with the financial statements of other entities. Essential characteristics of a liability 1. Present obligation (Legal or Constructive) 2. Arising from past events 3. Outflow of economic benefits Financial liabilities A financial liability is any liability that is a contractual obligation: a. to deliver cash or another financial asset to another entity; or b. to exchange financial assets or financial liabilities with another entity under conditions that are potentially unfavorable to the entity; or Examples of financial liabilities 1. Payables such as accounts, notes, loans, bonds payable and accrued expenses that are payable in cash. 2. Finance lease obligations. 3. Liabilities held for trading such as obligations to deliver financial assets borrowed by a “short seller” (i.e. an entity that sells financial assets it has borrowed and does not yet own). 4. Preference shares issued with mandatory redemption. 5. Security deposits received that are to be returned to tenants at the end of lease term. 6. Obligations to deliver a variable number of own shares worth a fixed amount of cash. CHAPTER 1 The following are not financial liabilities; 1. Unearned revenues and warranty obligations that are to be settled by future delivery of goods or services, rather than cash. 2. Taxes, SSS premiums, Philhealth and other payables arising from statutory requirements and not from contracts. 3. Commodity contracts that either cannot be settled in cash or which are expected to be settled by commodity exchange (e.g., coffee beans, gold bullion, oil, and the like). If a commodity contract is expected to be cash settled, it will be included as financial liability on the part of the cash payor. 4. Constructive obligations. These obligations do not arise from contracts. Recognition of liabilities An item is recognized as a liability when: 1. It meets the definition of a liability; 2. It is probable that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will result from its settlement; and 3. The settlement amount can be measured reliably. Measurement of financial liabilities o Initial measurement – fair value minus transaction costs, except financial liabilities at FVPL whose transaction costs are expensed immediately. o Subsequent measurement – amortized cost (except financial liabilities that are classified as held for trading and those that are designated; these are subsequently measured at fair value) Measurement of Non-financial liabilities o Non-financial liabilities are initially measured at the best estimate of the amounts needed to settle those obligations or the measurement basis required by other applicable standard. Examples: 1. Obligations arising from statutory requirements (e.g., income tax payable) 2. Unearned or deferred revenues 3. Warranty obligations 4. Commodity contracts that either cannot be settled in cash or which are expected to be settled by commodity exchange CHAPTER 1 Current liabilities are liabilities that are: 1. Expected to be settled in the entity’s normal operating cycle; 2. Held primarily for trading; 3. Due to be settled within 12 months after the end of the reporting period; or 4. The entity does not have the right at the end of the reporting period to defer settlement of the liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period. o All other liabilities are classified as noncurrent. Trade and non-trade payables Trade payables are obligations arising from purchases of inventory that are to be sold in the ordinary course of business. Other payables are classified as non-trade. Trade payables are classified as current liabilities when they are expected to be settled within the normal operating cycle or one year, whichever is longer. On the other hand, non-trade payables are classified as current liabilities only when they are expected to be settled within one year. Dividends payable Under IFRIC 17, the liability to pay a dividend is recognized when the dividend is appropriately authorized and is no longer at the discretion of the entity, which is: 1. the date when the declaration of the dividend (e.g., by management or the board of directors) is approved by the relevant authority (e.g., the shareholders) if the jurisdiction requires such approval, or 2. the date when the dividend is declared (e.g., by management or the board of directors) if the jurisdiction does not require further approval.