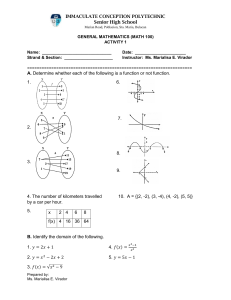
BPC E-Learning System Evaluation: Challenges & Effectiveness
advertisement

BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE (BPC) ______________________________ MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C. (L) RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. ROBLES, RANDY, A. JULY 2021 BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION ABSTRACT This paper evaluated the effectiveness and efficiency of Bulacan Polytechnic College's e-learning system in the teaching and learning experienced of its students and faculty members. Given the rise in using online teaching and learning platforms, more study needs to improve and develop e-Learning systems to maximize the generation and acquisition of knowledge. The study evaluated the software, Format, Quality of Operation, and content through functionality, accessibility; technical aspect; mobile designs; privacy and data protection; and social, cognitive, and teaching presence. Sets of questionnaires were used and answered by random students from BPC Malolos and faculty members from eight campuses of the BPC. The gathered data were analyzed using a qualitative data analysis method and descriptive statistics. The study found that the BPC e-Learning system was reliable, functional, and effective in all its aspects, from the software to its content. In addition, the e-Learning system was found efficient as a teaching tool that the instructors effectively facilitate teaching using it. Thus, the study recommended that to enhance further that e-Learning system, the administration may seek more funds as it suggested as one of the significant challenges in its development. Keywords: conceptualization, portal development, mechanics of the program, eLearning system, functionality, accessibility, technical aspect, mobile designs, privacy and data protection, social presence, teaching presence, cognitive presence VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Introduction On March 16, 2020, the Philippine government declared a "community lockdown” throughout the country because of the pronouncements from the World Health Organization (WHO) of the COVID-19 pandemic. It is almost the end of the second semester at BPC. Immediately the school management conceptualized measures to be followed in the first semester of SY-2020-2021, to ensure the delivery of quality education despite the crisis. The Vice-President of Academic Affairs (VPAA)and OIC- College President of the BPC along with the Vice-President for Administration, Vice- President for Research and Extension Service ,and Head of Management Information Systems (MIS) together with her team, and other officials of the College decided to develop a system that will offer a teaching and learning platform for every BPCians, so that the school will continue its vision , mission , goals and objectives (VMGO) in providing quality technical and vocational education amidst the pandemic. Theay mde a Learning Management System (LMS) and named it as BPC e-Learning System that will be used for the online education of the students of BPC. The system aims to deliver an efficient and effective learning experience for students, functional ways for the faculty members in administering their classes and monitoring the progress of students. Quinn, Alem, and Eklund (1997) proposed methodology for evaluating e-learning systems that will considers design factors and acceptance factors: the former comprises instructional goal, instructional content, learning tasks, learning aids, and assessment, whereas the latter include level of motivation use the product, level of active participation VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION entailed, quality of learning support, and level of user satisfaction. The BPC’s developed system has the same factors as Quinn’s model except that the e-learning system is only one of the systems of BPC portal and the baseline of the evaluation scheme of this research. The portal contains information on courses offered, transcripts, email programs, timetables, exam schedules and department contact numbers. It also offers links to useful web resources, such as research tools and online journals (Suzannah Windsor, 2020). The school portal developed by MIS is somewhat similar to Windsor’s, but BPC’s portal is more innovative and complex because there are six systems in it including the different information and features that direct the users to the other systems they needed. The BPC Portal consists of six systems to wit: 1. admission system; the requirements of enrollees will be stored and submitted through online 2. entrance exam system; the enrollees will answer and complete their exam through this system 3. enrollment system; this is where the registrar works on sorting the information and subjects of students accordingly 4. grading system; this is where the grades of the students will be stored 5. scholarship system, and 6. e-Learning system; this is where the teaching and learning process occur. The system plays a crucial role in the program because this is where the subjects, modules, assessments, and progress in the grades of the students were stored. This study focused on evaluating its software/ system in terms of its technical, pedagogical, other factors, and its effectiveness on the teaching and learning process. The research aims to address the challenges that the students and faculty members encountered while using the software/ system and to recommend or suggest possible solutions on the weaknesses that will be identified based on the data collected from the respondents of the VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION study. This may help the developers of the system on what considerations and action they will do to address the challenges and other factors to improve the present e-learning system/ software. To gather relevant and appropriate data to address and reach the objectives of this study, different instruments were used to evaluate the system/software’s effectiveness, technical aspects, and needs of the users. It is hoped that the results of the study may contribute to the development of a model e-learning system and be adopted/adapted by other higher institutions of learning to maximize generation and acquisition of knowledge amidst the covid-19 pandemic. Statement of the Problem The general problem of the study is: How may the BPC e-Learning be enhanced based on the evaluation of the system? Specifically, the study sought answers to the following questions; 1. How may the BPC e-Learning be described as regards; 1.1 conceptualization; 1.2 mechanics of the program; and 1.3 portal development in terms of: 1.3.1 ICT infrastructure for a successful e-learning implementation; 1.3.2 administrative support (commitment and policies); and 1.3.3 resource support (financial, human, technical)? 2. How may the BPC e-Learning software be evaluated in terms of; 2.1 software product evaluation; 2.2 quality; VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION 2.2.1 operation; 2.2.2 content; and 2.2.3 format? 3. How may the faculty members and students evaluate the BPC e-Learning in terms of its: 3.1 functionality; 3.2 accessibility; 3.3 technical aspect; 3.4 mobile designs; 3.5 privacy data, protection, and rights; 3.6 social presence; 3.7 teaching presence; and 3.8 cognitive presence? 4. What is the level of effectiveness of the BPC e-Learning system when used by the faculty as perceived by the students? 4.1 student-faculty contact; 4.2 cooperation among students; 4.3 active learning; 4.4 prompt feedback; 4.5 time on task; 4.6 high expectations; and 4.7 diverse talents and ways of learning? VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION 5. What is the level of effectiveness of the BPC e-Learning system when used by the students as perceived by the faculty? 5.1 cognitive aspect; 5.2 metacognitive aspect; and 5.3 affective aspect? 6. How may the faculty assess their Technical, Administrative, and Pedagogical Competencies using the Learning Management System (LMS) of the BPC eLearning? 7. What is the self-assessment of the students towards their experiences in using BPC e-Learning in the category of; 7.1 internet online skills; 7.2 software application skills; 7.3 content; 7.4 social support; 7.5 study habits; 7.6 abilities; 7.7 motivation; and 7.8 usefulness? 8. What are the challenges encountered by the faculty and the students while using the BPC e-Learning system? 9. What solutions/ suggestions were posited by the respondents to address the challenges observed? VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION 10. What may be proposed to enhance the present BPC e-Learning system based on the findings of the study? This study is deemed significant to the teachers, students, administration, system developer, and future researchers. The respondents in this research are some students of BPC- Malolos from degree, technical vocational courses, and including some class president of senior high school students. While some of the faculty members that also responds on our study came from BPC-Malolos and 7 satellite campuses. Literature Review The theories reviewed relevant to this study are a theory proposed by Linda Harasim (2012), Online Collaborative Learning (OCL) that concentrates on the internet's capabilities to create learning settings that encourage sharing of knowledge development, as well as the internet's usage as a tool to redefine formal, non-formal, and civic learning for the knowledge era (Harasim,2012). There are three stages of knowledge building through group discourse in OCL. These three stages are as follows: 1. Idea generating is the brainstorming stage, in which diverse ideas were accumulated. 2. Idea organizing is the stage in which ideas are reviewed, evaluated, and classified via debate and discussion. 3. Intellectual convergence according to Harasim, 2012 it is the stage at which cognitive synthesis and consensus occur, even agreeing to disagree, generally through an assignment, essay, or collaborative work piece. VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION There are three of the more popular theories in learning that are relevant to online education, according to Picciano, A. G. (2017). These are the Learning Theories (Behaviorism, Cognitivism, and Social Constructivism). In his paper "Theories and Frameworks for Online Education: Seeking an Integrated Model," learning theory explains and helps us understand how people learned. One of the categories of learning theories is Behaviorism. This learning theory is associated with Pavlov (1897) Behaviorism is a type of learning theory. This learning theory is connected with Pavlov (1897), who reported an experiment on conditioning after originally investigating the digestion of dogs. He observed that every stimulus or event that the dogs learnt to link with food elicited the same response. The psychology of learning stresses human cognition or intelligence as a unique gift that allows man to build hypotheses and grow intellectually. According to Harasim, 2012 Cognitivism is thought to be a reaction to behaviorists' "rigid" reliance on predicting stimuli and response. Moodle (2015), emphasize that Social Constructivism is characterized as a social community that builds things for each other and, producing a tiny culture of shared objects with common meanings. The evolution of scientific knowledge is governed by social factors, which are basically contingent and independent of logical techniques, and which may be analyzed on the basis of causal processes of belief formation. The related readings reviewed in this study are the following. There has been so much argument over online education that there are several claimed benefits and applications of online learning—the effectiveness of online learning in educating students, using teaching, and professional development. Some of the most VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION significant online learning challenges include the capacity to deliver a world-class learning to anybody with a data plan connection and the cost-effectiveness of battling the growing expense of post-secondary course equivalence at the post - secondary level (De la Varre et.al 2011). The teaching practices recommended by the Chickering, and Gamson’s Seven Principles framework are well-suited for guiding the design and delivery of quality of Internet-based instruction (e. g., Billings, 2000; Chickering & Erhmann, 1996). The Seven Principles emerged from a panel of higher education scholars who were asked to synthesize findings from research studies that identified effective college and university teaching practices. The college “classroom” certainly looks different these days. Due to campus closures in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, we no longer travel to a common space to learn together in physical proximity. Though most of us have transitioned to online instruction, there was insufficient time to prepare for this new model – instead, we are in the midst of “emergency distance learning,” with significant implications to student’s cognitive, affective and metacognition aspect (Isohätälä et al., 2019). E-learning is by far the most suitable option to acquire a higher education degree. To obtain their degree, many students participate in a flexible and self-paced form of instruction. When it came to technologies in education (Chomsky, 2014). The significant growth in the number of online courses is not surprising considering that many students want to earn degrees that will positively affect their careers while at the same time allow them to sustain family and work responsibilities. (Motiwalla & Tello, 2000; Phipps, VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Wellman, & Merisotis, 2000). The quality with the growing demand for e‐learning along with striving for excellence associated with globalization, there are worldwide calls for enhancing and assuring quality in e‐learning, specifically in the context of the developing countries. (D. Masoumi, B. Lindström, 2011). According to Claire Bradin (1999) to measure evaluate the quality of e-learning she divided it in to sub-categories the format, operation, and content. While Antsey and Gavan, 2018 proposed that in evaluating eLearning the combination of technical and pedagogical aspects should be considered the evaluation consists of eight (8) categories; (1) functionality- specifies how effectively a system fulfills the needs of users and the work necessary to change the system (Berger et al., 2013); (2) accessibility- the purpose of making your services as accessible as possible to as many target audience (Glaly, 2020); (3) technical- the usability and utilization of the interface of the system in technology (Antsey and Gavan, 2018); (4) mobile designs. The mobile device's design takes into account the limitations of a smaller-sized screen entirely. (Antsey and Gavan, 2018); 5) privacy, data protection, and rights- to provide consumer confidence, enterprise and protection for their information (Barker, 2007); 6)social presence- how students and teachers socially interact in online courses where asynchronous computer-mediated communication (CMC) is the major form of discourse; 7) teaching presence- the tool has an easy-to-use features that enhance more the instructors ability of teaching through online and can monitor learners’ performance (Antsey and Gavan, 2018); 8) cognitive presence- the tool enhances engagement in targeted cognitive task(s) that were once overly complex through other means and to exercise higher order thinking skills (Antsey and Gavan, 2018). VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION There are five researches that was found relevant in this study, some of it were done before the pandemic occurs. The first paper found is by Rosa Lanzilotti, Maria Francesca and Carmelo Ardito of University of Bari entitled “Systematic Evaluation of e-Learning Systems (2020)”. An Experimental Research focused on evaluating the eLearning systems by combining specific inspection with user testing. The inspector aims to have wide experience in using the e-Learning system and to perform accurate evaluations to confirm the efficiency of the systems. We also used the “Effects of eLearning on Students Academic Learning at University Level (2018)” by Imran Latif Saifi of The Islamia University of Bahawalpur Pakistan, conducted this research to find out the effects of e-learning on students interest and learning at the University level. This article is connected to this study since we are analyzing the efficiency of the BPC eLearning system on the cognitive, metacognitive, and emotional aspects of the students. In their study, they found that e-Learning is the dominant method in today's period for education, particularly for education programs, and that it inspires students to accomplish their job without the assistance of others. The study entitled “Automated e-Learning Quality Evaluation (2015)” by Rositsa Doneva and Silvia Gaftandzhieva of Plovdiv University Paisii Hilendarski was also used. It is an Experimental Research focused on evaluating the quality of e-Learnings for any up-to-date higher educational institutions. The paper is devoted on automation of related processes based on a modern technology approach of integration of heterogeneous systems. We also found the study of Zuhal Yonca Odabas, Huseyin Odabas and Aytul Kasapoglu of Ankara University Turkey entitled “E-Learning Programs: The Case of VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Ankara University Turkey (2013)” that is also relevant in our paper. It is an Evaluation Research focused on evaluating the e-Learning program and its human relations as a tool for creating a learning society. While the study of Edwidge Simon “The Impact of Online Teaching on Higher Education Faculty’s Professional Identity and the Role of Technology: The Coming of Age of the Virtual Teacher (2012)”, This related to our study on assessing the e-learning system to learn about its impacts on BPC faculty members, whereas Simon's (2012) article seeks to investigate how online education affects both instructors and the teaching profession in higher education. He studied the influence of online teaching on the professional identities of nineteen educators who had made the switch to online classes. He also addressed the impact that technology had in this process. Existing research indicates that creating a firm pedagogical persona is an important factor in teacher retention (Danielewizc, 2001) and an important contributor to classroom performance and effectiveness (Alsup, 2005; Day et al., 2006). He believes that a consistent teaching persona is just as crucial for educators. The paradigm developed in this study. Input Output Process Journals Articles Websites Semi-structured interview to the developer, administration, and teachers of Bulacan Polytechnic College Sorting of information from the gathered information through internet surfing Analyses of gathered data from interviews and questionnaires answered by the faculty members and students. Challenges identified and suggested solutions Proposed suggestions / recommendations to further enhance the elearning systems of the College Figure 1: The Conceptual Framework of the Study VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION The input-process-output model was adopted when this study was conceived as shown in Figure 1. In Frame 1 the input was the articles, journals, websites, and semi-structured interview to the developer, administration, and teachers that helps the researchers to sort and collect data. In Frame 2 the process was sorting of the details and research gathered from surfing, analyzing the gathered data from the questionnaires and interviews. While in Frame 3 the output that was gathered out of the data such as the challenges faced and coped up by the students, management, and faculty members. The proposed or recommendations for enhancement of the e-Learning system/ softwar The following are the assumptions of the study. 1. The e-Learning system of BPC will be convenient and reliable in terms of its functionality, accessibility, technical aspect, mobile design, and duration of privacy data protection and rights. 2. The e-Learning system of BPC will be an effective pedagogical tool to be used by the faculty and students in terms of social presence, teaching presence, and cognitive presence. The following terms are defined conceptually. Accessibility. The extent to which a commodity, gadget, service, or environment is accessible to the greatest number of individuals feasible. Defined as the "ability to get access to" (Disabled World- Website). VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Active learning. It consists of brief course-related individual or small-group exercises assigned to all students in a class during provided with fresh material (Felder and Brent, 2009). Affective Aspect. Elements of mental processes or behavior that are driven to action or change, such as impulse, desire, volition, and striving (yourdictionary.com). Cognitive Aspect. The incorporation and use of students' motives and methods over the course of their learning. (1987, J. B. Biggs').J. B. Biggs's, 1987). Cognitive Presence. The amount to which students can build and reinforce meaning via prolonged contemplation and conversation (Garrison, Anderson, & Archer, 2001). Conceptualization. The abstract, idealized perspective of a particular section of the world, comprising the objects, concepts, and other things considered to be of interest for some specific purpose, as well as the links between them. (artsandculture.com). Cooperation among students. Like excellent work, good learning is collaborative and sociable, rather than competitive and solitary. Collaborating with others frequently enhances participation in schooling. Discussing one's thoughts and responding to the reactions of others enhances thinking and increases knowledge (Chikering and Gamson, 1996). Content. The instructions are the information and experiences directed at an enduser or audience. "Content" is defined as "anything expressed by some media, such as speech, writing, or any of the many arts" (Cambridge English Dictionary). VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION E-learning. The delivery of learning and training through digital resources. Although eLearning is from formalized education, electronic devices such as computers, tablets, and even cellular phones connect to the internet. Format. An arrangement or plan for something written, printed, or recorded (Burns, 2011). Functionality. The ability to perform a task or function; that set of tasks that something is able or equipped to perform (Lumenlearning.com). High expectations. It refers to any attempt to ensure that all learners in a class, school, or education system are held to the same high educational standards (The Glossary of Education). Learning Material. Material for Learning. Any gathering of things, including animate and inanimate items, as well as human and non-human resources, that an instructor may utilize in classroom instruction contexts to aid in the achievement of desired learning outcomes (coursehero.com) Mechanics of the program. It is the motion or organization that follows by the software that runs on a computer, laptops, mobile phones, etc. (eduglobal.org). Metacognitive Aspect. It entails having a greater understanding of a) one's own thinking and learning, as well as b) oneself as a thinker and learner (Chick, 2013). Mobile Design. The design of user experiences for hand-held and wearable devices (interaction-design.org). Operation. It is the execution of practical work or something relating to the application of concepts or processes in practice (Merriam-Webster dictionary). VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Portal Development. A web portal is a fixed point of entry to various types of information. It can contain links to large amounts of data, such as articles, individuals, and so on. It frequently includes a membership aspect in which users check in and have access to their profiles (eduglobal.org). Privacy Data. A subset of data security related with data handling – permission, notice, and regulatory responsibilities (Peters, 2020). Prompt feedback. Must be performed or executed without delay (Bangert, 2004). Protection and Rights. It refers to the law structure that protects individuals' privacy. Any citizen has the right to manage and choose on their private details, which is referred to as privacy (to disclose information or not). The privacy rights is a basic human right (gilc.org) Quality. Refers to an evaluation of how good one thing is in contrast to other comparable things. To put it another way, its level of perfection. (Merriam-Webster dictionary). Social Presence. A term can take on vastly different meanings depending on the field of study. (Lowenthal, 2010). Software. Software is a collection of instructions and data that tell the computer how to work. In contrast to physical hardware, the system is built and performs the work. Software Product Evaluation. Regarding it being an instrument, it will support such control—the assessment of software product characteristics according to specified procedures (ISO14598, 1996). VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Student-faculty contact. Student traits such as sharing faculty interests and ambitions and seeking faculty mentoring were significant predictors of the frequency and quality of student interaction with professors (Pascarella, 1980). Teaching Presence. The organization of the learning experience occurs before the course start and throughout the course's run (Bruff, 2020). Technical. Relating to or produced by normal commercial processes without being subjected to remarkable purification (Merriam-Webster dictionary). Time on task. The proportion of instructional time spent by learners directly linked to learning activities (Crowley, 2008). Methodology The research methods used in the study are the qualitative research method and evaluation research since it intends to evaluate and measure the quality of the BPC eLearning system developed by the institution in terms of its development, feasibility, and effectiveness. The qualitative approach would be a good fit in this study since it aims to understand how effective the system was and what other parts can be enhanced or develop more. This study includes questionnaires and semi-structured interviews that will broaden the different challenges, weaknesses, and strengths that the system has. The sample taken from the population for this research is the students from degree courses and technical courses offered by school and class presidents of Senior High School (SHS) from BPC-Malolos. At the same time, some faculty members came from the eight (8) campuses of BPC who are conducting online classes. Thus, in this study, the accessible VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION respondents comprised 262 students, 24 faculty members, and four parents. Random sampling were used in collecting the respondents. The study used several instruments to gather relevant, valid, and reliable data to answer the survey's specific questions. 1. Interview Questions for Ms. Victoria Beth M. Sison, MAed- VPAA/ OIC College President, Ph. D Student. The researchers developed questions specifically for this study to have a broader knowledge of how the administrators created, planned, and implemented the system, the factors they have considered, and how they perceived or what their views of the program are so far. It contains ten questions that address the planning, conceptualization, and considerations they have done to pursue this program. 2. Interview Questions for Dr. Rosemarie S. Guirre The instrument answered by Dr. Guirre, specifically developed for this research, responds to how the program was designed, conceptualized its mechanics, and its significant components in evaluating the Online Technology Program of BPC accurately and efficiently 3. Questionnaire for Faculty Members towards the Development of BPC’s e- Learning System The instruments answered by the administrators and developers follow the assessment tool by Cecilia Mercado (2008), aiming to identify the potential aspects as a guide to achieve the online program's goal and know where it should invest. VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION 4. Instrument to Evaluate the Software Development of e-Learning The instrument used in this study adapts the Software Product Evaluation Survey “Software Evaluation” developed by Claire Bradin (1999), who offers a comprehensive look at evaluating software and important aspects of the software to consider when choosing the program for a particular setting. She divides the process of software evaluation into two parts. The first part is exploring the feasibility, and the second part is determining quality. 5. Instrument to evaluate the BPC e-Learning System The study used a multidimensional Likert scale instrument to evaluate BPC elearning system based on the “Rubric for evaluating e-Learning tools in Higher Education” developed in 2018 by Lauren Anstey. An e-Learning and Curriculum Specialist at Western University residing in London, ON, Canada and Gavan Watson the Associate Vice President, Teaching and Learning of the Memorial University of Newfound Land at Labrador, Canada. The instrument was developed by non-tech specialists and used in a variety of learning situations to help attract their attention to the goal of evaluating online programs to aid in the predictive evaluation of e-Learning tools 6. An instrument to perceive the effectiveness of the faculty in online teaching using the e-Learning system The basis of the instrument to measure the Online Teaching Effectiveness is on "The Student Evaluation of Online Effectiveness" developed by Arthur W. Bangert (2004) from Montana University. The wordings are explicit about eliciting responses about the quality of teaching within the context of online learning environments to assess each of the VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION constructivist-compatible learning practices recommended by the Seven Principles of Effective Teaching. 7. An instrument to perceive the Effectiveness of the e-Learning System to Students An instrument to assess the success of online learning in terms of cognitive, metacognitive, and affective outcomes for students, in general, is adapted from the instrument of J. B. Biggs et al. (1999). It is to assess students' cognitive and metacognitive abilities during online classes, and for the Affective aspect by Kristen A. Walker and Katherine E. Morales (2018). Recall or acknowledgment of knowledge and the improvement of intellectual abilities and skills are examples of cognitive skills. Individual desires, attitudes, and values are classified as affective skills. Finally, meta-cognition is the understanding of one's self and one's cognition of thinking about thinking. 8. Faculty self-assessment to their technical, administrative, and pedagogical competencies using the LMS tool of the BPC e-Learning The study used a Likert-type self-assessment based on "Penn State Faculty Competencies for Online Teaching (2011)” developed by Penn State University to measure teachers' technical, administrative, and pedagogical competencies. The instrument aims to know the competencies and readiness of the instructors and assumes that He has professional experience, as evidenced by questions concerning familiarity with LMS features and online teaching, for instances. Nonetheless, it emphasizes the skills and standards necessary for teachers new to online education. VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION 9. Self-Assessment of Students towards their experiences in using BPC e-Learning The instrument to assess students' experiences during the online technology program follows the Self-Assessment instrument of an e-Learning tool for Philippine Higher Education Institution developed by Ann D. Doculan (2014) of Ifugao State University. 10. Interview Questions for Teachers on how they are handling the challenges in Online Teaching using the e-Learning systems This instrument specifically develops to acknowledge the challenges faced/ experienced by the teachers and how they are handling them, or what solutions they have in mind. It has ten questions focused on extracting the program's possible weaknesses and strengths to adequately address the possible solution we may develop based on the data 11. Questionnaire for parents towards their feedback on the online class of their child This instrument for parent’s e-learning survey developed by Universal American School (UAS) Dubai (2020) aims to know the feedback of parents on the online classes of their child and what challenges they think their child encounters. The data were gathered through the use of different valid and reliable tools that was encoded to Google forms for easy access for the possible respondents. The gathered data then were statistically analyzed using descriptive statistics. VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Result and Discussion Based on the data collation and statistical analysis, the study had the following salient findings. 1. The institution developed the BPC e-learning to cope with the current situation and composed three (3) significant components; info sheets, assessments, and video conferencing. The management also forms a Learning Management Committee comprised of developers, subject area coordinators, proofreaders and uploaders, and non-teaching staff responsible for the system's mechanics. Figure 2: The Personnel involved in the BPC e-Learning’s Mechanics of the System 2. In terms of ICT infrastructure, administrative, and resource support, the management and developer were “supportive” and “successfully” executed the software/ system across their eight (8) campuses. Table II Descriptive Measures of the Portal Development Evaluation Category 1. ICT infrastructure 2. Administrative Support 3. Resource Support Mean 3.65 4.52 4.17 Verbal Interpretation Sufficient Supportive Supportive VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A Standard Deviation 0.2 0.17 0.31 Verbal Interpretation Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION 3. The software and feasibility study of BPC e-Learning were found "reliable" and "feasible" and can use it to aid virtual education during the pandemic. Furthermore, its quality in terms of format was “effective” to the users, its operation was "intelligible," which means that it was easy to comprehend, and the purpose of the software “fulfilled" its content. Table III Descriptive Measures of the Evaluation of the Respondents on the Developed BPC e- Learning Software Category 1. Software Product Evaluation 2. Feasibility 3. Quality 3.1 Format 3.2 Operation 3.3 Content 4. Mean 4.00 4.34 Verbal Interpretation Reliable Feasible Standard Deviation 0.10 0.10 Verbal Interpretation Homogenous Homogenous 4.10 4.03 4.12 Effective Intelligible Fulfilled 0.06 0.08 0.06 Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous On the aspect of functionality, e-learning was "functional" and easy to use. In a part of accessibility, the result shows that it was “accessible" and user-focused. The technical aspect was “efficient” while the mobile design resulted as "functional" and "accessible." The study also shows that the users of e-Learning account were "protected" in terms of privacy data, protection, and rights. It was "efficient" as it lets the faculty members facilitate and monitor their students in teaching presence. While in terms of the cognitive presence, it is "efficient" and promotes Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS). It also supports social presence, which means that the software was "collaborative." VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Table IV Descriptive Measures of the Evaluation of the Developed BPC e- Learning System Category 1. Functionality 2. Accessibility 3. Technical Aspect 4. Mobile Design 5. Privacy data, protection, and rights 6. Social Presence 7. Teaching Presence (teachers only) 8. Cognitive Presence (students only) 5. Mean 4.05 4.03 4.04 3.94 4.14 4.14 4.52 4.05 Verbal Interpretation Functional Accessible Efficient Functional Protected Efficient Efficient Collaborative Standard Deviation 0.05 0.01 0.05 0.25 0.05 0.07 .06 .04 Verbal Interpretation Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous The effectiveness of the BPC e-Learning when used by the faculty as perceived by the student resulted as "effective" because there is still a student-faculty contact in the class, cooperation among students, and active participation learning. It also shows that when the students have some queries, the teachers give prompt feedback. While in regards to time on task, the e-Learning was user-friendly and let the students finish their assignment by the allotted time set by the teachers. In addition, they are giving examples through video conferencing and info sheets in terms of high expectations. After that, the assessments and assignments will be open right after the class and answered during the asynchronous time. According to the results, even virtual class teachers still respect students' diverse talents and learning ways. Table V Descriptive Measures of the Effectiveness of the BPC e-Learning System when used by the faculty as Perceived by the Students Category 1. Student-faculty Contact 2. Cooperation Among Students 3. Active Participation Learning Mean 4.05 4.03 4.04 Verbal Interpretation Functional Accessible Efficient VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A Standard Deviation 0.05 0.01 0.05 Verbal Interpretation Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION 4. Prompt Feedback 5. Time on Task 6. High Expectations 7. Diverse talents and learning ways 6. 3.94 4.14 4.14 4.52 Functional Protected Efficient Efficient 0.25 0.05 0.07 .06 Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous The faculty perceived the effectiveness of the e-learning found "effective" in each aspect and conducted education even during pandemic through virtual classes. The teaching and learning process using the BPC e-learning tool was still able to reach students' cognitive, metacognitive, and affective domains. Table VI Descriptive Measures of the Effectiveness of the BPC e-Learning System when used by the students as Perceived by the Faculty. Category 1. Cognitive Aspect 2. Metacognitive Aspect 3. Affective 7. Verbal Interpretation Mean 4.24 4.21 4.21 Effective Effective Effective Standard Deviation 0.17 0.10 0.11 Verbal Interpretation Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Regarding the self-assessment of faculty members in using the LMS of the BPC, the study shows that they are “competent” and can navigate to the dashboards/ course space of BPC in terms of technical, administrative, and pedagogical competencies. Table VII Descriptive Measures of the Faculty Self-assessment on their Technical, Administrative, and Pedagogical Competencies using the LMS tool of the BPC e-Learning Category 1. Technical Competencies 2. Administrative Competencies 3. Pedagogical Competencies Mean 4.55 4.52 4.47 Verbal Interpretation Very Competent Competent Competent VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A Standard Deviation 0.17 0.10 0.11 Verbal Interpretation Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION 8. The self-assessment of students towards their experiences while using the BPC e- learning and during online class resulted as "effective." The students can execute their online internet skills in virtual class or while completing an assignment/task and utilize their software application skills while using the software of e-learning. They also comprehend its content (learning materials) and can still receive social support from the faculty and technical team of the software/system. Their study habits, abilities, and time management became effective since they have more time in their hands. It also shows that the software and virtual classes still effective in terms of motivation and usefulness as they served their purpose accordingly. Table VIII Descriptive Measures of the Self-assessment of Students towards their Experiences in using BPC e-Learning Category 1. Online Internet Skills 2. Software Application Skills 3. Content 4. Social Support 5. Study Habits 6. Abilities 7. Motivation 8. Time Management 9. Usefulness 9. Mean 4.20 4.11 4.13 4.10 3.96 4.11 4.05 3.94 4.03 Verbal Interpretation Effective Effective Effective Effective Effective Effective Effective Effective Effective Standard Deviation 0.10 0.04 0.03 0.09 0.08 0.07 0.06 0.13 0.07 Verbal Interpretation Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous Homogenous We found out that most of the challenges faced by the students and faculty members focused on the technical aspects of the system. However, one of the challenges encountered included the challenges related to their fulfillment and motivation, as mentioned by the faculty. VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Conclusion 1. The BPC e-Learning is convenient, reliable, and effective tool in terms of quality, functionality, accessibility, technical aspect, mobile design, privacy data protection, and rights in the teaching and learning process in virtual education. 2. It is also concluded that e-learning was effective as a pedagogical tool in terms of social presence, teaching presence, and cognitive presence for both the students and faculty. Recommendation Since only one of the major components was evaluated in this study (e-learning), future researchers should consider the evaluation of the other five components of the BPC Portal, viz-a-viz, admission, entrance examination, enrollment, grading, and scholarship systems to further enhance the learning management system of the institution. VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION BIBLIOGRAPHY ARTICLES Anstey, L., Watson, G., “A Rubric for Evaluating E-Learning Tools in Higher Education” EDUCAUSE, September 2018 Baldominos, A., Marquez, N., Nieto, M. “Digital Teaching Materials and Their Relationship with the Metacognitive Skills of Students in Primary Education” Technology Enhanced Education, April 2020 Downes, Stephen “E-learning 2.0” E-learn Magazine, Volume 2005, Issue 10, October 2015 Pappas, Christopher “Enhancing Metacognition in eLearning: What eLearning Professionals Should Know” e-Learning Industry, June 2015 CONFERENCE PAPER Ardito, C., Francesca, M., Lanzilotti, R. “Systematic Evaluation of e-Learning Systems” Proceedings of the 4th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Oslo, Norway, October 2020 Doneva, R., Gaftandzhieva, S., “Automated e-Learning Quality Evaluation” International Conference on e-Learning, Quality Evaluation, Berlin, September 2015 Kasapoglu, A., Odabas, H., Odabas, Z.Y. “e-Learning Programs: The Case of Ankara University Turkey” 3rd World Conference on Learning, Teaching and Educational Leadership, Turkey, 2013 JOURNALS Ahmad, G., Bakht, M.I., Saifi, I.L. “Effects of e–Learning on Students’ Academic Learning at University Level” Asian Innovative Journal of Social Sciences & Humanities (AIJSSH) - April 2018 Alrowwad, A., AL-Lozi, M., Kattoua, T. “A Review of Literature on E-Learning Systems in Higher Education” International Journal of Business Management and Economic Research (IJBMER), Vol 7(5), January 2016 Bangert, W.A. “The Development of an Instrument for Assessing Online Teaching Effectiveness” Journal of Educational Computing Research, 2006 VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan BACHELOR OF TECHNICAL-VOCATIONAL TEACHER EDUCATION Doculan, Jo Ann, D. “e-Learning Readiness Assessment Tool for Philippine Higher Education Institutions” International Journal on Integrating Technology in Education (IJITE) Vol.5, No.2, June 2016 Nguyen, Tuan “The Effectiveness of Online Learning: Beyond No Significant Difference and Future Horizons” MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching Vol. 11, No. 2, June 2015 Kim, H.S., Oh, E.G. “Understanding Cognitive Engagement in Online Discussion: Use of a Scaffolded, Audio-based Argumentation Activity” International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning- Volume 17, September 2016 Simon, Edwidge “The Impact of Online Teaching on Higher Education Faculty’s Professional Identity and the Role of Technology: The Coming of Age of the Virtual Teacher” ProQuest LCC, 2012 VIRTUAL EDUCATION, A BIG CHALLENGE: AN EVALUATION OF THE e-LEARNING SYSTEM OF THE BULACAN POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE MANALO, JHOLIENA LYNN, C., RUEME, JOSEPH CHRISTIAN, R. MALLARI, VANDOLF, A. and ROBLES, RANDY, A