Kami Export - Cambron Calbert - Honors Bio Chapter 37 vocab.docx
advertisement

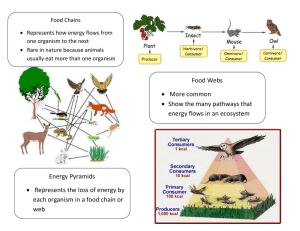
Honors Bio Chapter 37 Vocab Word Community Species diversity Definition/description a group of people living in the same place or having a particular characteristic in common. the number and relative abundance of species found in a given biological organisation Trophic structure the partitioning of biomass between trophic levels Competition the direct or indirect interaction of organisms that leads to a change in fitness when the organisms share the same resource. Competitive exclusion principle the exclusion of one of the species when the realized niche of the superior competitor encompasses the fundamental niche of the inferior competitor Niche the role an organism plays in a community Resource partitioning the division of limited resources by species to help avoid competition in an ecological niche Predation one organism kills and consumes another Predator an organism that consumes all or part of the body of another—living or recently killed—organism, which is its prey. " Prey Batesian mimicry mullerian mimicry organisms that predators kill for food a form of biological resemblance in which a noxious, or dangerous, organism (the model), equipped with a warning system such as conspicuous coloration, is mimicked by a harmless organism a form of biological resemblance in which two or more unrelated noxious, or dangerous, organisms exhibit closely similar warning systems, such as the same pattern of bright colours. Keystone species an organism that helps define an entire ecosystem Herbivores Coevolution an organism that feeds mostly on plants the process of reciprocal evolutionary change that occurs between pairs of species or among groups of species as they interact with one another Symbiotic relationship a close ecological relationship between the individuals of two (or more) different species Parasitism one organism, the parasite, lives off of another organism, the host, harming it and possibly causing death Pathogens 1. a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease. Commensalism an association between two organisms in which one benefits and the other derives neither benefit nor harm. Mutualism symbiosis that is beneficial to both organisms involved. Disturbances Ecological succession Primary succession Secondary succession Food chain the interruption of a settled and peaceful condition. limit the growth, abundance, or distribution of an organism or a population of organisms in an ecosystem ecological succession that begins in essentially lifeless areas, type of ecological succession (the evolution of a biological community's ecological structure) in which plants and animals recolonize a habitat after a major disturbance the sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food Producers from organism to organism organisms that produce energy Primary consumers eat producers Secondary consumers eat primary consumers Tertiary consumers Quaternary consumers a carnivore at the topmost level in a food chain that feeds on other carnivores; often top predators within the environment, and they eat the tertiary consumers Detritivores/decomposers break up other consumers for nutrients Detritus Decomposition Food web Ecosystem waste or debris of any kind. the break up of an organism how a ecosysem reacts to each other animals in a certain area Energy flow how the energy flows through an ecosystem Chemical cycling systems of repeated circulation of chemicals between other compounds, states and materials, and back to their original state Biomass renewable organic material that comes from plants and animals. Primary production Biogeochemical cycles Abiotic reservoir