Bond Valuation: Risks, Present Value, and Interest Rates
advertisement
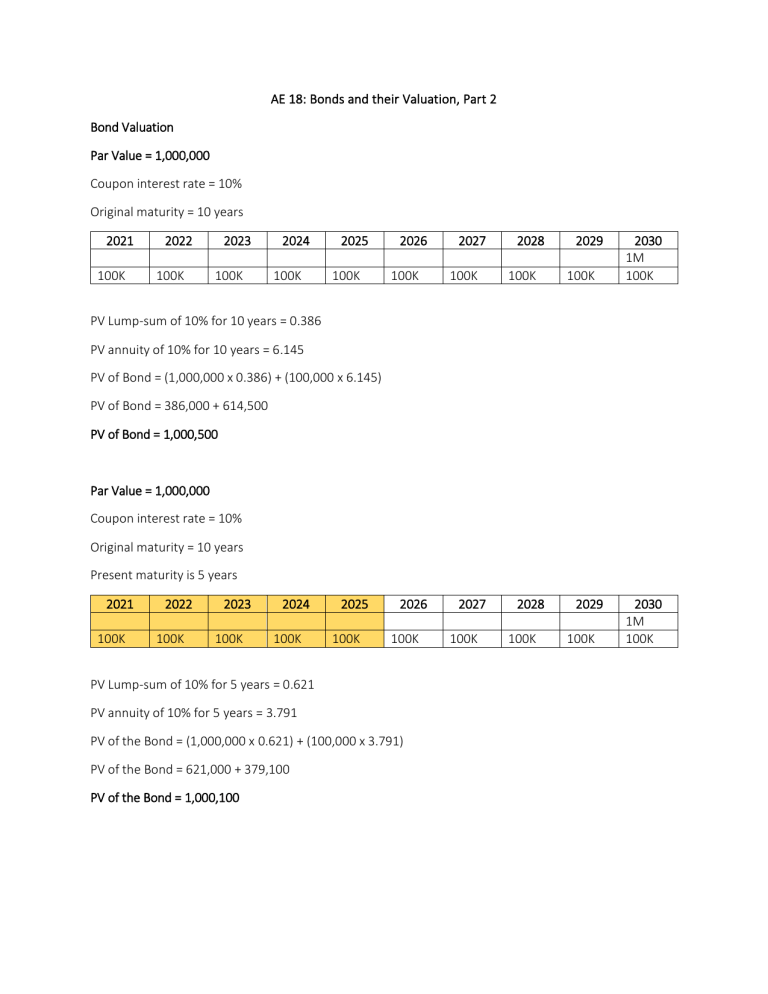
AE 18: Bonds and their Valuation, Part 2 Bond Valuation Par Value = 1,000,000 Coupon interest rate = 10% Original maturity = 10 years 2021 100K 2022 100K 2023 100K 2024 100K 2025 100K 2026 100K 2027 100K 2028 100K 2029 100K 2030 1M 100K PV Lump-sum of 10% for 10 years = 0.386 PV annuity of 10% for 10 years = 6.145 PV of Bond = (1,000,000 x 0.386) + (100,000 x 6.145) PV of Bond = 386,000 + 614,500 PV of Bond = 1,000,500 Par Value = 1,000,000 Coupon interest rate = 10% Original maturity = 10 years Present maturity is 5 years 2021 100K 2022 100K 2023 100K 2024 100K 2025 100K 2026 100K PV Lump-sum of 10% for 5 years = 0.621 PV annuity of 10% for 5 years = 3.791 PV of the Bond = (1,000,000 x 0.621) + (100,000 x 3.791) PV of the Bond = 621,000 + 379,100 PV of the Bond = 1,000,100 2027 100K 2028 100K 2029 100K 2030 1M 100K Par Value = 1,000,000 Coupon interest rate = 10% Market interest = 12% Original maturity = 10 years Present maturity – 5 years 2021 100K 2022 100K 2023 100K 2024 100K 2025 100K 2026 100K 2027 100K 2028 100K 2029 100K 2030 1M 100K PV Lump-sum of 12% for 5 years = 0.567 PV annuity of 12% for 5 years = 3.605 PV of the Bond = (0.567 x 1,000,000) + (3.605 x 100,000) PV of the Bond = 567,000 + 360,500 PV of the Bond = 927,500 1,000,000 (927,500) 72,500 Market Interest > Coupon Interest, bonds will sell at a lower price, price difference is the discount. Par Value = 1,000,000 Coupon interest rate = 10% Market interest = 8% Original maturity = 10 years Present Maturity = 5 years 2021 100K 2022 100K 2023 100K 2024 100K 2025 100K 2026 100K PV Lump-sum of 8% for 5 years = 0.681 PV annuity of 8% for 5 years = 3.993 PV of the Bond = (1,000,000 x 0.681) + (100,000 x 3.993) 2027 100K 2028 100K 2029 100K 2030 1M 100K PV of the Bond = 681,000 + 399,300 PV of the Bond = 1,080,300 1,080,300 (1,000,000) 80,300 Market Interest < Coupon Interest, bonds will sell at a higher price, price difference is the premium. Bond Risks Price Risk the risk of a decline in a bond’s price due to an increase in interest rates higher for bonds with longer maturities relates to current market value of bond portfolio Reinvestment Risk the risk that a decline in interest rates will lead to a decline in income from a bond portfolio higher for bonds with shorter maturities relates to the income the bond portfolio produces Investment Horizon – the period of time on investor plans to hold a particular investment Default Risk the risk that investors will receive less than the promised return Bankruptcy and Reorganization When a business becomes insolvent, a company can: o o 100, 15, 15% 150, 15, 10% Liquidate – sell its assets and pay its obligations Reorganization – negotiation between the creditors and the management Restructuring – reduce financial charges to level projected cash flows reducing interest rates of debt lengthening the term of maturity convert debt to equity – diluting position of common stockholders