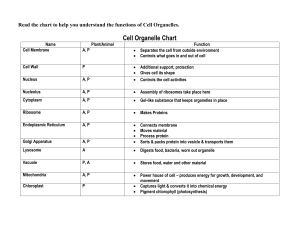
MYP 4 UNIT 1 Activity: Make A Cell-fie! You have heard previously that there are differences in cell structures, reproductive ways, build of the skeleton, autotroph/heterotroph between the different domains and kingdoms of life on earth. With this activity you will look further into these differences on the cellular organization level. There is a part A, part B and an extension when you have time left. At the end of this activity you have: - A poster from a cell with all the organelles. A legend with the names of the organelles and their function. An understanding of the differences in cell structures between an animal cell, plant cell, fungal cell, protist cell and bacterial cell. Approaches to learning: - Information literacy skills: Access information to be informed and inform others. Critical-thinking skills: Gather and organize relevant information. Critical-thinking skills: Analyze complex concepts and synthesize them to create new understandings. Assessment opportunities: In this activity you have practiced skills that are assessed using - Criterion A: Knowing and understanding Criterion C: Present data in visual forms 1 A) Differences between different kingdoms (and domain) of cell structures As mentioned there are difference between the cells from different eukaryotic kingdoms and they also differ from the prokaryotic domain of bacteria. Down below different cell structures are mentioned. In this activity you will investigate which structures the cells of the different kingdoms/domains of life have and what they are made of. Write down either Yes, No or Yes/No if both answers are possible. Contains? (Yes/No) Animal Plant Fungi Protist Bacteria Nucleus Cell wall Consists of: Cell membrane Chloroplasts Vacuole 2 B) Make A Cell-fie! You have completed some research into the differences in cell structure between different eukaryotic kingdoms and the prokaryotic domain bacteria. There are more cell structures (organelles) inside a cell than shown in the table above. In this activity you will make a poster from a complete plant cell with all its organelles/structures and look up their function. 1. Grab a sheet of A3 paper. 2. Cut out the cell membrane (page 4) and glue this somewhere on (a bit from) the edge of your paper sheet. Continue the cell membrane by drawing onto the paper into the shape of a cell. Make it big, because you will put all the other structures inside the cell. 3. Google multiple pictures of cells and look for the most common places for all the different cell structures down below. If you have determined the most common place for every cell structure, cut them out from page 4 and 5 and glue them on your poster in the right spot. 4. Number the cell structures 1 to 9. 5. This is a plant cell, so which cell structure is missing? Draw this on your poster. Number this structure number 10. 6. Write (or cut out and glue down) the right name of each cell structure in the table on page 6 behind the correct number. 7. Write the function of each cell structure behind the right name in the table on page 6. You can use your biology book (chapter 1) and the internet. 8. Encircle the numbers of the cell structures in the table you could see with the light microscope. (Max magnification = 400x) Compare the encircled numbers with the structures in the table from part A. What do you notice? Extension: - Which organelle provides the ability to organisms to produce their own food from the substances available in their surroundings and thus be autotroph? - What is the process of producing its own food in this organelle called? - What substances does this organelle need and what does it produce with these? - Which different types of autotroph organisms exist that do not use this organelle? How do they produce their own food and with what substances? 3 Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Golgi apparatus Nucleus with DNA Mitochondrion Cell membrane Cytoskeleton 4 Bevat ribosomen Lysosoom Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) Chloroplast Vacuole 5 Name of cell structure Description of function 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 6 7