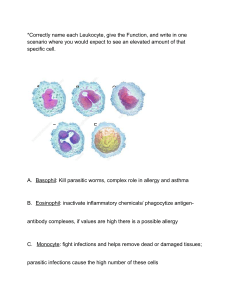
Antibiotics that Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis and Integrity Medication Name: Antibiotics Action Aztreonam Indication Administration Monobactams Weaken and destroy bacteria cell wall Cephalexin Treat infections by gram-negative aerobic bacteria Lower respiratory infection Urinary tract infections Abdominal and gynecologic infections IM, IV, and Inhalation Cephalosporins Weaken and destroy bacteria cell wall First generation that treat gram-positive bacteria cocci Amoxicillin Only capsules, tablets, or oral suspension Contraindication Hypersensitivity Allergy to cephalosporins antibiotics Allergy to penicillin (cross-sensitivity) Carnitine deficiency or milk protein allergy Alcohol can cause disulfiram-like reaction: cefotetan only Penicillin Weaken and destroy bacteria cell wall Treats gram-positive cocci and bacilli Ear and throat infections and UTI Treats gonorrhea caused by non-penicillinase-producing bacteria Adding clavulanic acid increases the spectrum of disorders treated by amoxicillin and its ability to kill bacteria Do NOT crush or chew extended-release form Chew chewable forms before swallowing Infants and children: place drop directly on tongue or mix with juice or formula Give at beginning of meals Give with probenecid Allergy to penicillin, hypersensitivity to procaine and benzathine Imipenem Carbapenems Beta-lactam antibodies weaken and destroy bacteria cell wall Treats serious infections caused by multiple organisms Only IM or IV Dilute when infusing IV doses Vancocin Allergy to carbapenems and penicillin Vancomycin Weaken and destroy bacteria cell wall Effective against grampositive bacteria Treats MRSA and C-Diff Orally for C-Diff infections IV for all other infections Administer slowly IV and dilute Infuse separately, incompatible in solution with many other IV drugs Allergy to vancomycin Hypersensitivity Education Laboratory Report pain, redness, swelling, at IV site Take with food Report watery or bloody diarrhea Stop drug for possible allergies Call 911 if difficulty breathing/severe symptoms Report unusual bruising or bleeding Report burning, pain, or swelling at IV site during infusion Nausea, vomiting, severe headache, and hypotension with combination of drug and alcohol May cause increase serum AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, LDH, BUN, creatinine. May cause positive results for Coombs’ test in patients receiving high doses or in neonates whose mothers were given cephalosporins before delivery. May rarely cause leukopenia, neutropenia, agranu- locytosis, thrombocytopenia, or eosinophilia. Report watery or bloody diarrhea Take drug at the start of meals Report mouth pain or inability to eat Report vaginal burning, itching, and discharge Stop drug for allergic reactions Call 911 for severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing Report nausea Report pain, swelling, or redness at IV site Report drug allergies Report mouth pain and difficulty chewing or swallowing Report vaginal irritation and discharge Report flushing or faintness feeling Report tinnitus or perceived hearing loss Report increase or decrease of urine output Report pain, swelling, and redness at IV site Report vertigo Antibiotics that Inhibit Protein Synthesis Medication Name: Antibiotics Action Indication Erythromycin Administration Macrolides Contraindication Education Laboratory Gentamicin Inhibits protein synthesis First Line of treatment for: Legionnaire’s disease, whooping cough, acute diphtheria, some chlamydia infections, certain pneumonias Treats common infections for client who have a penicillin allergy Ophthalmic ointment prevents eye infectious in neonates Erythromycin Base: tablets, capsules, topical, and ophthalmic ointment Erythromycin stearate: tablets Erythromycin ethylsuccinate (EES): tablets Erythromycin lactobionate: IV form Give base and stearate on an empty stomach 1hr before meal or 2hr after meal for best absorption; give with 8oz water Give with food if GI symptoms occur Give EES with or without meals For IV, make sure to dilute Allergy to erythromycin or another macrolide antibiotic History of prolonged QT syndrome Hypokalemia Hypomagnesemia Take with food Report continuing symptoms Report palpitations and fainting spells Report hearing loss, vertigo, and tinnitus Report watery or bloody diarrhea Report mouth pain with white patches on the oral mucosa, or vaginal discomfort and discharge Aminoglycosides Inhibits protein synthesis Gram-negative aerobic bacilli severe infection and severe infection that gram-positive cocci cause Topical form for skin and eye infection Topical, ophthalmic, IM, IV, and intrathecal forms Topical: Don’t apply to large skin areas and there is a risk for toxicity with systemic absorption Allergy to any aminoglycoside Pregnancy risk- teratogenic Report tinnitus onset, headache, vertigo, or hearing loss Perot and increase in dilute urine output Monitor renal function by urinalysis, specific gravity, BUN, creatinine, and CCr before and during therapy. Antibiotics that Inhibit DNA Replication & Cell Division Medication Name: Antibiotics Action Indication Administration Contraindication Education Laboratory Ciprofloxacin Fluroquinolones Inhibit DNA replication and cell division Treat wide range of bacterial infection, including severe urinary tract disorders Prevents anthrax in adults and children Oral and IV IV: infuse slowly for 60 minutes and incompatible with other IV drugs or tubing Allergy to any fluroquinolone Tendon pain Myasthenia gravis Report CNS symptoms Decrease caffeine use Report GI symptoms Report tendon pain Avoid sunlight and sunlamp exposure (wear fully cover clothing and sunscreen) Take antiacids, iron, calcium, dairy products, sucralfate 2hr after or 6hr before oral ciprofloxacin Drink 1.5L to 2L of fluids/day Antibiotics that Inhibit Folic Acid Synthesis Medication Name: Antibiotics Action Indication Administration Contraindication Education Laboratory Trimethoprim & Sulfamethoxazole Sulfonamides Inhibit folic acid synthesis Treat urinary tract infections Pneumocystis pneumonia Shigella enteritis (shigellosis, aka traveler’s diarrhea) Chronic bronchitis Acute otitis media in children Fixed-dose combination in tablets liquid solution in IV form Give oral dose with 8 ounces of water Intermittent IV infusion slowly for 60 to 90 minutes Drink 1.2L- 1.5L of water/day women who are pregnant or nursing Allergy to sulfonamides, trimethoprim, cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors Clients with megaloblastic anemia caused by folic acid deficiency children under 2 months Pharyngitis caused by Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci Hyperkalemia severely impaired urine creatinine clearance report symptoms take with food report rash and hives report fatigue, pallor, easy bruising. or new infections report watery or bloody diarrhea report pain and mouth difficulty eating and vaginal burning/discharge report rash onset or blisters on the skin warn decreasing effectiveness of oral contraceptives Urinary Tract Antiseptic Medication Name: Antibiotics Action Indication Administration Contraindication Education Laboratory Nitrofurantoin Urinary Tracy Antiseptic Treatment and prevention of UTI's Treat urinary tract infections available in oral capsules and liquid suspension capsule should be swallowed as the whole dilute liquid suspension and rinse mouth after taking Allergy to nitrofurantoin impaired kidney function history of jaundice caused by gallbladder disease more than 38 weeks pregnant during labor or delivery, lactating infants less than 1 month take with food or milk report acute or subacute respiratory symptoms: dyspnea, fever, or cough report numbness, tingling, and weakness of the extremities report fatigue, easy bruising, or repeated infections swallow capsules whole dilute liquid suspension rinse mouth after taking suspension