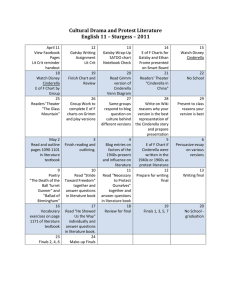
The 8 Elements of Fiction: A General Introduction English Unit Character A textual representation of a human being (or creature) How do we get to know a character? Through… Dialogue Actions Thoughts Narration Example Finding Nemo Why are we so interested in the characters and their problems if they are only aquatic animals and computer graphics? Plot The series of events that give a story its meaning and effect An event is comprised of a conflict and a resolution Foreshadowing (hints of what is to come) often reveals plot Example Disney’s Cinderella What’s the first conflict? Cinderella’s father dies. What’s the resolution? Her step mother becomes her guardian What’s the second conflict? Her step mother and step sisters are mean. What’s the resolution? She befriends mice. Disney’s Cinderella (Cont’d) What’s the third conflict? Cinderella wants to go to the ball. What’s the resolution? Her step mother says that she is allowed to go if she finishes her chores and has a suitable dress. What’s the fourth conflict? Her step sisters ruin her dress, so she can’t go to the ball. What’s the resolution? Her fairy godmother saves the day. Setting A story’s time and place Examples: Hoodwinked, Robin Hood, Bride and Prejudice, E.T., Cops, Lord of the Rings When and where does it take place? Theme The meaning or concept we are left with after reading a story How can you figure out a story’s theme? Ask yourself, “What is the author suggesting is true about human nature and/or life?” Look for: repeated opinions, feelings of the main character, conversations revealing thoughts Example What are some of the themes of The Pirates of the Caribbean? Good will always triumph over evil. Don’t judge a person before you get to know him or her. Love motivates some people to take risks. Point of View Refers to the source of the narrative voice (or person telling the story): 1st person (omniscient), 2nd person, 3rd person It answers the question, “Who is telling the story?” Example: Life is Beautiful The Red Balloon Style Refers to the manner in which an author tells his or her story Examples: Romeo and Juliet v. (Elaborate Language) The Girl Next Door (Simple Language) Literary Devices Devices that writers have used throughout the timeline of literary history. Include… o Symbols and Imagery (use 5 senses!) o Figurative Language: Metaphors, Similes, and Personification TONE vs. MOOD · TONE – The attitude a writer has towards the subject they’re writing about. · Sarcasm? Humor? Anger? Sorrow? Fear? · MOOD – Atmosphere created by the setting, and actions of characters/people in it. It can also refer to how readers emotionally respond to the storyline. ALL DONE And they lived happily ever after… THE END