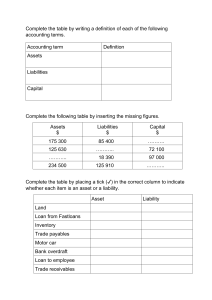
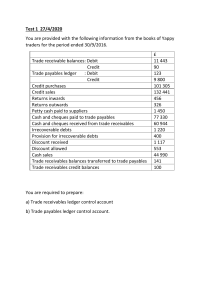
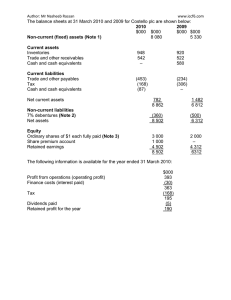
Introduction to Accounting What is Accounting? It is a process. It is an information system. It is a language of businesses. It a cycle. What is Accounting? It is a process. Identification Measurement Recording Summarizing Classifying Communicating Users of Accounting Information Performance Measurement Variables • • • • Liquidity Profitability Solvency Efficiency Need for Accounting Standards • An accounting standard is a common set of principles, standards, and procedures that define the basis of financial accounting policies and practices. • It creates comparable information. • It helps to prepare easily understandable report. IFRSs • International Financial Reporting Standards • Ethiopia issued a financial reporting law on December 5, 2014 which requires the use of IFRS by commercial businesses operating in Ethiopia. Proclamation No. 847/2014 Regulation No. 332/2014 1. 2. Adoption: Complete adherence to the IFRS. (Highly encouraged by IASB) Adaptation: Customizing the standard to specific need of the country. Financial Statements Types of Financial Statements Special Purpose Report General Purpose Report Fundamental qualitative characteristics 1. Relevance : financial information is capable of making a difference in decision making. • predictive value : can be used as an input in the process to predict future outcomes, • confirmatory value : if it provides feedback about previous evaluations. • materiality, entity-specific : if omitting it or misstating it could influence the decisions of users. 9 Fundamental qualitative characteristics 2. Faithful representation • Completeness : all information needed to understand the phenomena. • Neutrality : without bias • free from error : no errors or omissions Enhancing Qualities • Comparability • Verifiability • Timeliness • Understand ability 11 The Accounting Equation Assets They are resources Controlled by the entity as result of past event With expected future benefit Types of Assets 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Cash and cash equivalents Inventories Property, plant and equipments Investment properties Non current asset held for sales Financial Assets Biological Assets Mineral resources Liabilities They are present obligations Arise from past event With expected future out flow of economic benefit Types of Liabilities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Accounts payables Notes payables Salary payables Tax payables Unearned revenues Lease payables Bonds payable Interest payable Equities It is the right of the owners up on the assets of the entity It may be Invested capital Common stock Preferred stock It may be accumulated profit (retained earning) Items that Affect Equity Equity Increase Issued shares Revenue Other incomes Gains Decrease Treasury shares Expenses Losses Withdrawal dividends Case 1 • Indicate whether each of the following items below is an asset, liability, revenue, expense, gain or loss account a) Office furniture b) Income from services c) Salaries paid to workers d) Supplies on hand e) Salary payable to workers f) Cash g) Income from sale of a used truck h) Goods damaged by fire in the store