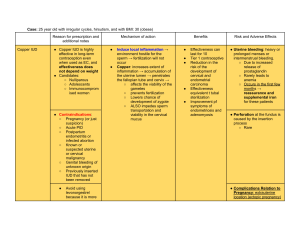
Contraceptive Options Ricci pg. 108 - 130 Method Abstinence Long – Acting Reversible Contraceptive (LARC) Hormonal Contraception How the Method Works No Intercourse AKA Celibacy Most effective reversible method. Provides effective contraception for extended periods of time. Intrauterine Device This is also known as an IUD Typically, a T shaped device inserted into the uterine cavity to prevent pregnancy There is a string attached to the IUD and is visible and palpable at the cervical OS Two Types – Hormonal and Nonhormonal Hormonal release progestin for either 3 years or 5 years The nonhormonal IUD is effective up to 10 years Advantages include: Effectiveness, reduced client error and is reversible Disadvantages include: bleeding, cramps, backache, a slight risk of tubal pregnancy. Slight risk of pelvic infection on insertion, displacement of the device and rarely perforation of the cervix and uterus. Implants A single rod subdermal implant, usually inserted inside the upper arm Good for 3 years Women can experience amenorrhea up to frequent bleeding Lactating women may also use the implant Oral contraceptives block ovarian stimulation by preventing the release of Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH). Without FSH a follicle will not ripen and ovulation does not occur. Progestin is the medication used, in addition to preventing ovulation, Progestin makes the cervix impermeable to sperm. Hormonal contraception comes in many forms: intrauterine, implantable, injectable, oral, transdermal patch or intravaginal ring. Revised by TMB Fall 22 Advantages include: Prevents unintended pregnancy Decreased cramps and bleeding Regular bleeding cycle Decreased incidence of anemia Decreased in acne with some formulations Protection from ovarian and uterine cancer Decreased incidence of ectopic pregnancy Protection from benign breast disease Decreased incidence of pelvic infection Risks include: Rare in healthy women Breakthrough bleeding / breast tenderness Nausea, weight gain and mood changes Small increased risk for developing blood clots, stroke or heart attack – smoking is a huge factor Possible increased incidence of benign liver tumors and gallbladder disorders No protection from Sexually transmitted infections Oral contraceptives = combination A pill that suppresses ovulation by combined action of estrogen and progestin. Pros Easy to use High rate of effectiveness Protection against ovarian and endometrial cancer Cons User must remember to take daily Possible undesirable side effects High cost for some women Prescription needed Patch (Ortho Evra) Transdermal patch that releases estrogen and progestin into circulation Pros Revised by TMB Fall 22 Easy system to remember Very effective Cons May cause skin irritation May fall off without notice Education – instruct woman to apply patch every week for 3 weeks and then not to wear one during week 4 Ring (NuvaRing) Vaginal contraceptive ring about 2 inches in diameter that is inserted into the vagin and releases estrogen and progestin Pros Easy system to remember Very effective Cons May cause a vaginal discharge Can be expelled without notice Education – if the ring is out for more than 3 hours, woman should use a back -up method Depo-Provera Injection An injectable progestin that inhibits ovulation Pros Long duration of action (3 months) Estrogen free May be used by smokers May be used by lactating women Cons Menstrual irregularities Return visit needed every 12 weeks for injection Weight gain Headaches Depression Return to fertility delayed up to 12 months Revised by TMB Fall 22 Go to ATI Pharmacology Book and review chapters on Medication Affecting the Reproductive System Sterilization Mechanical Barriers MEN – Vasectomy Diaphragm WOMEN – Tubal Ligation Refer to table 56-4 The diaphragm is an effective contraceptive device consisting of a round flexible spring covered with a domelike latex rubber cup. The diaphragm is used in conjunction with a spermicide, which is used to coat the diaphragm prior to inserting deep into the vagina, covering the cervix completely. Prior to use the diaphragm should be inspected for tiny holes or tears. Post coitus, the diaphragm should be left in place for 6 hours, but no longer than 12 hours. Disadvantages include: allergic reactions in those who are sensitive to latex and increased rate of UTI. Cervical Cap A cervical cap is smaller than a diaphragm and only covers the cervix. If a woman can feel her cervix she is usually able to use a cervical cap effectively. Major advantage is the cervical cap can be left in place for 2 days after coitus. The cap is used with spermicide. Disadvantage: can cause cervical irritation. Most PCP will do a PAP Smear and then repeat it in 3 months after the cervical cap has been used. Female Condom The female condom provides protection from STI, HIV and pregnancy. Refer to Figure 56-6 for a picture or the picture below. Disadvantages include cost and cannot be used in a standing position. Spermicides Spermicides are made from nonoxynol – 9 or octoxynol and are available over the counter as foams, gels, films, suppositories and also on condoms. Advantages: this is a nonhormonal option, user Revised by TMB Fall 22 controlled, does not cause systemic side effects and are immediately effective. Disadvantage: Do not protect from HIV or STI’s Male Condom The male condom is an impermeable, snug – fitting cover applied to the erect penis before entering the vaginal canal. Space needs to be left at the end of the condom for ejaculation. Advantages: provides a barrier against STI. An exception are natural condoms, which do NOT protect from HIV. Disadvantages: HPV can still be transmitted because of the skin to skin contact. If abraded skin is exposed to body fluids, the risk for STI transmission increases. Sponge Disk – shaped polyurethane device containing a spermicide that is activated by wetting with water. Coitus Interruption or Withdrawal Fertility Awareness – Based Methods Emergency Contraception This is the removal of the penis from the vagina before ejaculation. This method requires the woman to know when fertile time occurs during the menstrual cycle. This requires a lot of control by the male partner and is considered to be an unreliable source of birth control. These are methods that can be used by women after unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy. Emergency contraceptive pills – need to be taken as soon as possible and no later than 5 days after unprotected sex. Nausea, breast tenderness and irregular bleeding are potential side effects. Contraindicated in pregnancy. If a woman is breast feeding, a progestin – only formulation is prescribed. To avoid exposing an infant to hormones, the woman should manually express milk and formula Revised by TMB Fall 22 If using this method to prevent pregnancy, a couple should not have sex during fertile days. Up to 18% of couples using this method of birth control become pregnant within the first year. While using this method, couples should avoid sex during days 8 to 19 of the menstrual cycle. Advantages: not hazardous to health, inexpensive and approved by religions that do not approve of other methods of birth control. Disadvantage: requires discipline. feed baby for 24 hours. If no menstrual cycle after 3 weeks a pregnancy test should be performed. Postcoital intrauterine Device Revised by TMB Fall 22 This is a copper bearing IUD that needs inserted within five days of unprotected sex. The chemical reaction within the sperm prevent fertilization. The woman may experience discomfort on insertion, may have heavier menstrual bleeding and may cramp. Inserting this IUD into a woman who is already pregnant could cause termination of the established pregnancy. Revised by TMB Fall 22