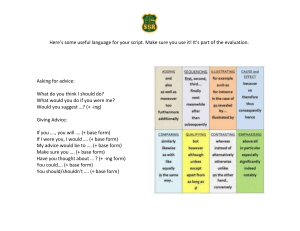
Intro to Documentary Film Sound Production Sound ➔ Audio captured during the shooting of the film ➔ Preparation is key ◆ Location scouting ◆ Unique sounds for every area ◆ Preparing your kit ◆ Gathering “wild sound” ➔ Different styles of filmmaking ◆ Run & Gun ◆ Sit-down interviews ◆ Observational ➔ VERY important! Take pride in your production sound Who’s Who in Production Sound? 1. SOUND RECORDIST • • • • • Primary, and often only, sound person (or ears) on set Works with the director to determine equipment needs and procures any additional materials (extra microphones, larger mixer) Records and monitors the audio Identifies and predicts potential audio problems. Hopefully has a fix! Records additional sounds like backgrounds and “wild sound” sound for b-roll footage 2. BOOM OPERATOR • • Handles the boom microphone The shot could be 30 seconds, or it could be 30 minutes Production Sound - On Set DIRECTOR • • • • • Hires crew First point of contact Provide the details for each shoot Scout locations Creatively, how should the story be told? DIRECTOR OF PHOTOGRAPHY (DP) CAMERA OPERATOR • Operates the camera • “Frames” the shot • Get into the directors head • Become their friend! This leads to many other gigs POST-PRODUCTION SOUND ➔ Audio finished during the post production phase ➔ Preparation is key (DO YOU SEE A THEME HERE?) ◆ Be involved/communicate in the pre-production and production phase if possible ◆ Understand distribution, tech specs, deliverables and deadlines ◆ Check and collect resources (sound libraries, plugs, time) ◆ Create any session templates and sound palettes needed ◆ Watch the content prior to starting – no surprises ◆ Spotting Session to Kick Off - after elements are received and prepped ➔ VERY important! Take pride in your work. (ANOTHER THEME) “Just because it’s done – doesn’t mean its good” Always Evaluate and Re-Evaluate your work. Who’s Who in Audio Post? Sound Supervisor • • • • • Otherwise known as Supervising Sound Editor Often is the cross over person working in all phases: pre-pro, production and post Hires, manages and evaluates sound team Works closely with the director Often wears other hats Music Roles • • • • Composer Music Editor Arranger Music Supervisor Sound Supervisor is the head honcho Engineering Roles • • • Automatic Dialog Replacement Foley (see Sound Design) Narration Record Dialogue Editor/ Sound Editor • • • • • HUGE role in documentary film Can involve noise reduction and sweetening Leveling to spec Includes NAT/SYNC If not mixing – give plenty of options in delivery of ”going back” Sound Designer • • • Often a team of people, with each specializing in different parts of the design Foley is a noun and a verb Wild Sounds Big value, especially in Documentary Big Post Crew for Documentary Usual Post Crew for Documentary Sound …One is the loneliest number…….. ever Workflows It all starts with METADATA Pre production Planned For and Discussed With Sound Mixer and Editor or AE Production Properly Dialed in ON Recorder, Handed Off of Ingested with MetaData PostProduction Editor needs to maintain metadata. Nested Merged Clips strips Metadata. EEDED With MetaData With Out MetaData ASSETS linkable in NLE YES somewhat PT Field Recorder Work Flow YES NO Editor can strip MetaData during ingestion Nested Clips Can destroy Audio Metadata SOLO - or small sound team Import assets and or PT Field recorder workflow Pull sounds needed Prep Divide Watch Spotting Session Edit Voice Narration Dialogue Music NAT/Sync Pre-Mix as you go leveling out – especially voice to LKFS spec. Sound Design Foley BGs (or ambiances) Hard Effects Cinematics Effects Good Time To have a more formal Mid Review Impressionistic Larger stage mixes split mix duties between dial, music and sound design Depends on the content, but mixing this first saves time on solo mixes Proceed To Mix These Elements in NAT/Sync Voice MIX Music Sound design Foley Mix Review Deliverables/Outputs QC TERMINOLOGY DIEGETIC NON-DIEGETIC Sounds whose source is visible on the screen or whose source is implied to be present by the action of the film Sound whose source is neither visible on the screen nor has been implied to be present in action • Voices of the character • Narrator’s commentary • Sounds made by objects in the story • • Sound effects which are added for dramatic effect Music coming from instruments the characters are playing • Mood music (Score from Jaws) • Diegetic can be on or off screen depending whether the source is within or outside of the frame Non-diegetic sound is represented as coming from a source outside the story space * Source: filmsound.org SHOT TYPES SHOT TYPES CONT’D. O.S. : Over the shoulder POV: Point of View of character or object Depth of Field: Part of the image in focus. Deep DOF means all is in focus. Shallow DOF means only a small part is in focus 5 SHOT TYPES/SETUPS From Dean Miles’ Location Audio Simplified • Interview • • • B-roll • • • When shooting several shots at a location that will be edited together to form a seamless sequence Voice-Over or VO • • Also called b-reel, cutaways, filler, or pictures only. MOS: “We’re doing this MOS.” = We don’t need sound. Scene or Sequence • • Could be a short, five minutes, or a long two-hour marathon Think of this as the primary voiceover for documentary. A great deal will be edited and placed over b-roll, so it is essential to capture clean dialog Recorded narration in the field. Becoming more common as producers try to save production costs. Try and save this until last, and pick the best sounding spot as picture doesn’t matter! Stand-ups • A news industry term that involves a person talking directly into the camera. Used for intro’s to programs, a transition to a new scene, or a quick wrap-up. VIDEO LINGO Cut-in/Insert Shot – Usually close-up of objects being manipulated J-Cut: Sound of the next scene precedes the picture L-Cut: Picture changes but the audio continues Jump Cut: Abrupt transition where character seems to move location – mostly bad, but can be used creatively. Used to explain a lot in short periods of time. Timelapse – Each frame is captured slower so it moves faster ASSIGNMENT OTT/TWI #1