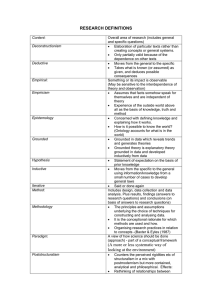
SEMINAR ON GROUNDED THEORY INTODUCTION Grounded theory is the study of a concept it is not descriptive study of a descriptive problem DEFINITION A grounded theory design is a systematic qualitative used to generate a theory that explains at a broad conceptual level , a process an action or an interaction about a substantive topic -CRESWELL DEVELOPMENT OF GROUNDED THEORY Two sociologist BARNEYS.G and A.NSELN.LSTRANUS developed grounded theory in late 1960 University of California san Francisco ,medical center with patients who were terminally ill-recorded and published their methods of research. WHEN DO YOU USE GROUNDED THEORY? When you need a broad theory or explanation Especially helpful when current theories about phenomena When you whish to study some process such as how student develop as writers. METHODS The basic idea of the grounded theory approach is to read a textual database and discover or label variables DATA COLLECTION: Interview Observation Documents Historical record Videotapes CONDUCTING A GROUNDED THEORY STUDY Rather than beginning by researcher and developing a hypothesis the first step is data collection ,through a variety of methods From this concept categories are formed which are the creation of a theory Decide if grounded theory design best addresses the research problems, Identify the process to study Seek approval and access Conduct theoretical sampling Code the data Use selective coding and develop the theory Validate your theory TYPES OF GROUNDED THEORY There are three dominant design for grounded theory Systematic design Data analysis Axial coding Selective coding Emerging design constructivist approach HOW DO YOU EVALUATE GROUNDED THEORY RESEARCH When evaluating the quality of a grounded theory study. Ask about the process of research ADVANTAGES Researchers have to analyze the data early It encourages systematic and detailed analysis of the data Researchers need evidence to back up their claims Constant interplay between data collection and analysis DISADVANTAGES First time researchers can get overwhelmed at the coding level Open coding takes long time It can be difficult to scale up to larger concepts or theme Tends to provide lower level theories only