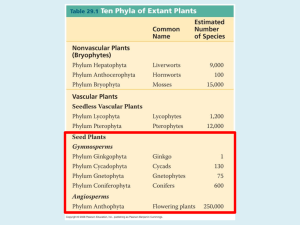
Plants Green Algae Closely related to land plants Charophyceae (stoneworts) Nonvascular Plants 1 cm Major Morphological Differences Among Plants Seedless Vascular Plants Seed Plants Have vascular tissue but no seeds (Ex. Ferns) Have vascular tissue & make seeds (Ex. Pines, Flowering plants) 5 mm No vascular tissue to conduct water & provide support (Ex. mosses) Most major morphological innovations: stomata, vascular tissue, roots, leaves First evidence Extensive of land plants: cuticle, spores, coal-forming swamps sporangia 475mya 416 359 299 Five Major Events in Plant Diversification Both wet and dry environments blanketed with green plants for the first time Diversification of flowering plants 145 Five time intervals encompass the five major events in plant diversification Present Glaucophyta (glaucophyte algae) PLANTAE Rhodophyta (red algae) GREEN ALGAE Chloroplasts containing chlorophyll a + b and b-carotene GREEN PLANTS Ulvophyceae (ulvophytes) Coleochaetophyceae (coleochaetes) Charophyceae (stoneworts) Common ancestor to all green plants NONVASCULAR PLANTS LAND PLANTS Hepaticophyta (liverworts) Bryophyta (mosses) Ability to live on land Anthocerophyta (hornworts) SEEDLESS PLANTS Bacteria Archaea Lycophyta (lycophytes) Psilotophyta (whisk ferns) Eukarya PLANTAE VASCULAR PLANTS Pteridophyta (ferns) Vascular tissue Equisetophyta (horsetails) GYMNOSPERMS SEED PLANTS Ginkgophyta (ginkgo) Molecular Phylogenies of Plants Cycadophyta (cycads) Cupressophyta (redwoods et al.) Pinophyta (pines et al.) Seeds Gnetophyta (gnetophytes) ANGIOSPERMS Anthophyta (angiosperms) Preventing Water Loss: Cuticle & Stomata Leaf cross section Cuticle is a waxy layer that prevents water loss from stems & leaves Cuticle Moist photosynthetic cells Stomata have pores that allow gas exchange in photosynthetic tissues Pore Guard cell Cuticle 25 µm Stoma Cuticle & stomata are the most fundamental plant adaptations to life on land Upright Growth & Water Transport: Vascular Tissue Simple waterconducting cells Primary wall (with cellulose) First vascular tissue Ends have pits in secondary cell wall (inside) Primary wall (with cellulose) Primary wall (with cellulose) Lignin Tracheids Secondary wall (with lignin) Vessel elements Ends have gaps through primary & secondary cell walls Primary wall (with cellulose) Secondary wall (with lignin) Elongated cells with little structural support Some structural support Increased structural support Found in fossils & present-day mosses Found in fossils Found in all vascular plants Found in gnetophytes & angiosperms Red algae GREEN ALGAE Ulvophytes Stoneworts NONVASCULAR PLANTS Liverworts Mosses Cuticle, pores Most key innovations for living on land evolved only once Hornworts Stomata SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS Early vascular plants Lycophytes Vascular tissue Roots, tracheids True leaves Vessel elements evolved more than once Whisk ferns Ferns Horsetails GYMNOSPERMS Ginkgo Cycads Redwoods et al. Pines et al. Wood Vessel elements Vessel elements Gnetophytes ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperms LAND PLANTS A Series of Evolutionary Innovations Allowed Plants to Adapt to Life on Land Coleochaetes Spores or zygotes encased in tough coat of sporopollenin Reproduction in Dry Conditions Producing Gametes in Protected Structures Male Moss gametophytes are either male or female Female Antheridia (containing sperm) Eggs 0.2 mm Archegonia In all land plant groups but Angiosperms, gametes are produced in gametangia 0.2 mm Alternation of Generations M Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) SIS O I E M ITO Spores (n) (2n) Gametophyte (multicellular, haploid) Sporophyte (multicellular, diploid) M IT O SIS MITOSIS Zygote (2n) Gametes (n) M SIS FERTILIZATION IT IS S O (n) Gametophyte-Dominant to Sporophyte-Dominant Trend in Life Cycles Haploid (n) MITOSIS Mature sporophyte (2n) SIS O I ME Spores dispersed by wind (n) MITOSIS MIT OSI S Developing gametophytes (n) Sperm swim to egg Developing sporophyte (2n) Mature female gametophyte (n) Zygote (2n) MIT OSI S Diploid (2n) Egg (n) Sperm 2 µm develop in antheridia 2 µm Mature female FERTILIZATION Eggs develop gametophyte in archegonia (n) Archegonium Mature male gametophyte (n) The gametophyte-dominant life cycle evolved early and occurs in today’s mosses Gametophyte-Dominant to Sporophyte-Dominant Trend in Life Cycles Haploid (n) MITOSIS S SI O EI M MIT OS IS Spores dispersed by wind (n) Developing gametophyte (n) Spores are produced in sporangia 1 mm Sporophyte (2n) M IT OS IS Diploid (2n) Mature gametophyte (n; underside) Sperm develop in antheridia Zygote (2n) Sperm swim to egg Egg (n) Mature sporophyte (2n) Gametophyte (n; side view) FERTILIZATION Archegonium Eggs develop in archegonia The sporophyte-dominant life cycles evolved later in lineages such as ferns Homosporous & Heterosporous Plants Nonvascular plants and most seedless vascular plants are homosporous Seed plants are heterosporous Seeds Embryo Nutritive tissue Protective coat Seeds contain an embryo and a food supply and can be dispersed Gametophyte-Dominant to Sporophyte-Dominant Trend in Life Cycles SIS MEIO Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Cones with microsporangia Pollen grains disperse via wind MITOSIS Microspore (n) forms pollen grain Pollen grain (male gametophyte) PO LL IN AT IO N Megasporangium Mother cell (2n) S MEIOSI Ovulate cone Ovules (contain megasporangia) Embryo (2n) Mature sporophyte (2n) Developing sporophyte Seeds (disperse via wind or animals) Female gametophyte (n) Egg (n) Pollen tube ION AT Z I TIL SIS Pollen tube delivers sperm FER MITO to egg The heterosporous, sporophyte-dominant life cycle of gymnosperms Four meiotic products; one is large and forms the megaspore (n) Three meiotic products die Pollen grain Megaspore divides to form female gametophyte (n), which forms eggs by mitosis. (Only one egg is fertilized and develops.) Gametophyte-Dominant to SporophyteDominant Trend in Life Cycles Pollen grains disperse via wind or animals MITOSIS SIS MEIO Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Microspore (n) forms pollen grain Anther Top of stamen Ovule Pollen grain (male gametophyte) PO L LIN AT ION Sperm travel down growing pollen tube to reach egg MITOSIS MEIOSIS Ovary Pollen lands near female gametophyte; produces pollen tube and sperm Egg (n) Megaspore (n: retained in ovary) Embryo (2n) Endosperm (3n) forms nutritive tissue in seed Nutritive tissue (3n) Mature sporophyte (2n) Developing sporophyte (2n) O MIT Seed (disperses via wind or animals) FE DO RT UB ILI LE ZA TIO N Bottom of carpel Megasporangium Female gametophyte (n: retained in ovary) SIS Zygote (2n) Fruit (develops from ovary wall) containing seed The heterosporous, sporophyte-dominant life cycle of angiosperms