Green Algae and Land Plants
advertisement

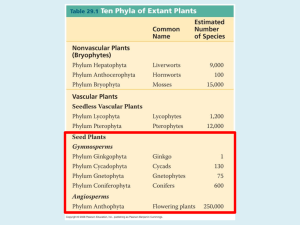
Green Algae and Land Plants Bacteria Archaea AMOEBOZOA Lobose amoebae 7 lineages of eukaryotes Cellular slime molds OPISTHOKONTA UNIKONTA Plasmodial slime molds Fungi Choanoflagellates EUKARYOTES All eukaryotes are protists except for the fungi, animals, and land plants Animals EXCAVATA Parabasilids Diplomonads Euglenids Kinetoplastids PLANTAE Glaucophyte algae Red algae Green algae Green plants RHIZARIA Foraminifera Chlorarachniophytes ALVEOLATA Ciliates Apicomplexa STRAMENOPILA Oomycetes Diatoms Brown algae CHROMALVEOLATA Dinoflagellates BIKONTA Land plants Chlamydomonas Volvox Volvox reproduction Ulva Red algae GREEN ALGAE Ulvophytes Coleochaetes Spores or zygotes encased in tough coat of sporopollenin Stoneworts NON-VASCULAR PLANTS Liverworts Vascular tissue Mosses Cuticle, pores Hornworts Stomata SEEDLESS VASCULAR PLANTS Most key innovations for living on land evolved only once Early vascular plants (fossils only) Lycophytes Whisk ferns Horsetails Roots, tracheids Ferns GYMNOSPERMS Cycads True leaves Ginkgo Redwoods et al. Pines et al. Vessel elements evolved more than once Wood Gnetophytes Vessel elements ANGIOSPERMS Vessel elements Angiosperms LAND PLANTS Vascular tissue Hepaticophyta (a) Simple waterconducting cells (b) First vascular tissue (c) Tracheids (d) Vessel elements Ends have pits in secondary cell wall (inside) Primary wall (with cellulose) Primary wall (with cellulose) Lignin Little structural support. Found in fossils and present-day mosses Primary wall (with cellulose) Primary wall (with cellulose) Secondary wall (with lignin) Secondary wall (with lignin) Some structural support. Found in fossils Increased structural support. Found in all vascular plants Ends have gaps through primary and secondary cell walls Found in gnetophytes and angiosperms Lycophyta Equisetophyta Pteridophyta gymnosperms Microspore (n) forms pollen grain Cones with microsporangia Pollen grain (male gametophyte) Megasporangium Ovulate cone Pollen grain Ovules (contain megasporangia) Female gametophyte (n) Mother cell (2n) Archegonia Embryo (2n) Eggs (n) Mature sporophyte (2n) Developing sporophyte Seed (disperses via wind or animals) Pollen produces sperm Anther Microspore (n) forms pollen grain Pollen grain (male gametophyte) Top of stamen Ovule Ovary Bottom of carpel Megasporangium Mature sporophyte flower (2n) Megaspore (n: retained in ovary) Nutritive tissue (3n) Female gametophyte (n: retained in ovary) Endosperm (3n) forms nutritive tissue in seed Embryo (2n) Zygote (2n) Developing sporophyte Seed (disperses via wind or animals) Egg