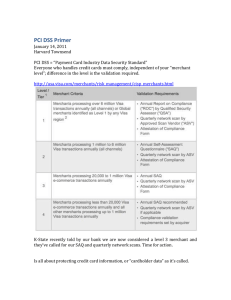
Strategies for Complying with the Requirements of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCIDSS) Keith Conlee conlee@cod.edu College of DuPage Joel Garmon garmonjs@wfu.edu Wake Forest University What is PCI-DSS? • PCI-DSS = Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard • Common set of industry tools and measurements to ensure safe handling of sensitive information. • The PCI-DSS is a multifaceted security standard that includes requirements for security management, policies, procedures, network architecture, software design and other critical protective measures. • Established by the credit card industry in response to an increase in identity theft and credit card fraud. • Every merchant who handles credit card data is responsible for safeguarding that information and can be held liable for security compromises and must comply with PCI-DSS. • Credit Card = Debit Card. 2 Scope of the Standard Manual Credit Card Electronic Handwritten Manual 3 Background • • • • 7/1/2006 - PCI DSS v1.0 1/1/2011 – PCI DSS v2.0 - begin 3-year cycle) 1/1/2014 – PCI DSS v3.0 1/1/2017 (projected) – v4.0 Merchants Merchant Level Background (cont.) Description 1 • • • • 2 • 1M-6M xacts/year 3 • 20K-1M ecommerce xacts/year 4 • <20K ecommerce xacts/year • All others <1M xacts/year Over 6M xacts/year (all acceptance channels) Suffered a breach Discretion (e.g. Visa) Labelled Level-1 by other CC brand Merchants Background (cont.) Compliance Action Level Comply w/ PCI DSS Validation Actions On-Site PCI SAQ / ROC Security Audit Network Scan Req’ed Annually Req’ed Annually Req’ed Qtr’ly 1 Req’ed 2&3 Req’ed Req’ed Annually Req’ed Qtr’ly 4 Req’ed Recommended Annually Recommended Quarterly Guidelines for Protecting Cardholder Data Elements A C C O U N T D A T A Data Element Cardholder Data Sensitive Authentication Data Storage Permitted Protection Required If Allowed to Store- Must Render Unreadable YES Primary Account Number (PAN) YES Yes Cardholder Name YES YES NO Service Code YES YES NO Expiration Date YES YES NO Full Magnetic Stripe Data NO n/a n/a CAV2/CVC2/CVV2/CID NO n/a n/a PIN / PIN Block NO n/a n/a 7 Merchant SAQs/AOCs - Background (cont.) • • Eight (8) SAQs – A, A-EP, B, B-IP, C-VT, C, P2PE, D Eight (8) AOC – one for each SAQ - Your company must attest it is complying w/ the PCI DSS annually SAQ Eligibility Questions • Purpose it is measure a merchant’s risk • Eligibility section dictates which SAQ applies – by identifying your CDE infrastructure, business process, and technology used • Increased risk = increased cost to comply and vice versa. • In PCI terms - “scope” defines a level of risk. • A big scope = increased risk and cost to comply and vice versa • You want to work towards reducing your scope 9 Merchant SAQs - Background (cont.) • • Must be able to answer Yes or n/a with comments Document Compensating Controls “meet the intent and rigor” of the original PCI DSS requirement. “Provide similar level of defense” See Appendix B “Compensating Controls” guidelines – PCI DSS 3.1 SAQ vs ROC - Background (cont.) • • If you “Self-Assess” you submit an SAQ If you use a QSA to assess your compliance, the QSA must use the ROC for your institution Executive Support • Old cliché – Need executive buy-in Socialize and network with different departments Finance Legal Compliance Audit Provost Athletics Bookstore Advancement (Alumni Affairs) • Document card transactions Total number and $$ amount by departments Fees paid for PCI non-compliance Split the infrastructure cost among the card merchants • Provide documentation on real higher education examples of PCI breach and associated costs • Average cost for higher education data breach $300/record (Reference: 2015 Cost of Data Breach Study: Global Analysis Benchmark research sponsored by IBM Independently conducted by Ponemon Institute LLC May 2015) 12 Governance Model • Executive Sponsorship Individual such as CFO or existing committee of senior executive leadership • PCI Committee Usually chaired by CISO and someone from Finance Include all major areas that accept credit cards Written policy and procedures – you will get push back Training and education to key stakeholders New merchant IDs reviewed and approved by PCI Committee 13 Getting Certified • Identify senior person in the department for each merchant ID Can be responsible for multiple merchant IDs Is responsible to insure all requirements are met and documented Highly recommend using bank or QSA website to maintain documentation. Keep copy on your systems as completed Signs off on PCI certification Signature of Merchant Executive Officer (signature block from PCI DSS Attestation of Compliance) Highlights that this is a merchant requirement, not an IT requirement • IT Security Assists merchants with understanding of requirements Provides or coordinates any technical support required Firewalls, patching, AV, … Assists with documentation Internal Security Assessor (ISA) also signs certification (if used) Encourages use of P2PE where ever possible • Work closely with Finance since they already have a relationship with the departments / merchants • Progress should be monitored by PCI committee or other governance body 14 Determine What Questionnaire to Complete Per Merchant • Identify the applicable SAQ for your environment – refer to the Self-Assessment Questionnaire Instructions and Guidelines document on PCI SSC website for information. • SAQ A. Card-not-present merchants (e-commerce or mail/telephone-order), that have fully outsourced all cardholder data functions to PCI DSS compliant third-party service providers, with no electronic storage, processing, or transmission of any cardholder data on the merchant’s systems or premises. Not applicable to face-to-face channels. • SAQ A-EP. E-commerce merchants who outsource all payment processing to PCI DSS validated third parties, and who have a website(s) that doesn’t directly receive cardholder data but that can impact the security of the payment transaction. No storage, processing, or transmission of cardholder data on merchant’s systems or premises. Applicable only to e-commerce channels. • SAQ B. Merchants using only: Imprint machines with no electronic cardholder data storage, and/or Standalone, dial-out terminals with no electronic cardholder data storage. Not applicable to e-commerce channels. 15 Determine What Questionnaire to Complete Per Merchant • SAQ B-IP. Merchants using only standalone, PIN Transaction Security (PTS) approved payment terminals with an IP connection to the payment processor with no electronic cardholder data storage. Not applicable to e-commerce channels. • SAQ C-VT. Merchants who manually enter a single transaction at a time via a keyboard into an Internet-based, virtual payment terminal solution that is provided and hosted by a PCI DSS validated third-party service provider. No electronic cardholder data storage. Not applicable to e-commerce channels. • SAQ C. Merchants with payment application systems connected to the Internet, no electronic cardholder data storage. Not applicable to e-commerce channels. • SAQ P2PE. Merchants using only hardware payment terminals included in and managed via a validated, PCI SSC-listed P2PE solution, with no electronic cardholder data storage. Not applicable to e-commerce merchants. • SAQ D All merchants not included in descriptions for the above SAQ types. 16 Requirements Overview Requirement Sub-Requirements Build and Maintain a Secure Network and Systems 1. 2. Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data Do not use vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters Protect Cardholder Data 3. 4. Protect stored cardholder data Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program 5. 6. Protect all systems against malware and regularly update anti-virus software or programs Develop and maintain secure systems and applications Implement Strong Access Control Measures 7. 8. 9. Restrict access to cardholder data by business need to know Identify and authenticate access to system components Restrict physical access to cardholder data Regularly Monitor and Test Networks 10. Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data 11. Regularly test security systems and processes Maintain an Information Security Policy 12. Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel These 12 sub-requirements can be further refined into 240 requirements depending on the type of merchant. 17 Example -- SAQ B Information Requirement 3 - Protect stored cardholder data Total Number of Questions 5 4 - Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks 7 - Restrict access to cardholder data by business need to know 1 9 - Restrict physical access to cardholder data 12 12 - Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel 17 Total Questions 38 3 SAQ B only requires 38 out of the potential 240 questions to be answered 18 Additional Helpful Documents • PCI DSS (PCI Data Security Standard Requirements and Security Assessment Procedures) Guidance on Scoping Guidance on the intent of all PCI DSS Requirements Details of testing procedures Guidance on Compensating Controls • SAQ Instructions and Guidelines documents Information about all SAQs and their eligibility criteria How to determine which SAQ is right for your organization • PCI DSS and PA-DSS Glossary of Terms, Abbreviations, and Acronyms Descriptions and definitions of terms used in the PCI DSS and self-assessment questionnaires 19 Requirements for Compliance 1. Assess your environment for compliance with the PCI DSS. 2. Complete the Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ A) according to the instructions in the Self Assessment Questionnaire Instructions and Guidelines. 3. Complete the Attestation of Compliance in its entirety. 4. Submit the SAQ and the Attestation of Compliance, along with any other requested documentation, to your acquirer, payment brand, or other requester • May also include Regular network or web site scanning by an Approved Scanning Vendor Report on Compliance by a Qualified Security Assessor (only needed by the very largest companies) 20 Discussion Questions • What is the difference between or relationship of PCI DSS and Europay, MasterCard® and Visa® (EMV) chip technology • How does P2PE assist with DSS • Are merchants using Council-listed P2PE solutions out of scope for PCI DSS • Are there card readers that are both P2PE and EMV compliant • Do I still have PCI requirements if I only take cards through a portal supported by another company • Do I have to use a QSA • Do I have to have 3rd party external network scans 21 Discussion Questions • What is a Payment Application Data Security Standard (PA-DSS) compliant application • How do I find if an application is PA-DSS certified • www.pcisecuritystandards.org/assessors_and_solutions/payment_applications • Is encrypted data still in scope for PCI DSS • Is VoIP in scope for PCI DSS • Are operating systems that are no longer supported by the vendor noncompliant with the PCI DSS • Can I fax payment card numbers and still be PCI DSS Compliant • Can an entity be PCI DSS compliant if they have performed quarterly scans, but do not have four “passing” scans 22 Discussion Questions • Can I store the security code (CAV2/CVC2/CVV2/CID) in paper format • Are hashed Primary Account Numbers (PAN) considered cardholder data that must be protected in accordance with PCI DSS • Does PCI DSS apply to debit cards, debit payments, and debit systems • Are digital images containing cardholder data and/or sensitive authentication data included in the scope of the PCI DSS • Can VLANS be used for network segmentation 23