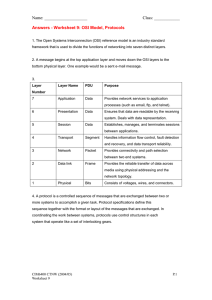
1.What is computer network,its types and importance Computer network refers to the group of two or more computing divices connected via form of communication technology for example bisness might use a computer network connected via cable or internet in order to gain acces to a common service or to share program,files and other informations Typs of computer network a) Local Area Network LAN These types of computer networks connect network devices over a relatively short distance. Quite often, a networked office building, home or school contains a single LAN although it is normal to come across a building that contains a few small LANs. On a few occasions, a LAN may also span over a group of nearby buildings. Such computer networks are usually owned by one organisation. b) Area Wide Network WAN As the name suggests, a WAN spans over a large physical distance. It may be regarded as a collection of LANs dispersed over a geographical area. The internet is a very good example of a WAN. LANs are connected to a WAN through a device referred to as a router. In IP networking, both the LAN and WAN addresses are maintained by the router. Most WANs exist under distributed or collective ownership and management and unlike the LANs, are not necessarily owned by one organisation. c) Wireless Local Area Network WLAN These types of computer networks refer to LANs that are based on Wi-Fi wireless network technology. d) Metropolitan Area Network MAN This is a network that spans over a physical area like a city that is smaller than a WAN but larger than a LAN. Quite often, such computer networks are owned and operated by single entities such as government bodies or large corporations. e) Campus Area Network CAN This type of network spans over multiple LANs but is generally smaller than a MAN. You could find such computer networks in universities or local business campuses. f) Storage Area Network SAN This type of computer network connects servers to devices for data storage using technology such as Fibre channel. g) System Area Network This type of computer network is also referred to as a Cluster Area Network. It links high-performance computers in a cluster configuration with high-speed connections. As indicated, there are different types of computer networks and which you’ll need depends on the physical distance that is covered by the given network as well as the technology that is used. Contact us if you would like more information. Importance of computer network Information and communication,today nearly every organization uses a substantial number of computers and communication tools (like telephone or fax), they are often still isolated. While managers today are able to use applications like wordprocessors or spreadsheets, not very many of them use computer-based tools to communicate with other departments or information program To overcome these obstacles in an effective usage of information technology, computer networks are necessary. They are a new kind (one might call it paradigm) of organization of computer systems produced by the need to merge computers and communications. At the same time they are the means to converge the two areas; the unnecessary distinction between tools to process and store information and tools to collect and transport information can disappear. Computer networks can manage to put down the barriers between information held on several (not only computer) systems. Only with the help of computer networks can a borderless communication and information environment be built. Computer networks allow the user to access remote programs and remote databases either of the same organization or from other enterprises or public sources. Computer networks provide communication possibilities faster than other facilities. Because of these optimal information and communication possibilities, computer networks may increase the organizational learning rate, which many authors declare as the only fundamental advantage in competition. Besides this major reason why any organization should not fail to have a computer network, there are other reasons as well: cost reduction by sharing hard- and software resources high reliability by having multiple sources of supply cost reduction by downsizing to microcomputer-based networks instead of using mainframes greater flexibility because of possibility to connect devices from various vendors 2.define internet and email and its significance The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to link several billion devices worldwide. It is a network of networks that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries an extensive range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), the infrastructure to support email, and peer-to-peer networks for file sharing and telephony. Advantages: 1) Information on almost every subject imaginable. 2) Powerful search engines 3) Ability to do research from your home versus research libraries. 4) Information at various levels of study. Everything from scholarly articles to ones directed at children. 5) Message boards where people can discuss ideas on any topic. Ability to get wide range of opinions. People can find others that have a similar interest in whatever they are interested in. 6) The internet provides the ability of emails. Free mail service to anyone in the country. 7) Platform for products like SKYPE, which allow for holding a video conference with anyone in the world who also has access. 8) Friendships and love connections have been made over the internet by people involved in love/passion over similar interests. 9) Things such as Yahoo Answers and other sites where kids can have readily available help for homework. 10) News, of all kinds is available almost instantaneously. Commentary, on that news, from every conceivable viewpoint is also available. Email electronic mail, e-mail or email is a message that may contain text, files, images, or other attachments sent through a network to a specified individual or group of individuals. The first e-mail was sent by Ray Tomlinson in 1971. By 1996, more electronic mail was being sent than postal mail. Importance and valid of email a. Importance of internetAs mentioned earlier, an e-mail must have a username followed by an @ (at sign) which is followed by the domain name with a domain suffix. b. The username cannot be longer than 64 characters long and the domain name should have no more than 254 characters. c. There should be only one @ sign in an e-mail address. d. The space and special characters: ( ) , : ; < > \ [ ] are allowed. Occasionally, a space, backslash, and quotation mark work but must be preceded with a forward slash. Although valid some e-mail providers do not allow these characters. e. The username and e-mail addresses as a whole cannot begin or end with a period. f. The e-mail must not have two or more consecutive periods. 3.what are computer network protocal A set of rules or procedures for transmitting data between electronic devices, such as computers. In order for computers to exchange information, there must be a preexisting agreement as to how the information will be structured and how each side will send and receive it. Without a protocol, a transmitting computer, for example, could be sending its data in 8-bit packets while the receiving computer might expect the data in 16-bit packets. Protocols are established by international or industrywide organizations. Perhaps the most important computer protocol is OSI (Open Systems Interconnection), a set of guidelines for implementing networking communications between computers. The most important sets of Internet protocols are TCP/IP, HTTP, and FTP. 4.What is network topologies Is the arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network. Essentially, it is the topological structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically. Physical topology is the placement of the various components of a network, including device location and cable installation, while logical topology illustrates how data flows within a network, regardless of its physical design. Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, or signal types may differ between two networks, yet their topologies may be identical. 5. Advantages and disadvantages of each network topology In Ring Topology, all the nodes are connected to each-other in such a way that they make a closed loop. Each workstation is connected to two other components on either side, and it communicates with these two adjacent neighbors. Data travels around the network, in one direction. Sending and receiving of data takes place by the help of TOKEN. Token Passing (in brief) : Token contains a piece of information which along with data is sent by the source computer. This token then passes to next node, which checks if the signal is intended to it. If yes, it receives it and passes the empty to into the network, otherwise passes token along with the data to next node. This process continues until the signal reaches its intended destination. The nodes with token are the ones only allowed to send data. Other nodes have to wait for an empty token to reach them. This network is usually found in offices, schools and small buildings. Ring Topology & token Advantages of Ring Topology a) This type of network topology is very organized. Each node gets to send the data when it receives an empty token. This helps to reduces chances of collision. Also in ring topology all the traffic flows in only one direction at very high speed. b) Even when the load on the network increases, its performance is better than that of Bus topology. c) There is no need for network server to control the connectivity between workstations. d) Additional components do not affect the performance of network. e) Each computer has equal access to resources. Disadvantages of Ring Topology packet of data must pass through all the computers between source and destination. This makes it slower than Star topology. If one workstation or port goes down, the entire network gets affected. Network is highly dependent on the wire which connects different components. MAU’s and network cards are expensive as compared to Ethernet cards and hubs. Types of network media (i) Twisted pair cables (ii) Coaxial cables (iii) Fiber optic cables. 6.Advantages of network media Advantages of Social Networking Social networking offers many benefits. It is now easier than ever to keep in contact with old friends and colleagues. The professional networking site LinkedIn even allows users to request introductions to business people who are known to their contacts. The potential of this enhanced connectivity is huge; whereas once you would be left sifting through business cards after a networking event, trying to remember details about each person, you can now easily look up a connection’s credentials and business interests on their social media profile. LinkedIn is a particularly valuable business tool; over 200 million people are members, including hiring managers from many top companies. Your profile is designed to function as an online resume, detailing your education, career history (with recommendations from your colleagues), and creative portfolio. The platform encourages users to connect with people working in their organizations, and to endorse their colleagues for the skills they display in their daily work. You can learn how to take advantage of all that LinkedIn has to offer with this LinkedIn Training Course. Social networking is particularly vital for entrepreneurs. Freelancers can find contacts via professional groups on LinkedIn and Twitter, while business owners can make use of the large user bases of Facebook and Twitter to market their products and services. Facebook has a range of services designed to help businesses market themselves more effectively, including the ability to target advertising at the precise demographic groups that are likely to respond favorably. Find out how to Create a Successful Facebook Advertising Campaign with this free online course. Disadvantages of Social Networking The primary disadvantage of social networking is that most people do not know how to network effectively. As a result, the few benefits they get from their networking activity are not worth the time invested. The best way to avoid being disappointed in this way is to decide on a strategy for using social sites, and stick to it. For example, if you are going to use Twitter to draw attention to exciting new content on your website, then resist the temptation to waste time tweeting about unrelated topics. Stay focused on what you want to achieve and don’t let yourself get distracted. 8.What are network OSI model and its layers Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Seven Layered reference model is only just a reference model. All the problems which are related to the communications are answered by specific protocols operating at different layers. The following image shows the seven layers described in Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. Seven Layers of Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model Layer 1. Physical Layer The first layer of the seven layers of Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) network model is called the Physical layer. Physical circuits are created on the physical layer of Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. Physical layers describe the electrical or optical signals used for communication Layer 2. Datalink Layer The second layer of the seven layers of Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) network model is called the Datalink layer. The Data Link layer resides above the Physical layer and below the Network layer. Datalink layer is responsible for providing end-to-end validity of the data being transmitted.. Layer 3. Network Layer The third layer of the seven layers of Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) network model is the Network layer. The Network layer of the OSI model is responsible for managing logical addressing information in the packets and the delivery of those packets to the correct destination. Routers, which are special computers used to build the network, direct the data packet generated by Network Layer using information stored in a table known as routing table. The routing table is a list of available destinations that are stored in memory on the routers. The network layer is responsible for working with logical addresses. The logical addresses are used to uniquely identify a computer on the network, but at the same time identify the network that system resides on. The logical address is used by network layer protocols to deliver the packets to the correct network. Layer 4. Transport Layer The fourth layer of the seven layers of Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) network mode is the Transport layer. The Transport layer handles transport functions such as reliable or unreliable delivery of the data to the destination. On the sending computer, the transport layer is responsible for breaking the data into smaller packets, so that if any packet is lost during transmission, the missing packets will be sent again. Missing packets are determined by acknowledgments (ACKs) from the remote device, when the remote device receives the original message packets. At the receiving system, the transport layer will be responsible for opening all of the packets and reconstructing the. Layer 5. Session Layer The position of Session Layer of the Seven Layered Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is between Transport Layer and the Presentation Layer. Session layer is the fifth layer of seven layered Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model. The session layer is responsible for establishing, managing, and terminating connections between applications at each end of the communication. Layer 6. Presentation Layer The position of Presentation Layer in seven layered Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is just below the Application Layer. When the presentation layer receives data from the application layer, to be sent over the network, it makes sure that the data is in the proper format. If it is not, the presentation layer converts the data to the proper format. On the other side of communication, when the presentation layer receives network data from the session layer, it makes sure that the data is in the proper format and once again converts it if it is not. Layer 7. Application Layer The Application Layer the seventh layer in OSI network model. Application Layer is the topmost layer of the seven layered Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) network model. Real traffic data will be often generated from the Application Layer. This may be a web request generated from HTTP protocol, a command from telnet protocol, a file download request frm FTP protocol etc 9.What is web browser and website and its examples web browser (commonly referred to as a browser) is a software application for retrieving, presenting and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI/URL) and may be a web page, image, video or other piece of content.[1] Hyperlinks present in resources enable users easily to navigate their browsers to related resources. Although browsers are primarily intended to use the World Wide Web, they can also be used to access information provided by web servers in private networks or files in file systems.The major web browsers are Firefox Internet Explorer Google Chrome Opera Safari. Website A website, also written as web site,[1] or simply site,[2] is a set of related web pages typically served from a single web domain. A website is hosted on at least one web server, accessible via a network such as the Internet or a private local area network through an Internet address known as a uniform resource locator (URL). All publicly accessible websites collectively constitute the World Wide Web. 10. What are webbrowser and website with its types web browser Is a software that is used to access the internet. A browser lets you visit e.g. websites and do activities within them like login, view multimedia, link fro one site to another, visit page, print send and receive email, amore many other activities. Website is a related collection of World Wide Web (www) files that includes a beginning file called a home page. A company or an individual tells you how to get to their website by giving you the address of their home page. The following are the types of website. Personal websites: your internet service provide or domain register may offer you free server space for you to create own website that might include some family photos and an online diary. Photo sharing websites: These types of websites are cropping up like fleas on dog. There are websites like flick r.com, photosite.com and Google’s Picasa. Writers/Authors websites. Mobile device websites. The use of mobile device smart phones, tablets watches’ has become ubiquitous. Blogging websites: people took the words web logs and shortened it to blogs – online diaries journals, or editorials, if you will. Information websites: a major information site is Wikipedia, thee online encyclopedia and its unique because it allows members to contribute and edit articles. The following are the types of web browser: Lynx: is a full featured World Wide Web browser for users on unix, VMS and other plat forms running cursor addressable character – all terminals. Opera: Is smaller and faster than most other browser, yet it is full – featured. Safari: is a web browser developed by Apple Inc. and included in Mac OS x. Firefox: is a new browser derived from Mozilla. It was released in 2004 and has grown to be the second most popular browser on the internet. Mozilla: Is an open – source web browser, designed for standards compliance, performance and portability. 11.what is email its parts and procedures on how to creat Electronic mail, most commonly referred to as email or e-mail since c 1993,[2] is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients. Modern email operates across the Internet or other computer networks. Some early email systems required that the author and the recipient both be online at the same time, in common with instant messaging. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simultaneously; they need connect only briefly, typically to a mail server, for as long as it takes to send or receive messages. Historically, the term electronic mail was used generically for any electronic document transmission. For example, several writers in the early 1970s used the term to describe fax document transmission.[3][4] As a result, it is difficult to find the first citation for the use of the term with the more specific meaning it has today. How to make a personal email address So, if you want to create a personal yet professional email, there are few simple steps to follow. First, log into your 123-reg Control Panel, scroll down the page to the Email section and click on “Manage email”. Next, click on “Create your email address”. Then enter the prefix you want for your email in the box on the left such as info, sales etc. Now choose the domain name you want to set the account up for from the drop down box to the right. Enter a password and type it again in the Repeat password box. Click “Save” and you’re all done. 12.What do you understand by E-commerce and its state E-commerce (electronic commerce or EC) is the buying and selling of goods and services, or the transmitting of funds or data, over an electronic network, primarily the Internet. These business transactions occur either business-to-business, business-to-consumer, consumer-to-consumer or consumer-to-business. E-commerce is conducted using a variety of applications, such as email, fax, online catalogs and shopping carts, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), File Transfer Protocol, and Web services. Most of this is business-to-business, with some companies attempting to use email and fax for unsolicited ads (usually viewed as spam) to consumers and other business prospects, as well as to send out e-newsletters to subscribers. The benefits of e-commerce include its around-the-clock availability, the speed of access, a wider selection of goods and services, accessibility, and international reach. privacy effectiveness sequrity 13.What is network sequrity,firewall Network security[1] consists of the provisions and policies adopted by a network administrator to prevent and monitor unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of a computer network and network-accessible resources. Network security involves the authorization of access to data in a network, which is controlled by the network administrator. Users choose or are assigned an ID and password or other authenticating information that allows them access to information and programs within their authority. Network security covers a variety of computer networks, both public and private, that are used in everyday jobs conducting transactions and communications among businesses, government agencies and individuals. Networks can be private, such as within a company, and others which might be open to public access. Network security is involved in organizations, enterprises, and other types of institutions. It does as its title explains: It secures the network, as well as protecting and overseeing operations being done. The most common and simple way of protecting a network resource is by assigning it a unique name and a corresponding password firewall is a network security system that controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on an applied rule set. A firewall establishes a barrier between a trusted, secure internal network and another network (e.g., the Internet) that is assumed not to be secure and trusted. Firewalls exist both as software to run on general purpose hardware and as a hardware REFERENCE Cem Ersoy, Shivendra Pan War ;Topological Design of Interconnected LAN-MAN Networks ;IEEE INFOCON 1992. . ST.Edward’s University; Section 4 – parts of an email address Cherokee Regional libray; Three parts of an E –mail address. Document from E .Lawley Document from Shaaban