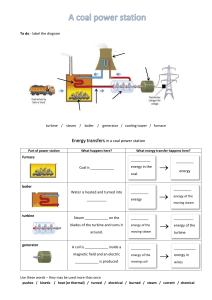
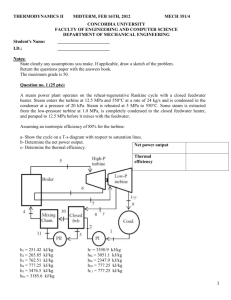
Power Plant Vapor Power Cycles 2-4 Reheat There are some methods to improve cycle performance. The thermal efficiency of the cycle can be improved by following methods: (i) By reheating of steam (ii) By regenerative feed heating (iii) By water extraction (iv) By using binary vapour Reheating System The T-s diagram of the ideal reheat Rankine cycle and the schematic of the power plant operating on this cycle are shown in Fig. 2.9. In the first stage (the high pressure turbine), steam is expanded isentropically to an intermediate pressure and sent back to the boiler where it is reheated at constant pressure, usually to the inlet temperature of the first turbine stage. Steam then expands isentropically in the second stage (lowpressure turbine) to the condenser pressure. Thus the total heat input and the total turbine work output for a reheat cycle become: 23 Power Plant Vapor Power Cycles Figure 2.9: The ideal reheat Rankine cycle 24 Power Plant Vapor Power Cycles Advantages (or) effects of Re-heating: (1) Network done increases (2) Heat supply increases (3) Thermal efficiency increases (4) The turbine exit steam dryness fraction increases, thus moisture decreases, therefore blade erosion becomes minimum, and that lead to increase the life of the turbine. (5) Erosion and corrosion problems in the steam turbine are eliminated/or may be avoided Disadvantages of Reheating: 1- Reheating requires more maintenance. 2- The increase in thermal efficiency is not appreciable in comparison to the expenditure incurred in reheating. 25 Power Plant Vapor Power Cycles EXAMPLE 5 Consider a steam power plant operating on the ideal reheat Rankine cycle. Steam enters the high-pressure turbine at 15 MPa and 600°C and is condensed in the condenser at a pressure of 10 kPa. If the moisture content of the steam at the exit of the low-pressure turbine is not to exceed 10.4 percent, determine (a) the pressure at which the steam should be reheated and (b) the thermal efficiency of the cycle. Assume the steam is reheated to the inlet temperature of the high-pressure turbine. SOLUTION: 26 Power Plant Vapor Power Cycles 27 Power Plant Vapor Power Cycles H.W A smaller power plant produces s The first turbine section expands to 500 kPa, and then flow is reheated followed by the expansion in the low-pressure turbine. Find the reheat temperature so that the turbine output is saturated vapor. For this reheat, find the total turbine power output and the boiler heat transfer. [Answer. (Reheat temperature= 529ºC , total turbine power output= 6487 kW, the boiler heat transfer= 16 475 kW)] 28 Power Plant Vapor Power Cycles 2.5 The Ideal Regenerative Rankine Cycle A practical regeneration process in steam power plants is accomplished by steam, which could have produced more work by expanding further in the turbine, is used to heat the feedwater instead. The device where the feedwater is heated by regeneration is called a regenerator, or a feedwater heater (FWH). Most modern steam power plants use between 5-8 feedwater heaters. A feedwater heater is basically a heat exchanger in which heat is transferred from the steam to the feedwater. There are two types of feedwater as follow: 1.Open or direct contact type. 2.Closed type with: a- drains cascaded backward b- drains pumped forward. feedwater Closed feedwater heaters without mixing them Open feedwater heaters mixing the two fluid streams Backward cascaded drain 29 Forward pumped drain