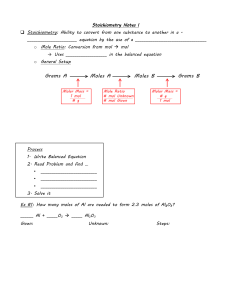
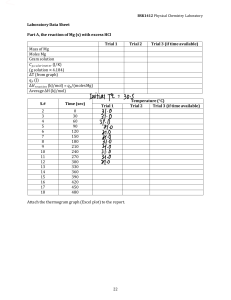
Safety Powder extinguishers available in lab are suitable to extinguish fires from flammable liquids and energized electrical equipment T F What should be done if your fellow student faints in class: a) rise students’ shoulder (put a bag under head and shoulders) and call TA b) make artificial breathing c) flap the cheeks, until student conscious During hot summer, there is no need to wear long pants in chemistry lab T F Being in lab, it’s OK to take off goggles for a moment, just to wipe moisture T F Being in lab, it’s OK to take off goggles after you completed an experiment T F What chemical/solution is not hazardous? a) silver nitrate b) H2SO4 conc c) chlorine in water d) NaCl If chemical spilled all over your body, you should: a) take off coat and goggles and use shower b) take off coat and use shower In the case of fire in lab, you should: a) run b) call TA c) extinguish fire Broken glass should be disposed to: b) special container a) trash To remove an acid from eyes wash eyes first with: a) water b) base Close-toe shoes are required in the chemistry lab T F Unused chemicals should be collected and returned to their containers, if they look pure TF When diluting acids, concentrated acid is added to water, to avoid overheating and spillage T F Concentrated HCl should be used in a hood, because HCl is: a) corrosive b) volatile c) light-sensitive Exp 1&2 questions Mass and volume are the examples of intensive property T F Mass 5.4321 g was obtained on a balance reading 4 decimals. Indicate amount of significant figures: a) 4 b) 5 c) 4 or 5 How many decimals in volume reading 2.1 mL? a) 0 b)1 c) 2 Match the columns (write a letter only, in a space provided): e pump ____ a. measures mass b graduated cylinder ____ b. measures volume a ____ balance c. holds test tube d Bunsen burner ____ d. heat source e b. attached to a pipet c clamp ____ Match the columns (write a letter only, in a space provided): a balance ____ a. milligrams c ____ thermometer b. milliliter b buret ____ c. degrees Reaction of sodium metal with an unknown should be done in a hood T F Keeping balances clean helps to avoid errors in weighting T F Is it Physical (P) or Chemical (C) property? Ethanol boils at 79 oC P C NaCl dissolves in water P C Metal conducts electricity P C Compounds A and B reacts with each other P C Product of reaction has a density 0.95 g/mL P C Given the following experimental data for volume and mass of ethanol: Volume: 5.0 mL Mass: 3.935 g d= 3.935g/5.0mL =0.787 g/mL, round up to 0.79 Volume: 6.2 mL Mass: 4.713 g d= 4.713g/6.2mL =0.76 g/mL Volume: 8.1 mL Mass: 6.320 g d= 6.320g/8.1mL =0.78 g/mL Calculate average density of ethanol: a) 0.778 b) 0.8 c) 0.78 average d = (0.79+0.76+0.78)/3=0.776, round to 2 sig fig, to 0.78 A liquid fills a container (200 mL). Density of liquid is 1000 g/L. What is the weight of a liquid? a) 1000 g b) 200 g c) 100 g Measurement is the process of obtaining: a) quantities b) qualities To weight solid on balances, one needs to put solid: first on a) weighting pan b) weighting paper c) filter paper mL vs. cm3: a) mL > cm3 b) mL < cm3 Meniscus is: a) glassware b) curved shape of water layer c) mL = cm3 Intensive properties depend on the size of sample c) solid T F Describe briefly the correct technique to smell chemical Density units are: a) mL/g b) g/mL c) moles To heat unknown chemical the following is used: a) hot plate b) Bunsen burner c) water bath heated with Bunsen burner Bunsen burner flame color is adjusted by regulation gas : air ratio on Bunsen burner. Correct color of natural gas flame is: a) red b) yellow c) pale blue Water bath is used for: a) cleaning b) heating Sodium metal is cleaned (wiped) from oil before the reaction with unknown, because oil will: a) make beaker cleaning difficult b) delay or prevent reaction c) boil Sodium is not stored in open air, because it reacts with air components T F Exp 3 questions Group of elements in the periodic table, reacting vigorously with water: a) period b) halogens c) alkali metals d) base Color of litmus indicator in a base is: a) red b) blue Color of litmus indicator in an acid is: a) red b) blue Solid lead waste is disposed in: a) sink b) trash c) waste bottle in hood d) special waste can in hood For the reaction CuSO4*5H2O Æ CuSO4 + 5 H2O calculate theoretical amount of CuSO4 produced from 1.00 g of pentahydrate (Cu = 64, S = 32, O = 16, H = 1) a)b)c) MWCuSO4x5H2O = 64+32+4x16+5x18=250 g/mol; MWH2O=18 g/mol Theor. g CuSO4=(1.00g/250g mol-1)*160g mol-1 = 0.64g For the reaction CuSO4*5H2O Æ CuSO4 + 5 H2O calculate theoretical amount of water produced from 1.00 g of pentahydrate (Cu = 64, S = 32, O = 16, H = 1) a)b)c)MWCuSO4x5H2O = 64+32+4x16+5x18=250 g/mol; MWCuSO4=160g/mol Theor. g H2O=(1.00g/250g mol-1)x5x18 g mol-1 = 0.36 g For the reaction 2 Mg + O2 Æ 2 MgO calculate the theoretical mass of product, if 2.4 g magnesium was burnt in the oxygen (Mg=24, O=16): a)b)c) AW Mg=24g/mol; mols Mg=2.4g/24g*mol-1=0.10mol, same as mols MgO MW MgO=24+16=40g/mol; g MgO=mols MgO*MW MgO=0.10x40=4.0 g Hydrate CaSO4 * x H2O (3.44 g) was heated in a crucible to the constant mass (2.72 g). Ca=40, S=32, O=16, H=1. Calculate x: Product is CaSO4. Calculate mols of CaSO4. a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 Calculate grams and mols of H2O. Divide Classify the reaction Zn + HNO3 = Zn(NO3)2 + H2O + NO2 according to the type: a) methathesis b) redox or reduction/oxidation c) acid-base d) decomposition Classify the reaction Zn(NO3)2 + Na2CO3 + H2O = ZnCO3 + CO2 + NaNO3 according to the type: a) methathesis b) redox,, or reduction/oxidation c) acid-base d) decomposition What law or principle you will try to prove in today’s experiment? a) 1st law of thermodynamics b) Dalton’s law c) Principle of mass conservation When doing experiment with combustion of magnesium, why do you need to lift the lid occasionally? a) to release vapors b) to allow air come into c) to cool down the reaction Balance the reaction Mg + O2 Æ MgO and calculate mass of MgO in grams that you could get from 1.00 g of Mg (Mg=24, O=16): a) 1.70 b) 1.67 c) 1.20 Balance the reaction Mg + O2 Æ MgO and calculate mass of O2 in grams used in reaction with 1.00 g of Mg (Mg=24, O=16): a) 0.70 b) 0.67 c) 1.20 If reactants are solids and products are gases, the Principle of Conservation of Mass is: a) valid b) not valid For sodium metal, physical properties are: Dissolving in mercury to form an alloy T F Dissolving in water to form sodium hydroxide T F Principle of conservation of mass is not valid in vacuum T F Principle of conservation of mass is not valid if reagents are solids and products are gases T F Reaction Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI Æ PbI2 + 2KNO3 is an example of: a) metathesis b) acid-base c) decomposition Pb2+ (lead) in the salt Pb(NO3)2 is: a) cation b) anion c) base Mass of the product after combustion of magnesium in air is higher than starting mass of magnesium, because of: a) oxygen b) water c) contamination Combustion of 1.0 g magnesium produces 1.6 g magnesium oxide. Calculate amount of oxygen consumed, when 0.20 g of magnesium was burned in air. (1.6/1.0)x0.20 = 0.32 g Mass of the product after heating of copper sulfate pentahydrate is lower than starting mass of solid, because of losing of: a) oxygen b) water c) due to contamination Heating of 2.5 g copper sulfate pentahydrate CuSO4*5H2O produces 1.6 g of anhydrous copper sulfate CuSO4 and water. Calculate amount of water, in grams and moles DO NOT USE HINT produced, if 1.0 g of CuSO4*5H2O was used for the heating experiment (Hint - atomic weights are: Cu=64, S=32, O=16, H=1) 2.5g CuSO4*5H2O produces 2.5-1.6=0.9g H2O Neutralization reaction is: a) acid-base 1.0 g --"--"---- will give 1.0*0.9/2.5=0.36g H2O b) decomposition c) metathesis Lead salts are toxic T F Copper sulfate could exist as pentahydrate T F Decomposition reaction leads to more then one product T F Crucible cleaning procedure includes: a) washing with water b) heating in flame Magnesium metal could evaporate, if it burning violently T F Ammonia vapors are: a) safe for health b) dangerous to inhale Sodium hydroxide is: a) caustic b) corrosive - c) both Exp 4 questions After the completion of the reaction sequence: Cu Æ Cu(NO3)2 Æ CuCO3*Cu(OH)2 Æ CuO Æ CuSO4 Æ Cu, mass of the product is higher than mass of starting material. Does it mean that Principle of Conservation of Mass is not valid? Explain your answer. No. All the reactions are giving <100% yield CuSO4 + Mg Æ MgSO4 + Cu is a metathesis reaction T F H2SO4 + Mg Æ MgSO4 + H2 is a redox (reduction-oxidation) reaction T F Why the reaction Zn + HNO3 Æ Zn(NO3)2 + H2O + NO2 should be performed in a hood? Balance the reaction. NO2 is toxic gas Heating of CuCO3*Cu(OH)2 produces toxic gas T F Filtrate is: a) solution that passed filter b) residue on filter c) solution poured on filter The purpose of washing the solid on filter is: a) to remove impurities b) to dissolve the solid Dissolving the solid copper oxide CuO on filter is an example of: a) washing b) reaction The purpose of adding Mg to copper sulfate solution is: a) producing copper metal from salt b) consuming of excess sulfuric acid c) dissolving of magnesium The purpose of adding sulfuric acid to the precipitate, copper + excess of magnesium, is: a) dissolving copper b) dissolving magnesium c) both Reaction of magnesium and sulfuric acid H2SO4 produces flammable gas T F Reaction of CuO and sulfuric acid produces toxic gas T F Reaction of copper nitrate Cu(NO3)2 and sodium carbonate Na2CO3 produces CO2 T F Exp 5 questions To prepare diluted acid: a) add acid to water b) add water to acid c) either a. or b. will work Hot glassware after glassblowing work looks the same as the cold one T F HCl gas could be prepared on the bench T F. Explain your answer HClgas is toxic Ammonia gas NH3 is collected by air substitution. Explain why. NH3 (MW=17g/mol) lighter than air (ave. MW=29g/mol) Calculate amount of hydrogen gas formed in the reaction: Zn + HCl Æ ZnCl2 + H2, if 2 mL of 1M HCl (limiting reagent) was used. (Hints: balance the reaction; 1M = 1 mole per 1 liter, or 0.001 mol per 1 mL) 2mL 1MHCl gives 0.002 mol HCl, or 0.001 mol H2 (because 2mol HCL produces 1molH2) Complete and balance the equation: CaCO3 + HCl Æ CaCO3 + 2HCl --> CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 Complete and balance the equation: NH4Cl + NaOH Æ NH4Cl + NaOH --> NH3 + H2O + NaCl Exp 6 questions What temperature units are used for calculations related to the Charles’ Law: a) oC b) oF c) K? Name at least 3 gas laws you will study in today’s experiment See answer in manual Sketch Boyle’s Law graph, which is #books vs. 1/V. Could the graph cross x-axis, i.e., could 1/V=0? Why? NO, because it's true only for V=infinity See answer in manual For Boyle’s Law calculations, #books vs. 1/V, why the mass of the book is not important? We only need to prove linearity of changing volume vs #books Avogadro’s Law describes relationship volume of gas produced vs. mass of reagent T F vs. #mols, not vs. mass Complete and balance the equation, and calculate the theoretical volume of gas produced from 0.10 g Zn (atomic weight, Zn=65): Zn + HCl Æ Zn + 2HCl --> ZnCl2 + H2; mols Zn=0.10g/65g mol-1=0.0015; mols H2=mols Zn =0.0015; Liters H2=0.0015mols*22.4Lmol-1=0.034L Calculate number of moles in 0.10 g Zn (atomic weight, Zn=65). See above Calculate volume of 3M HCl needed to completely dissolve 0.1 g Zn (Zn=65, H=1, Cl=35.5) See above: mols Zn=0.0015. One mol Zn reacts with 2 mols HCl. mols HCl needed=0.0030. 3MHCl means 3 mols/1L or 0.003 per mL Complete and balance the equation, and calculate mols of gas produced from 0.65 g Zn (atomic weights: Zn=65, H=1, Cl=35.5): Zn + HCl Æ Same as above, but easier Charles’ Law concerns relationship between volume and temperature T F What coolant is used in exp 6, to get temperature below oC: a) ice-salt b) Freon c) dry ice – isopropanol? What thermometer would you choose to measure temperature below −40 oC: a) mercury-filled b) alcohol-filled Exp 6 questions rate Graham’s Law of diffusion states that diffusion is inversely proportional to the molecular weight of gas T F Gas occupies all the volume available T F Calculate the final pressure formed after the containers 1 and 2 were connected: Total volume= 1L+2L=3L; total amount of gas Container 1, 1L under 2 atm of gas Container 2, 2L under 1 atm of gas at normal pressure= 4L*atm (2 L in Container 1 and 2 L in Container 2) Final pressure=4L*atm/3L=1.33atm Graham’s Law experiment allows to calculate: a) the molecular weight of any gas b) ratio of molecular weights of gases involved c) volume of gas vs. temperature Exp 7 questions For the Ideal Gas Law equation PV=nRT, what are the units for P, V, n and T (hint: units for R=atm*L/mole*K)? See in manual For the Ideal Law Equation PV=nRT, define “n” = number of mols For the Ideal Law Equation PV=nRT, what parameter in not measurable in exp 7? R Calculate the volume of 1.6 g natural gas (mostly CH4, MW=16 g/mol) at standard temperature and pressure. V=(mass/mols)*22.4 L/mol = (1.6/16)*22.4 =2.24L Units for molar mass are: a) g/mol b) mol/g c) mol/L d) L/mol For molecular mass measurement, manual instructs you to take about 3 mL of unknown liquid. How molecular mass will change if 10 mL of liquid will be used in the experiment? Will not change: excess of vapors will escape from flask Derive formula for molecular mass determination from the 2 equations: PV=nRT and n=g/MM. Calculate the molecular mass of unknown, if P=1.0 atm, V=145 mL, R= 0.082 L*atm*K-1 *mol-1, T=300K, m = 0.50 g MM=(m in g * RT)/PV = 85 g/mol. [Use V in liters] at Given that 0.77g of certain gas occupies volume 140 mL at 970C and 1.0 atm, what is the molecular mass of gas? MM gas = 167 g/mol, or ~ 170 g/mol after rounding up to 2 sig figs Gaussian distribution is: a) distribution of molecules b) distribution of numbers Why the real scientist does not bases any conclusion on just one result? Try to answer yourself. Hint: statistics Exp 8 questions What the First law of Thermodynamic states? Energy may be transferred but never created or destroyed Where goes the energy gained by a process in thermochemistry lab experiment? It is consumed by surrounding Define specific heat. What are the units for specific heat? cal/g*0C See in manual Express the heat change in terms of mass, specific heat and temperature change. What is the surrounding in thermochemistry experiment? Water Express heat change of process in terms of heat change of water and heat change of calorimeter Heat change Qprocess = -(Qwater + heat absorbed by calorimeter) What is used as calorimeter for experiment 8 For calorimeter heat capacity, why mass of calorimeter is not measured? Using m x c is OK for the purpose, we don't need to know "c" for calorimeter Describe briefly the procedure how to measure specific heat capacity of metal. Calculate heat change of metal, if: mass of metal = 25 g temperature of metal before transferring to calorimeter = 95 oC temperature of cold water = 20 oC maximum temperature of mixture = 30 oC specific heat of metal = 0.2 cal/g* oC See example of calculations in manual or use link: Calculate heat change of cold water, if: http://www.chem.uh.edu/Freshman/Labs/ mass of cold water = 25 g Chem111x/calculations/Exp%208% temperature of cold water = 20 oC 20calculations.xls temperature of mixture = 40 oC 2.8 g of NaOH produces 1800 cal when dissolved in water. Calculate the molar heat of solution (atomic weight Na=13, H=1, O=16), if heat capacity of calorimeter = 0 cal. Molar heat = 1800 cal/(2.8g/40g mol-1)= 25714 cal/mol or ~26 kcal/mol Calculate the energy of reaction KOH (1.1 mol) + HNO3 (1.0 mol) Æ KNO3 + H2O, if: temperature change ΔT= 30o Calculate as above, for limiting reagent mass of solution = 1000 g heat capacity of calorimeter = 10 cal/oC Heat capacity of colorimeters: A, 50 cal/oC; B, 100 cal/oC. Which one is better one? Why? A, because it consumes less heat Exp 9 questions - Practice yourself to answer those questions Device you will use to study light (emission spectrum): a)b)c) Planck’s equation gives relationship of frequency of photon and: a)b)c) What property of light is measured in terms of Hz: a)b)c) Calculate what wavelength is expected for light of photons produced due to n = 4 to n = 2 transition in a hydrogen atom (R = 3.25x1015 Hz, c = 3.00x1010 cm/sec): a)b)c) What wavelength is expected for light composed of photons due to n=5 to n=2 transition in hydrogen atom? (ν = R(1/n1-1/n2), R = 3.25 x 1015 Hz, c= 3.00x1010 cm/sec): a)b)c) What device will you use today to study electron excitation from ground state: a) spectrometer b) Bunsen burner What is the relationship between the energy of light and its frequency? a)b)c) What spectroscope is used for? a)b)c) When transferring from ground state to excited state, electron: a) absorbs energy b) emits energy When transferring from excited state to ground state, electron: a) emits photon b) absorbs photon What the relationship between photon energy (E) and its frequency (ν)? a) E = hν b) E = νmc2 c) E = λν A green line of wavelength λ = 4.86 x 10-7 m is observed in the emission spectra of hydrogen. Calculate the energy for this line. (c = 3 x 108 m/sec, h = 6.63 x 10-34 J x sec) a)b)c) What energy level is higher: a) -6 x 10-19 J b) -5 x 10-19 J? Exp 10 questions How elements are organized in the Periodic Table? (Check one) a) mass b) electronic structure c) melting points d) size of nucleus Lithium, Sodium and Potassium metals react vigorously with water T F Blue litmus paper in acid: a) change color b) does not change color Elemental halogens are toxic. It is dangerous: a) to breathe them b) to handle them with bare hands c) both The most electronegative element in whole periodic system is: a) hydrogen b) fluorine c) lithium d) helium Atomic size of elements across the period from left to right generally: a) increases b) decreases c) stays the same Atomic size of elements across the group from top to bottom generally: a) increases b) decreases c) stays the same If 2Br- + Cl2 Æ Br2 + 2Cl-, and 2Cl- + Br2 Æ no reaction, what is more reactive? a) chlorine b) bromine Dry ice should be taken with: a) tongs b) paper towel c) hand Exp 12 questions Define: solvent. Define: solute -minor component of solution - major component of solution Physical properties of solution, which are dependent only on the number of solute particles, are called …colligative Solution of the ionic compound sodium chloride freezes at lower temperature than solution of non-ionic naphthalene of the same molality. Explain, why. Ionic NaCl dissociates giving twice more Molality is the concentration in terms of: particles than napht-ene a) moles of solute/kg of solvent gives b) moles of solute/g of solvent c) moles of solute/L of solution Calculate the freezing point constant of the solvent, if freezing temperature of camphor solvent dropped by 15.5 oC after 5.1 mg of non-ionic organic compound (MW=207) was dissolved in 63.5 mg of camphor solvent. Kf=15.5/((51.5*10-3/207)/63.5*10-6)=0.206 Kf=deltaT/m; m=(mass solute/MM solute)/kg of solv. Give at least 2 examples of colligative properties. Vapor pressure, boiling point Sketch the graph for experiment 12, freezing of cyclohexane solvent Calculate molality of solution, 2.0 g of naphthalene (MW=128) in 100 g of cyclohexane. m=(2.0g/128g*mol-1)/0.100kg=0.156 mol/kg Cyclohexane is: a) flammable b) toxic c) both Solution of the unknown compound (1.0 g) freezes at higher temperature than solution of naphthalene (1.0 g). Compare molecular weights of the unknown and naphthalene. delta T unkn<delta T naphth, so MM unknown> MM naphtalene, because: delta T~1/MM Explain how sodium chloride works when used to melt ice on pavement in northern part of USA. What will work better for the purpose: 1 g of NaCl or 1 g of Na2SO4 (atomic weights are Na=23, Cl=35.5, S=32, O=16)? In the presence of salt, water freezing point depression occurs MM NaCl=23+35.5=58.5g/mol; moles NaCl=(1/58.5)=0.017, or 0.134 "moles" of particles, because NaCl dissociates giving 2 particles: Na+ and ClMM Na2SO4=23*2+32+16*4=152g/mol; moles Na2SO4=(1/152)=0.0066, or 0.0066*3= 0.0198 "moles" of particles, because Na2SO4 = 2Na+ + SO42- (3 particles per each Na2SO4) "Moles" of particles NaCl < "moles" of particles Na2SO4, so Na2SO4 works better Exp 13 questions Define: amphiphilic compound. Give an example of the one having affinity to both water and organic substances; soap What is used as the starting material to prepare soap in exp 13? Lard Define: polymer - large compound made up of repeating units Describe/sketch the correct smelling procedure Why glacial acetic acid is dangerous? It is very corrosive Glacial acetic acid is: a) concentrated b) diluted acid Why the container for solid NaOH should be kept closed all the time? Solid NaOH is hygroscopic (attracts water) Exp 14 questions In A = εbc, what is ε: a) absorptivity b) molar absorptivity c) path length For the reaction S2O82-(aq) + 3I-(aq) Æ 2SO42-(aq) + I3-(aq) decrease in transmittance of solution was recorded. What are the colored species? b) I-(aq) c) SO42-(aq) d) I3-(aq) a) S2O82-(aq) For the reaction S2O82-(aq) + 3I-(aq) Æ 2SO42-(aq) + I3-(aq) 86 % transmittance was recorded. Assuming εl = 45, calculate concentration of I3-(aq): a)b)c) A=log(100/%Trans); A=epsilon x l x c, so c=(log(100/%Trans)/epsilon x l =0.001456, or 1.5E-3 In calculations for the completed reaction S2O82-(aq) + 3I-(aq) Æ 2SO42-(aq) + I3-(aq) we use the fact that concentration of product triiodide ion is equal to: a) initial concentration of S2O82-(aq) b) initial concentration of I-(aq) c) both For the reaction H2 (g) + I2 (g) Æ 2HI (g) the rate constant k1 = 2.7 x 10-4 L/(mol*sec) at 600 K and 3.5 x 10-3 L/(mol*sec) at 650 K. Find the activation energy Ea (R = 8.31 J/mol*K): ln(k2/k1)=-Ea*(1/T2-1/T1)/R; Ea=-ln(k2/k1)*R/(1/T2-1/T1)= a)b)c) =-ln(3.5E-3/2.7E-4)*8.31/(1/650-1/600)=166070 J, or 170kJ Find the concentration of the stock solution of (NH4)2S2O8, if 0.016 M (NH4)2S2O8 solution was obtained immediately after mixing the stock solution (3 mL), KI solution (6 mL) and water (1 mL): Final volume = 3+6+1=10 mL; Initial vol = 3 mL a)b)c) Final conc = 0.016M x 3mL/10mL = 0.0048M Find the concentration of (NH4)2S2O8 immediately after addition of KI solution (6 mL) and water (1 mL) to 0.020 M (NH4)2S2O8 (3 mL): Final volume = 6+1+3=10 mL; Initial vol = 3 mL a)b)c) Final conc = 0.020M x 3mL/10mL = 0.0060M 2For the reaction S2O8 (aq) + 3 I-(aq) Æ 2 SO42-(aq) + I3-(aq), calculate the rate constant given the following: rate = 0.005 M/min, [S2O82-] = 0.01 M, [I-] = 0.15 M, rate = k [S2O82-]a [I-]: a)b)c) a=1; k=rate/[S2O82-][I-] =0.005M*min-1/(0.01M x 0.15M)=3 M-1*min-1 The following affects the rate of reaction S2O82-(aq) + 3 I-(aq) Æ 2 SO42-(aq) + I3-(aq): a) temperature b) humidity c) light The rate constant for reaction S2O82-(aq) + 3 I-(aq) Æ 2 SO42-(aq) + I3-(aq) depends on: a) temperature b) humidity c) light The following does not affect the rate of reaction S2O82-(aq) + 3 I-(aq) Æ 2SO42-(aq) + I3a) concentration b) catalyst c) time from start d) water solvent The following does affect the rate constant, S2O82-(aq) + 3 I-(aq) Æ 2 SO42-(aq) + I3a) concentration b) catalyst c) time from start d) water solvent Exp 15 questions Which of the following relationships between %absorbance and % transmittance is not correct? b) A = 2- log10(%T) c) A = log10(1/%T) a) A = log10(100/%T) At equilibrium (select correct answer): a) forward and reverse reactions continue to occur b) forward reaction is fast c) reverse reaction is fast d) forward and reverse reactions do not proceed e) none of the above For the reaction 2A + B = C, initial concentrations [A]ini = 0.020 M and [B]ini = 0.005 M. At equilibrium, [C]eq = 0.001 M. Calculated equilibrium concentration [A]eq is: a)b)c) [A]eq=[A]ini-[A]consumed; to get 1 mole of C, 2 mols of A is needed, so [A]eq=0.020M-0.001M*2=0.018M For the reaction 2A + B = C, initial concentrations [A]ini = 0.020 M and [B]ini = 0.005 M. At equilibrium, [C]eq = 0.001 M. Calculated equilibrium concentration [B]eq is: a)b)c) [B]eq = [B]ini-[B]consumed=0.005-0.001=0.004M Studying the reaction Fe3+ + SCN- Æ Fe(SCN)2+ we record: a) transmission b) absorption c) color changes d) temperature calculate Studying the reaction Fe3+ + SCN- Æ Fe(SCN)2+ we record absorbance of: a) Fe3+ b) SCNc) Fe(SCN)2+ For the reaction 2A + B = C, where [A] = 0.3 M, [B] = 0.1 M, [C] = 0.2 M calculate Kc: a)b)c)d)f) Kc=[C]/[A]^2[B]=0.2/(0.3^2*0.1)=20 M-2 Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc for reaction CO (g ) + 3H2 (g) = CH4 (g) + H2O(g), if [CO] = 0.2 M, [H2] = 0.3 M, [CH4] = 0.1 M, [H2O] = 0.1 M Kc=[H2O][CH4]/[CO][H2]^3=0.1*0.1/(0.2*0.3^3)= 1.85, or ~2 M-2 The equilibrium constant Kc = 400 for Fe3+ + SCN- = Fe(SCN)2+. Calculate concentration [Fe(SCN)2+], if [Fe3+] = 9.45 x 10-4 M and [SCN-] = 1.45 x 10-4 M: a)b)c) Kc=[FeSCN]/[Fe][SCN]; [FeSCN2+]=Kc*[Fe3+][SCN-]=400*9.45E-4*1.45E-4=5.48E-05 M An equilibrium constant is independent on the temperature: T F Transmittance of solution is 72%. Calculate the absorbance. a)b)c) A=log(100/%Trans)=log(100/72)=0.14 Exp 16 questions Diluted acid and bases are disposed in: a) waste bottle in hood b) sink After addition of 0.1 M HCl (10 mL) to 0.2 M NaOH (6 mL) solution becomes: a) basic b) acidic c) neutral After addition of 0.2 M NaOH (4 mL) to 0.1 M HCl (10 mL) to solution becomes: a) basic b) acidic c) neutral Exp 19 questions Why we used a paper bridge soaked with KNO3 to connect solutions in Carrou cell: a) ? to balance charge of the system If Eo > 0 reaction is (hint: ΔGo = -n*F*ΔEo): a) spontaneous b) non-spontaneous Calculate half-reaction potential for I-/I3-: S2O82-(aq) + 2e Æ 2SO42-(aq) E= +2.010 V 3I (aq) Æ I3 (aq) + 2 e E=______ V E=2.010-1.475=0.535 V ______________________________ S2O82-(aq) + 3I-(aq) Æ 2SO42-(aq) + I3-(aq) Ereaction= +1.475 V Solutions from Carrou cell could be disposed in sink T F Species gaining electrons are reduced T F Species losing electrons are oxidized T F Species at anode lose electrons T F Species at cathode gaining electrons T F In redox reaction species gaining electrons are oxidized T F Oxidation takes place at anode while reduction takes place at cathode T F Reaction Cl2(g) + 2e Æ 2Cl-(aq) represent reduction of chlorine T F Redox potential (Eo) is expressed in Joules T F Acid and base conduct an electric current T F moles of For the half-reaction BrO3- Æ Br2 number of electrons transferred per mole of Br2 is: a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 5 e) 10 Zn metal dissolves in Cu2+ solution. What of the following is not true? a) Cu is easier to oxidize than Zn b) Cu2+ is easier to reduce than Zn2+ c) Zn is better reducing agent than Cu d) Cu2+ is better oxidizing agent than Zn2+ Cathode is an electrode where oxidation occurs T F Anode is an electrode where oxidation occurs T F The following is an example of a reduction reaction? Yes Ni2+(aq) + 2e - Æ Ni(s) The ampere is the unit of measure used to quantify potential T F The potentials measured in Experiment #19 are standard potentials T F Standard potentials are to be measured at standard state: 1M at 25oC In a galvanic cell, reduction occurs at the anode T F The standard potential can be used to predict the spontaneity of a redox reaction T F The more positive the potential of a half-reaction for a particular element (compound) the T F more likely that element (compound) will accept electrons The more negative the potential of a half-reaction for a particular element (compound), the more likely that element (compound) will accept electrons T F The more positive the potential of a half-reaction for a particular element (compound), the more likely that element (compound) will act as a reducing agent in a reaction T F The more negative the potential of a half-reaction for a particular element (compound), the more likely that element (compound) will act as a reducing agent in a reaction T F K+ has a standard reduction potential of -2.92, so it is a reducing agent T F The element with the highest reduction potential is most easily reduced T F For reduction to take place, the following process should also proceed: a) dilution b) oxidation c) evaporation