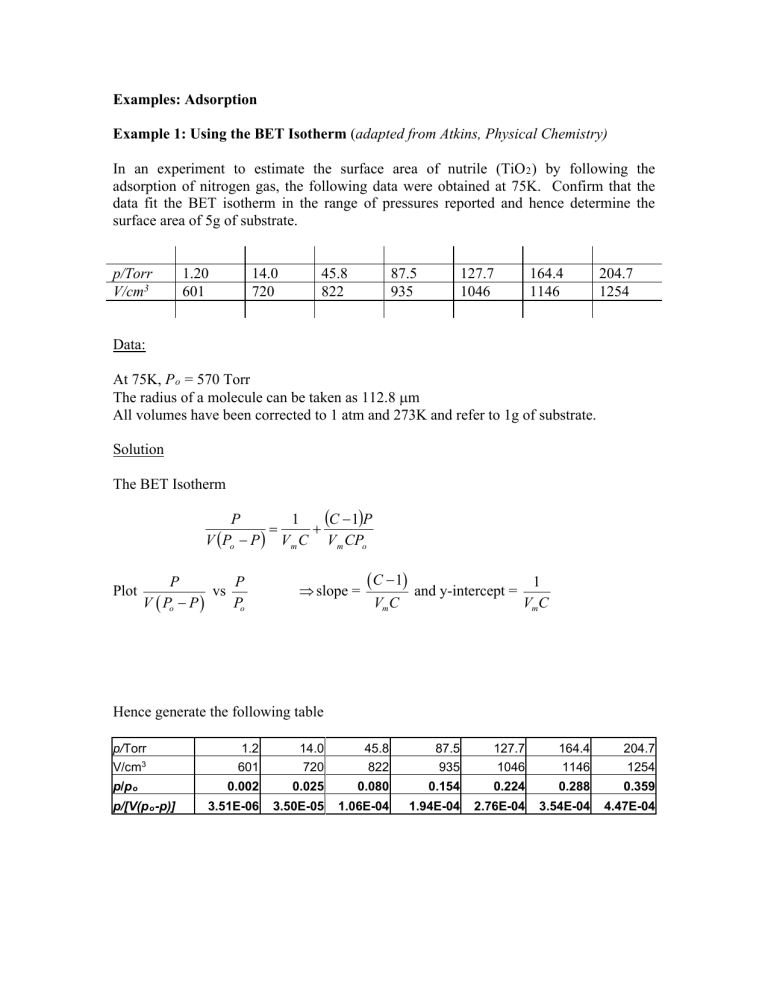
Examples: Adsorption Example 1: Using the BET Isotherm (adapted from Atkins, Physical Chemistry) In an experiment to estimate the surface area of nutrile (TiO 2 ) by following the adsorption of nitrogen gas, the following data were obtained at 75K. Confirm that the data fit the BET isotherm in the range of pressures reported and hence determine the surface area of 5g of substrate. p/Torr V/cm3 1.20 601 14.0 720 45.8 822 87.5 935 127.7 1046 164.4 1146 204.7 1254 Data: At 75K, P o = 570 Torr The radius of a molecule can be taken as 112.8 µm All volumes have been corrected to 1 atm and 273K and refer to 1g of substrate. Solution The BET Isotherm (C − 1)P P 1 = + V (Po − P ) V m C V m CPo Plot P P vs Po V ( Po − P ) ⇒ slope = ( C − 1) VmC and y-intercept = 1 VmC Hence generate the following table p/Torr 1.2 14.0 45.8 87.5 127.7 164.4 204.7 V/cm3 601 720 822 935 1046 1146 1254 0.002 0.025 0.080 0.154 0.224 0.288 0.359 3.51E-06 3.50E-05 1.06E-04 1.94E-04 2.76E-04 3.54E-04 4.47E-04 p/p o p/[V(p o -p)] Plot of P/[V(Po-P)] vs P/Po 5.00E-04 4.50E-04 4.00E-04 P/[V(Po-P)] 3.50E-04 y = 1.23E-03x + 4.06E-06 3.00E-04 2.50E-04 2.00E-04 1.50E-04 1.00E-04 5.00E-05 0.00E+00 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.25 0.20 0.30 P/Po From the graph • Y-intercept: • Slope: 1 = 4.06 x 10−6 cm −3 VmC ( C − 1) = 1.23 x 10−3 cm −3 VmC Solving the equations gives: 1.23 x 10−3 C −1 = = 303 4.06 x 10−3 Vm = ⇒C = 304 1 = 813 cm3 −3 304 x 4.06 x 10 PV At 1 atm and 273 K:= n = RT (1.01 x 10 ) 813 x 10= 5 8.314 x 273 −6 0.036 mol But there are 6.022 x 1023 molecules/mole. Hence, we have 0.036 x 6.022 x 1023 = 2.18 x 1022 molecules The surface area of each molecule = 4πr2 = 0.16 x 10-18 m2 Surface area/g = 3488 m2 For 5 g = 17440 m2 0.35 0.40 Example 2: Using the Langmuir Isotherm (from Atkins, Physical Chemistry) The data below are for the adsorption of CO on charcoal at 273K. Confirm that they fit the Langmuir isotherm, and find the constant K and the volume corresponding to complete coverage. In each case V has been corrected to 1atm. p/Torr V/cm3 100 10.2 200 18.6 300 25.5 400 31.5 500 36.9 Solution strategy The Langmuir isotherm is θ= where θ = Kp 1 + Kp (1) V → V m = volume corresponding to complete coverage Vm Rearrange (1): ⇒ Kpθ + θ = Kp ⇒ Hence plot ⇒ Kp V V + = Kp Vm Vm p P 1 = + V Vm KVm p vs p V ⇒ slope = 1 1 and y-intercept = Vm KVm 600 41.6 700 46.1 Example 3: Determination of the enthalpy of adsorption (Atkins, Physical Chemistry) The data below show the pressures of CO needed for the volume of adsorption (corrected to 1 atm and 273 K) to be 10.0 cm3 using the same sample as in Example 2 above. Calculate the adsorption enthalpy at this surface coverage. T/K P/Torr 200 30.0 210 37.1 220 45.2 230 54.0 240 63.5 Solution Strategy The Langmuir isotherm is θ = ⇒ ln K + ln p= ln Kp 1 + Kp θ ⇒ Kp = 1−θ θ = const 1−θ o ∆H ads ∂ ln K = RT 2 ∂T θ o ∆H ads ∂ ln P ∂ ln K ⇒ = − = − RT 2 ∂T θ ∂T θ 1 o d ∆ H ∂ ln P ads T ⇒ = R dT ∂T θ o ∂ ln P ∆H ads ⇒ = 1 R ∂ T θ o ∆H ads Plot ln P vs 1/T and slope = R 1 1 ⇐ T = − 2 dT T d 250 73.9