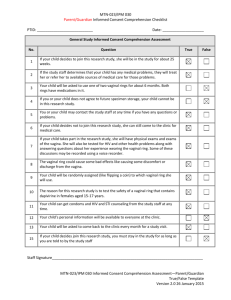
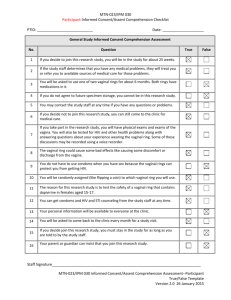
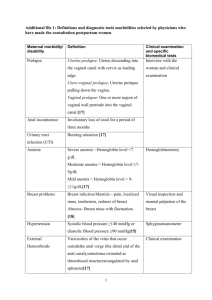
Gynaecological investigation & Procedures History: C/o Past medical and surgical history Vaginal discharge LMP, menses Infection: Sexually transmitteddiseases: E.g. Herpes simplex virus (HSV), syphilis, gonorrhoea, Chlamydia, (HIV), (HPV) Pelvic inflammatoryDisease (PID) Obstetric history (G_P_) Breast history Abdominal exam Inspection of external genitalia Bimanual examination Speculum examination (see /obtain vagina+cervix specimen, e.g HVS or Pap smear Papanicolaou smear(Pap smear): Screen for cervical cancer Specimens are collected from 3 sites: vaginal pool or the posterior fornix of vagina cervix endocervix Do not obtain during menses, or with heavy infectious discharge Avoid douching, vaginal suppository or sexual intercourse at least 24 hours before taking the smear Abdominal USG See any mass (e.g.Uterine fibroids), differentiate solid from cystic lesion (e.g.ovarian cyst), confirming pregnancy Preparation: inform patient to drink water and not to void to make the uterus easier to visualize Laboratory examination urethra, cervix,external os or high vagina swab X microscopy, cultures & sensitivity test e.g. Candidae, Trichomonas, Gonorrhea cultures Pregnancy test (PT): Serum /Urine test of (HCG) Appears in blood and urine~14-26 days after conception Vaginal packing Purposes stop bleeding keep absorb discharge & blood Aftercare: Bed rest usually removed on the next day, should not be keep in vagina more than 48hours Aftercare for removal of vaginal packing: After removal, perform a per vaginal examination. Douching & vulval toilet Documentation Vaginal supportive pessaries Purposes: correct retroversion of uterus treat uterine prolapse especially for elderly women or those who are too ill to tolerate surgery. Act as temporary measures for uterine prolapse before elective surgery